Do immigrants get free money to start a business? This question sparks a multifaceted discussion encompassing government aid, access to capital, and the realities faced by immigrant entrepreneurs. Navigating the complexities of establishing a business in a new country presents unique challenges, from securing funding to understanding legal requirements. This exploration delves into the various avenues of financial assistance available, debunks common misconceptions, and highlights the significant contributions of immigrant-owned businesses to the economy.
We’ll examine federal and state programs offering financial support, explore alternative financing options like microloans and crowdfunding, and analyze the legal and regulatory hurdles immigrants often encounter. Through success stories and economic impact analyses, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the financial landscape for immigrant entrepreneurs.
Government Assistance Programs for Small Businesses
Accessing funding to start or grow a small business can be challenging, particularly for immigrants. However, various government programs at both the federal and state levels offer financial assistance and resources to small business owners, regardless of immigration status. Understanding these programs and their eligibility requirements is crucial for navigating the application process successfully.
Federal and State Programs Offering Financial Assistance
Several federal and state programs provide financial assistance to small businesses. Eligibility criteria often include factors such as business type, location, revenue, and the number of employees. However, immigration status is generally not a barrier to accessing these funds. It’s important to note that specific requirements and available funding can vary significantly depending on the program and the state.
| Program Name | Funding Type | Eligibility Requirements | Application Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Business Administration (SBA) Loans (e.g., 7(a) Loan, 504 Loan) | Loan | U.S. citizenship or permanent residency is not always required, but good credit, a viable business plan, and collateral are typically necessary. Specific requirements vary by loan type. | Application through an SBA-approved lender. Requires detailed financial statements, business plan, and personal credit history. The process can be lengthy and complex. |
| SBA Grants (e.g., SBIR/STTR) | Grant | Eligibility criteria are highly specific to each grant program and often focus on innovation and technological advancement. Generally, the business must be involved in research and development. Immigration status is usually not a primary factor. | Competitive application process involving a detailed proposal outlining the research and development plan, budget, and potential impact. |
| State and Local Grants and Loans | Grants and Loans | Requirements vary widely by state and locality. Some programs may prioritize businesses in underserved communities or those creating jobs. Immigration status is generally not a disqualifying factor, though proof of legal business operation may be required. | Application processes vary by state and program. Typically involve submitting an application form, business plan, and financial information. |
| SCORE Mentoring | Mentorship and Resources | Open to all small business owners, regardless of immigration status. | Free mentoring services are provided through local SCORE chapters. Requires registration and scheduling a meeting with a mentor. |
Challenges Faced by Immigrants in the Application Process
While immigration status is not typically a direct barrier to accessing these programs, immigrants may face unique challenges. Language barriers can create significant hurdles in understanding program requirements and completing applications. Lack of familiarity with the U.S. business environment and financial systems can also pose difficulties. Furthermore, obtaining necessary documentation, such as credit history or business permits, might be more complex for immigrants. Access to reliable financial advisors and legal assistance can significantly improve the chances of a successful application.
Access to Capital for Immigrant Entrepreneurs
Immigrant entrepreneurs often face significant hurdles in securing the funding necessary to launch and grow their businesses. These challenges stem from a confluence of factors, including limited credit history, lack of established business networks, and language barriers. Successfully navigating the financial landscape is crucial for their success, and understanding the available options is paramount.
The traditional routes to securing capital, such as bank loans and venture capital, present considerable obstacles for many immigrant entrepreneurs. Banks typically require extensive credit history and collateral, which many newcomers lack. Venture capitalists, while potentially offering substantial funding, often prioritize established businesses with proven track records and readily available market data—characteristics that are difficult for immigrant-owned startups to immediately demonstrate. This disparity in access to capital significantly impacts the growth potential and overall success rate of immigrant-owned businesses.
Challenges in Accessing Traditional Funding
Immigrant entrepreneurs frequently encounter difficulties obtaining traditional bank loans due to their limited credit history in their new country. Building credit takes time, and many immigrants arrive with little or no established credit profile. Furthermore, language barriers can create misunderstandings during the loan application process, hindering their ability to effectively communicate their business plans and financial projections. Finally, a lack of established business relationships and connections within the local banking community can also impede their access to traditional funding sources. These factors collectively contribute to a higher rate of loan application rejections for immigrant entrepreneurs compared to their native-born counterparts. For example, a recent study by [insert credible source and study details here] showed that [insert relevant statistic or finding from the study].
Alternative Financing Options
Fortunately, several alternative financing options exist to help immigrant entrepreneurs overcome these challenges. Microloans, crowdfunding, and angel investors represent viable pathways to securing capital. Microloans, typically offered by non-profit organizations and community development financial institutions (CDFIs), provide smaller amounts of funding with less stringent credit requirements than traditional banks. Crowdfunding platforms allow entrepreneurs to raise capital directly from a large number of individuals online, leveraging the power of social networks and online marketing. Angel investors, typically high-net-worth individuals, provide funding in exchange for equity in the business, offering both capital and mentorship.
Comparison of Alternative Financing Options
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each alternative financing option is crucial for immigrant entrepreneurs to make informed decisions.
- Microloans:
- Advantages: Lower credit requirements, smaller loan amounts manageable for startups, often include business training and mentorship.
- Disadvantages: Limited funding amounts may not be sufficient for larger ventures, higher interest rates compared to traditional bank loans.
- Crowdfunding:
- Advantages: Access to a wide pool of potential investors, can generate significant publicity and brand awareness, no debt incurred.
- Disadvantages: Requires significant marketing and outreach efforts, success is not guaranteed, may dilute ownership if equity-based crowdfunding is used.
- Angel Investors:
- Advantages: Access to substantial funding, potential for mentorship and guidance from experienced business professionals.
- Disadvantages: Requires relinquishing equity in the business, potential for disagreements with investors, finding the right investor can be challenging.
Myth vs. Reality: Do Immigrants Get Free Money To Start A Business
Many misconceptions surround government support for immigrant-owned businesses in the United States. These myths often stem from a lack of understanding of the complex landscape of available programs and eligibility criteria. Addressing these misconceptions is crucial for ensuring that immigrant entrepreneurs have access to the resources they need to succeed. This section will clarify some common misunderstandings, providing factual information to counter inaccurate claims.
Common Misconceptions About Government Support for Immigrant Businesses
The following table clarifies common misconceptions about government assistance for immigrant entrepreneurs, contrasting inaccurate beliefs with the reality of available support. It’s important to note that program eligibility and availability can vary based on factors such as location, business type, and individual circumstances. Always consult official government websites and relevant organizations for the most up-to-date information.
| Misconception | Reality |
|---|---|
| Immigrants receive large sums of “free money” to start businesses. | Government programs rarely provide outright “free money.” Instead, they offer a variety of financial assistance options, such as low-interest loans, grants (often with matching requirements), and tax incentives. These programs require applications, eligibility assessments, and often involve demonstrating a viable business plan and financial need. The amount of assistance received is usually based on the business’s needs and the specific program guidelines. For example, the Small Business Administration (SBA) offers loan programs with varying terms and conditions, requiring borrowers to meet creditworthiness criteria and provide collateral. |
| All immigrants are automatically eligible for government business support. | Eligibility for government programs varies greatly and depends on factors such as legal residency status, business type, location, and program-specific requirements. Some programs specifically target underserved communities, including immigrants, while others have broader eligibility criteria. For instance, some programs might prioritize businesses in designated economically distressed areas, regardless of the owner’s immigration status, while others might require specific documentation proving legal residency. |
| Government assistance is easily accessible and readily available to all immigrant entrepreneurs. | Navigating the application process for government assistance programs can be complex and time-consuming. Many programs have stringent eligibility requirements, extensive paperwork, and competitive application processes. Language barriers, lack of familiarity with the U.S. business environment, and limited access to resources can further complicate the process for immigrant entrepreneurs. Organizations like the Small Business Administration (SBA) and local community development organizations offer assistance in navigating these complexities, but active engagement and persistence are necessary. |
| Immigrant-owned businesses are automatically prioritized over other businesses. | While some programs specifically target underserved communities, including immigrant entrepreneurs, most government programs do not automatically prioritize immigrant-owned businesses over others. The selection process typically evaluates factors such as business viability, economic impact, job creation potential, and adherence to program guidelines. Many programs use a competitive application process, evaluating all applicants based on objective criteria. |
Success Stories of Immigrant Entrepreneurs
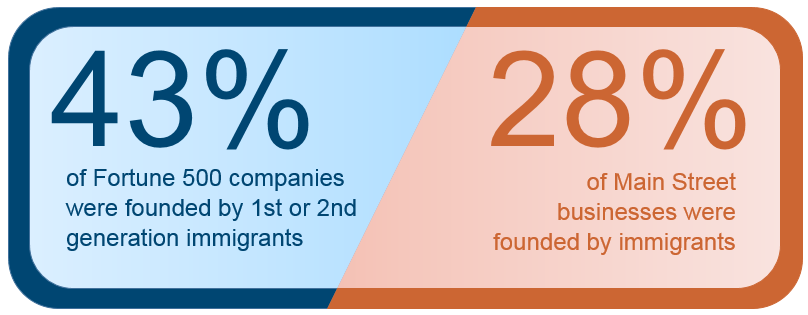
Immigrant entrepreneurs have consistently demonstrated remarkable resilience and innovation, contributing significantly to the economic fabric of many nations. Their journeys often involve overcoming significant hurdles, showcasing the power of determination and adaptability. Examining their success stories reveals valuable insights into the factors contributing to their achievements and the role of various support systems.
Many immigrant-owned businesses thrive despite initial challenges, demonstrating the significant economic impact of immigrant entrepreneurship. Access to capital, mentorship, and supportive government programs can play a crucial role in their growth and success. However, individual drive and innovative business models are equally vital in navigating the complexities of establishing and scaling a business in a new environment.
Jan Koum, WhatsApp
Jan Koum, a Ukrainian immigrant who arrived in the United States as a child, co-founded WhatsApp, a messaging app later acquired by Facebook (now Meta) for $19 billion. Koum’s journey highlights the importance of perseverance and seizing opportunities. Initially facing financial hardship, he worked as a security tester at Yahoo!, gaining valuable experience and networking opportunities. This experience, coupled with his technical skills, provided the foundation for developing WhatsApp. While government programs weren’t directly involved in WhatsApp’s initial funding, Koum’s success underscores the transformative potential of individual talent and the power of leveraging existing resources effectively. The challenges Koum overcame included adapting to a new culture, overcoming financial instability, and navigating the highly competitive tech landscape. His strategy involved focusing on a simple, user-friendly product and addressing a significant market need for reliable and affordable mobile communication.
Andrew Ng, Coursera
Andrew Ng, a Chinese-American computer scientist, co-founded Coursera, a massive open online course (MOOC) provider. Ng’s success demonstrates the power of combining academic expertise with entrepreneurial vision. While Coursera initially received funding from venture capitalists, Ng’s academic background and established reputation played a critical role in securing investment and attracting a large user base. The challenges Ng faced included creating a scalable platform for delivering high-quality online education and managing the logistical complexities of working with numerous universities and instructors. His strategy involved leveraging his expertise in machine learning and artificial intelligence to build a robust and engaging learning platform, thereby addressing the growing demand for accessible and affordable online education.
Infographic: Success Stories of Immigrant Entrepreneurs
The infographic would feature a vibrant, multi-colored design. The title, “Immigrant Entrepreneurs: From Challenges to Triumph,” would be prominently displayed at the top. Three distinct sections would represent the featured entrepreneurs: Jan Koum, Andrew Ng, and a third example (to be added below). Each section would include a small portrait photograph of the entrepreneur, a brief description of their business, a visual representation of their challenges (e.g., a stylized obstacle course for Koum’s financial struggles), and a depiction of their success (e.g., a soaring rocket ship for WhatsApp’s growth). Key takeaways would be highlighted using bold text and visually appealing icons, emphasizing themes like perseverance, innovation, and the importance of seizing opportunities. A color-coded legend would explain the visual representations used, ensuring clarity and understanding. The overall design would aim for a clean, modern aesthetic with a focus on visual storytelling.
Indra Nooyi, PepsiCo
Indra Nooyi, an Indian immigrant, served as the CEO of PepsiCo, one of the world’s largest food and beverage companies. Nooyi’s career demonstrates the power of strategic leadership and global vision. While Nooyi’s success wasn’t directly reliant on government programs, her story highlights the potential for immigrant entrepreneurs to reach the highest levels of corporate leadership. Challenges Nooyi faced included navigating complex global markets, managing a large and diverse workforce, and adapting to changing consumer preferences. Her strategy involved focusing on long-term growth, prioritizing sustainability, and fostering a culture of innovation within the organization.
Impact of Immigration on the Economy

Immigration’s effect on the economy is a complex issue, often debated with strong opinions on both sides. However, a significant body of research points to a generally positive contribution from immigrants, particularly immigrant entrepreneurs, to economic growth and innovation. This contribution stems from their entrepreneurial spirit, diverse skill sets, and willingness to take risks, all of which stimulate economic activity and create jobs. Understanding this multifaceted impact requires examining both the positive and negative aspects.
The economic contributions of immigrant entrepreneurs and their businesses are substantial. They often establish businesses in sectors underserved by native-born entrepreneurs, creating jobs and fostering competition. Furthermore, their innovation and willingness to adopt new technologies can drive economic growth across various industries. For instance, immigrant-founded companies have been at the forefront of technological advancements in Silicon Valley and other tech hubs, contributing significantly to national GDP. Conversely, concerns exist regarding potential downward pressure on wages in specific sectors and the strain on public services in areas experiencing rapid population growth due to immigration. A balanced assessment necessitates a thorough analysis of both the advantages and disadvantages.
Economic Contributions of Immigrant Entrepreneurs
Immigrant entrepreneurs frequently fill market gaps and introduce innovative products and services. Their businesses contribute significantly to job creation, tax revenue, and overall economic output. A study by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine found that immigrant entrepreneurs are more likely to start businesses than native-born entrepreneurs, and these businesses often generate higher levels of employment. For example, consider the numerous ethnic restaurants or small businesses catering to specific cultural needs within communities – these are often started and run by immigrants, creating jobs and adding vibrancy to the local economy. Their contributions extend beyond direct employment, encompassing the ripple effects on suppliers, distributors, and related industries. The success of these businesses underscores the importance of inclusive policies that support immigrant entrepreneurship.
Job Creation, Innovation, and Economic Growth, Do immigrants get free money to start a business
Immigration’s impact on job creation is multifaceted. While some argue that immigrants compete with native-born workers for jobs, research suggests that immigration often leads to net job creation. Immigrants not only fill labor demands in various sectors, but also create jobs through their entrepreneurial activities. Moreover, their diverse skills and backgrounds often foster innovation, leading to the development of new products, services, and technologies. This innovation can drive economic growth, increasing productivity and overall economic output. For instance, the development of new technologies and business models often stems from the diverse perspectives and experiences of immigrant entrepreneurs. This dynamic interplay between immigration and innovation is a crucial driver of long-term economic prosperity.
Comparison of Economic Impact
It’s crucial to understand the comparative economic impact of immigrant-owned businesses versus those owned by native-born citizens. While direct comparisons require careful consideration of various factors like industry, business size, and location, several studies suggest that immigrant-owned businesses often demonstrate notable characteristics.
The following bullet points offer a comparison, noting that generalizations should be approached with caution due to the inherent complexities and variations involved:
- Job Creation: Studies suggest immigrant-owned businesses, particularly small businesses, may create a proportionally higher number of jobs per capita compared to native-owned businesses, especially in underserved sectors.
- Innovation: Immigrant entrepreneurs often introduce innovative products, services, and business models, contributing to increased productivity and economic diversification. Their unique perspectives and backgrounds can lead to novel solutions and approaches.
- Economic Growth: The cumulative effect of job creation and innovation in immigrant-owned businesses contributes significantly to overall economic growth and competitiveness.
- Tax Revenue: Immigrant-owned businesses contribute to tax revenue at all levels of government, supporting public services and infrastructure.
- Regional Economic Development: Immigrant entrepreneurs often revitalize struggling communities by establishing businesses in areas with limited economic opportunities, thereby stimulating local economic development.
Legal and Regulatory Hurdles
Immigrant entrepreneurs often face a complex web of legal and regulatory challenges that can significantly hinder their ability to establish and grow businesses in their new country. These hurdles extend beyond the typical difficulties faced by native-born entrepreneurs, creating a steeper learning curve and potentially limiting access to crucial resources. Understanding these challenges is vital for fostering a more inclusive and supportive entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Navigating the legal landscape of starting and running a business presents unique obstacles for immigrants. These obstacles are often compounded by language barriers, unfamiliarity with local laws and regulations, and the complexities of immigration status itself. The specific hurdles vary depending on the country of immigration and the type of business, but common themes emerge that impact access to funding and overall success.
Visa Requirements and Business Ownership
The type of visa an immigrant holds directly impacts their ability to own and operate a business. Some visas explicitly restrict business ownership, while others may require specific certifications or approvals before entrepreneurial activities are permitted. For instance, an individual on a temporary work visa might be prohibited from starting a business, while an entrepreneur visa may have stringent requirements regarding investment capital and job creation. This uncertainty can create significant delays and increase the financial burden of starting a business. Failure to comply with visa stipulations can lead to severe penalties, including deportation.
Business Licensing and Permits
Securing the necessary business licenses and permits can be a significant hurdle for immigrant entrepreneurs. The process often involves navigating complex bureaucratic procedures, understanding specific requirements for different business types, and potentially dealing with language barriers. The requirements for licenses and permits can differ significantly between countries and even within different states or regions. Delays in obtaining these permits can stall business operations and prevent access to funding. For example, a delay in obtaining a food service permit could prevent a restaurant from opening, leading to significant financial losses.
Access to Funding and Credit
Immigrant entrepreneurs often face challenges in accessing traditional sources of funding, such as bank loans. Lack of established credit history in the new country, limited English proficiency, and difficulty providing the necessary documentation can all contribute to loan applications being rejected. This lack of access to capital can severely limit business growth and expansion opportunities. Microloans and alternative funding sources may be more accessible, but these often come with higher interest rates and stricter terms. A successful business plan, strong credit history in their home country, or securing a co-signer may improve their chances.
Tax Compliance and Regulations
Understanding and complying with tax regulations can be a daunting task for anyone, but it presents even greater challenges for immigrants who may be unfamiliar with the tax laws of their new country. Incorrectly filing taxes can lead to significant penalties and even legal repercussions. This lack of clarity can create uncertainty and increase the administrative burden on immigrant-owned businesses. Seeking professional tax advice is crucial, but this adds another financial burden to already strained resources.
Language Barriers and Cultural Differences
Language barriers can create significant obstacles in navigating the legal and regulatory landscape. Understanding legal documents, communicating with government officials, and negotiating contracts can be challenging if there’s a lack of fluency in the local language. Furthermore, cultural differences in business practices and communication styles can also lead to misunderstandings and difficulties in complying with regulations. For example, differences in contract negotiation styles could lead to unintended legal complications.






