How to set up a PO box business? It’s a question many entrepreneurs ponder, especially those seeking a professional yet cost-effective address solution. This guide navigates the entire process, from selecting the right PO box provider and handling legal requirements to managing your mail efficiently and leveraging your PO box for effective marketing. We’ll cover everything you need to know to establish a successful business using a PO box, ensuring you understand the practical steps and legal considerations involved.
We’ll delve into crucial factors like comparing different PO box providers, understanding the various service types available (street address, virtual mailbox, mail forwarding), and addressing the legal and business implications of using a PO box. Learn how to optimize your mail management system, create a budget, and mitigate security risks to protect your business information. Finally, we’ll explore how to present your PO box address professionally in your marketing materials to maintain a credible business image.
Choosing the Right PO Box Service: How To Set Up A Po Box Business
Selecting the appropriate PO box service is crucial for the success of your business. The right service will streamline your mail handling, enhance your professional image, and ultimately save you time and money. Several factors need careful consideration, including pricing, location, and the specific features offered by different providers.
PO Box Provider Comparison
Choosing a PO box provider involves comparing several key aspects. The following table compares three popular providers, illustrating the variations in pricing, location availability, and additional services. Remember that pricing and features can change, so it’s vital to check the provider’s website for the most up-to-date information.
| Provider | Pricing (Example: Small Box/Month) | Location Options | Additional Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| USPS | Varies by location and box size; generally $10-$30/month | Wide range of locations nationwide, typically within post offices | Mail forwarding, package acceptance (depending on box size), registered mail acceptance |
| Private Mailbox Provider (Example: Anytime Mailbox) | Varies by location and box size; generally $20-$50/month | Locations often in more convenient, accessible areas than USPS | Mail scanning, package acceptance, virtual mailbox services, notification services, notary services (often at additional cost) |
| Virtual Mailbox Service (Example: iPostal1) | Varies by plan; generally $10-$30/month | No physical location; mail is received and scanned at a central facility | Mail scanning, forwarding, digital mail management, virtual address for online services |
PO Box Location Considerations
The location of your PO box significantly impacts your business operations. Proximity to clients or suppliers can reduce delivery times and shipping costs. Accessibility is also key; choose a location that is easily accessible during your business hours. Security is paramount; consider providers offering secure facilities with access controls and surveillance. For example, a business relying heavily on overnight deliveries might benefit from a PO box located near a major shipping hub, ensuring faster processing. Conversely, a business prioritizing client interaction might prefer a location easily accessible to clients for in-person pickups.
Types of PO Box Services
Different types of PO box services cater to various business needs. Street address PO boxes provide a physical address for your business, enhancing professionalism. Virtual mailbox services offer a digital alternative, allowing you to manage mail online. Mail forwarding services allow you to receive mail at one location and have it forwarded to another. The choice depends on your business model, volume of mail, and budget. For instance, a small online business might find a virtual mailbox sufficient, while a larger business with significant mail volume might require a physical PO box with mail forwarding services.
Setting Up Your PO Box
Securing a PO Box involves several key steps, from choosing a provider and location to understanding the addressing process and potentially setting up mail forwarding. This section details the practical aspects of establishing your PO Box and ensuring its smooth operation. Careful planning during this phase minimizes future complications and maximizes the efficiency of your business operations.
PO Box Application Process
The application process for a PO Box varies slightly depending on the provider (USPS, private mailbox companies, etc.), but generally involves these common steps. First, you’ll need to select a location and box size. Consider factors like accessibility, proximity to your business, and the expected volume of mail. Next, you’ll typically complete an application form, either online or in person. This form will request personal information such as your name, address, and contact details, along with potentially a form of identification (driver’s license, passport, etc.). You will also be required to pay the applicable fees, which vary depending on box size and rental period. Once your application is processed and the fees are paid, you will receive access to your assigned PO Box. Some providers might offer additional services, such as package acceptance, which may necessitate additional fees.
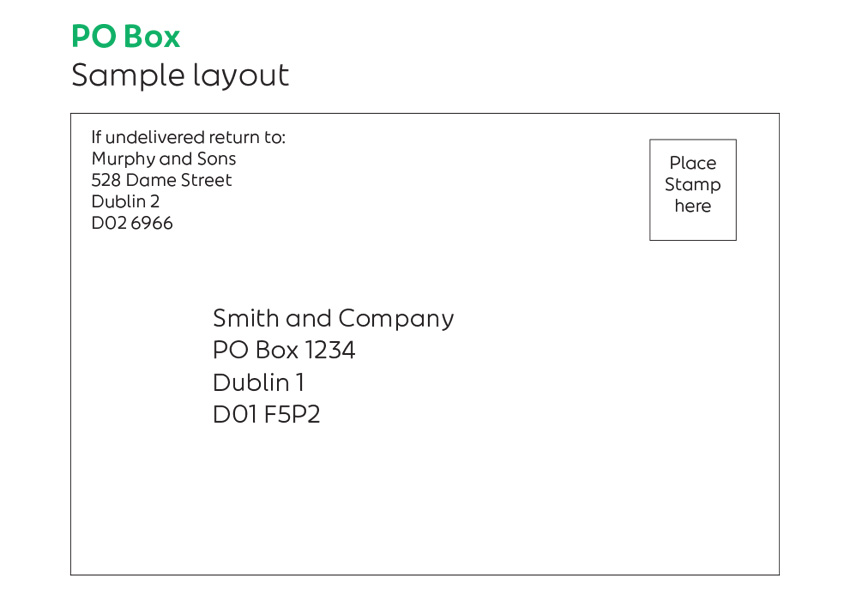
Addressing Mail to a PO Box
Correctly addressing mail to your PO Box is crucial for reliable delivery. Incorrect addressing can lead to delays or even lost mail, impacting your business operations. The format should be precise and consistent. The address should follow this structure:
Your Name or Business Name
PO Box Number
City, State, Zip Code
For example:
Acme Corp
PO Box 123
Anytown, CA 91234
Ensure the information is clearly legible and printed or written neatly. Using a label is recommended to minimize errors. Remember to always use the correct PO Box number and the official city, state, and zip code provided by your PO Box provider.
Mail Forwarding Setup
Mail forwarding is a valuable service if your business’s physical address differs from your PO Box location. This ensures that mail sent to your physical address is redirected to your PO Box. To set up mail forwarding, you will typically need to contact your current postal service provider (USPS, for example) and fill out a change of address form. This form will require your old address (the one you’re forwarding from) and your new address (your PO Box). You’ll need to specify the duration of the forwarding period. There might be a fee associated with this service, depending on the length of time and the provider. This ensures that you don’t miss any important correspondence.
Legal and Business Considerations

Operating a business from a PO Box requires careful consideration of legal and regulatory requirements to ensure compliance and maintain the integrity of your operations. Failure to adhere to these regulations can lead to penalties and negatively impact your business reputation. Understanding these aspects is crucial for a smooth and successful business journey.
Business Registration and Licensing
The legal requirements for operating a business from a PO Box vary depending on your business structure, location, and the nature of your activities. Sole proprietorships may only require a business license from their local municipality, while corporations and LLCs typically require state-level registration and may need additional licenses depending on their industry. It’s imperative to check with your state’s Secretary of State office and your local government to determine the specific registrations and licenses required for your business type and location. For example, a food-based business will require additional health and safety permits, whereas a consulting firm may only need a general business license. Failing to obtain the necessary licenses can result in significant fines and legal repercussions. It’s advisable to consult with a legal professional or business advisor to ensure full compliance.
Maintaining Business Records and Compliance
Maintaining accurate and organized business records is crucial for tax purposes, legal compliance, and effective business management, regardless of whether you use a PO Box or a physical address. Keep meticulous records of all financial transactions, including income, expenses, and invoices. These records should be readily accessible for audits by tax authorities. Additionally, maintain records of all contracts, agreements, and communications relevant to your business operations. For example, a detailed record-keeping system might involve using accounting software to track finances, a cloud-based system for storing contracts, and a dedicated filing system for important documents. Regularly backing up your records is essential to protect against data loss. Compliance with relevant regulations, such as data privacy laws (like GDPR or CCPA), is crucial and should be factored into your record-keeping practices.
Handling Sensitive Documents and Confidentiality
When using a PO Box for business, safeguarding sensitive documents and maintaining client confidentiality is paramount. Avoid including sensitive information, such as credit card numbers or social security numbers, directly on mail sent to your PO Box. Instead, consider using secure digital methods for transmitting such data. If physical documents must be sent, use registered mail or courier services that provide tracking and require signatures upon delivery. When retrieving mail from your PO Box, ensure you do so in a secure manner, avoiding public display of sensitive information. Consider shredding any sensitive documents after they are no longer needed to prevent unauthorized access to confidential data. Implementing robust security measures is vital to protecting your business and your clients’ information.
Managing Your PO Box Effectively

Efficiently managing your PO Box is crucial for maintaining a smooth workflow and preventing missed opportunities. A well-organized system ensures you receive and process all your mail promptly, minimizing the risk of delays or lost correspondence. This includes establishing clear procedures for handling different mail types and creating a regular schedule for mail retrieval.
A robust mail management system for your PO Box requires careful planning and consistent execution. Consider your business volume and the types of mail you expect to receive when designing your system. The goal is to streamline the process, making it as efficient and effective as possible. This section Artikels key steps for achieving this.
Mail Organization System
Implementing a structured system for organizing incoming mail prevents chaos and ensures timely processing. This system should be tailored to your specific business needs, but the following components are essential.
- Categorization: Upon retrieval, immediately sort mail into pre-defined categories (e.g., invoices, marketing materials, client correspondence, personal mail). Using clearly labeled folders or trays helps expedite this process.
- Prioritization: Prioritize urgent mail (e.g., invoices, time-sensitive client communications) for immediate attention. Less urgent items can be processed later.
- Record Keeping: Maintain a log of all incoming mail, noting the date received, sender, and a brief description of the contents. This helps track important documents and simplifies searching for specific items.
- Digitalization: Scan important documents and store them digitally for easy access and backup. This reduces reliance on physical files and simplifies organization.
- Disposal: Establish a clear process for discarding unwanted mail, ensuring compliance with any relevant data protection regulations.
Mail Collection Schedule, How to set up a po box business
Regular mail collection is essential to prevent a backlog and ensure timely processing of important documents. The frequency of collection should align with your business needs and the volume of mail you expect.
A sample schedule might look like this:
| Day | Action |
|---|---|
| Monday | Collect mail, process high-priority items. |
| Wednesday | Collect mail, process remaining items, scan and file important documents. |
| Friday | Collect mail, review the week’s mail log, dispose of unwanted mail. |
Adjust this schedule based on your individual requirements. For high-volume businesses, daily collection may be necessary, while less active businesses might only need to collect mail twice a week.
Handling Different Mail Types
Different types of mail require different handling procedures. A clear system for processing each type ensures efficiency and reduces the risk of errors.
- Invoices: Process invoices immediately to ensure timely payment and avoid late fees. Record payment details in your accounting software.
- Letters: Read letters promptly and respond accordingly. File important letters for future reference.
- Packages: Handle packages carefully to prevent damage. Sign for packages appropriately and ensure they are delivered to their intended recipient.
- Marketing Materials: Review marketing materials for potential opportunities and discard unwanted items.
Security and Privacy Best Practices
Using a PO Box offers convenience, but it also introduces unique security and privacy challenges. Protecting your mail and sensitive business information requires proactive measures to minimize risks and maintain confidentiality. Failing to do so can lead to identity theft, financial losses, and damage to your business reputation.
Implementing robust security and privacy protocols is crucial for any business using a PO Box. This involves a multifaceted approach encompassing physical security, data protection, and awareness of potential vulnerabilities. The following sections detail practical steps to enhance the security and privacy of your business operations when utilizing a PO Box.
PO Box Security Measures
Protecting your mail from theft or loss requires vigilance and a layered security approach. Regularly checking your PO Box is the first line of defense, preventing mail from accumulating and becoming a target. Consider the frequency of your mail volume; a high-volume business might need daily checks, while a low-volume business could manage with weekly checks. If you cannot check your box frequently, consider authorizing a trusted individual to do so on your behalf. Additionally, choosing a well-lit, highly trafficked PO Box location can deter potential thieves. Some postal services offer secure, larger boxes with added locking mechanisms; investigating these options may be worthwhile depending on your needs and the available options at your location. Finally, report any suspicious activity or suspected theft immediately to the postal authorities.
Privacy Best Practices for Sensitive Business Information
Maintaining the privacy of sensitive business information when using a PO Box necessitates careful consideration of how you handle documents and data. Avoid including sensitive information such as bank account details or credit card numbers in mail sent to your PO Box. Instead, utilize secure electronic methods for transmitting such data. When disposing of sensitive documents, ensure they are properly shredded to prevent unauthorized access. Consider using a secure document destruction service for large volumes of sensitive materials. Never leave your PO Box key unattended or leave your PO Box key in a place that is easily accessible. Use strong passwords for any online accounts associated with your PO Box or business. Regularly review your privacy policies and procedures to ensure they are up-to-date and effective.
Risks Associated with Using a PO Box and Mitigation Strategies
Using a PO Box presents several inherent risks. The most significant is the potential for mail theft or loss. Another risk is the perception of unprofessionalism or lack of legitimacy among some clients. Finally, there’s the risk of missed deliveries if the PO Box is not checked frequently. To mitigate these risks, businesses should implement the security measures described above. To address the perception of unprofessionalism, consider including a professional business address on your website and marketing materials, alongside your PO Box information. This can reassure clients that you are a legitimate business. To prevent missed deliveries, establish a system for regularly checking the PO Box and forwarding important mail promptly. Implementing these strategies will help minimize the risks associated with using a PO Box.
Cost Considerations and Budget Planning
Establishing a PO box for your business requires careful consideration of the associated costs. Understanding these expenses and creating a realistic budget is crucial for maintaining financial stability and ensuring the long-term viability of your mail management strategy. Failing to account for all potential costs can lead to unexpected financial burdens and impact your business’s bottom line.
The overall cost of operating a PO box depends on several factors, including the location, the size of the box, the provider, and any additional services required. A thorough budget should encompass all these elements to provide a comprehensive financial picture. This allows for informed decision-making and helps prevent unforeseen expenses from derailing your business operations.
PO Box Budget Sample
The following sample budget Artikels the typical ongoing costs associated with maintaining a PO box. Remember that these are estimates, and actual costs may vary depending on your specific circumstances. It’s advisable to contact potential providers directly for precise pricing information.
| Expense Category | Monthly Cost (Estimate) | Annual Cost (Estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| PO Box Rental | $15 – $50 | $180 – $600 |
| Packaging Supplies (Envelopes, Boxes) | $10 – $25 | $120 – $300 |
| Shipping Supplies (Tape, Labels) | $5 – $15 | $60 – $180 |
| Additional Services (e.g., Mail Forwarding, Package Receiving) | $0 – $30 | $0 – $360 |
| Total Estimated Monthly Cost | $30 – $120 | $360 – $1440 |
This budget demonstrates a wide range in potential costs. The lower end reflects a basic setup with a small PO box and minimal additional services, while the higher end accounts for larger boxes, frequent mail volume, and the utilization of extra services.
Cost Comparison of PO Box Options
Different PO box providers offer varying pricing structures and services. Comparing options is essential to find the most cost-effective solution for your needs. Factors to consider include the size of the box, the length of the rental term (longer terms often offer discounts), and the inclusion of additional services. Some providers may offer discounts for online payments or annual contracts. Direct comparison shopping through multiple providers is crucial for securing the best value.
Cost Minimization Strategies
Several strategies can help minimize PO box costs without compromising efficiency. Negotiating rental rates, opting for smaller boxes if your mail volume is low, and choosing providers with competitive pricing are key considerations. Additionally, utilizing cost-effective packaging and shipping supplies can significantly reduce expenses over time. Careful consideration of your mail volume and needs is paramount to avoid overspending on services you don’t require.






