Grow Financial auto loan rates, like those of other lenders, are influenced by a complex interplay of economic factors and borrower characteristics. Understanding these influences is crucial for securing the best possible loan terms. This guide delves into the current trends, the factors affecting rate increases, and strategies for obtaining lower rates, empowering you to navigate the auto loan landscape effectively. We’ll examine how credit scores impact your interest rate, compare different lender options, and illustrate the financial implications of various loan scenarios.
From the impact of inflation and Federal Reserve policy to the role of your credit score and the used car market, we’ll unpack the key drivers behind auto loan interest rates. We’ll also provide practical strategies to help you improve your chances of securing a favorable rate, including tips for negotiating with lenders and choosing the right loan type. By the end, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions and secure the best possible financing for your next vehicle.
Current Trends in Auto Loan Rates: Grow Financial Auto Loan Rates
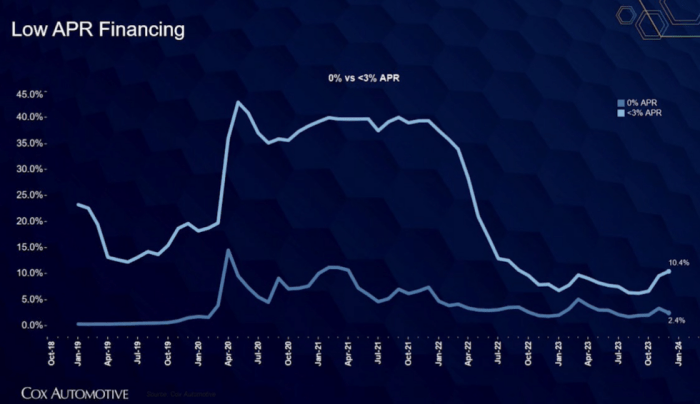
Auto loan interest rates are a dynamic element of the financial landscape, influenced by a complex interplay of economic factors. Understanding these trends is crucial for both borrowers seeking financing and lenders assessing risk. Currently, rates are exhibiting some volatility, reflecting broader economic uncertainty and shifts in monetary policy.
Current auto loan interest rates reflect a fluctuating market. Several key factors contribute to these fluctuations, resulting in periods of higher and lower rates. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy, inflation rates, and overall economic growth significantly impact borrowing costs. Additionally, the creditworthiness of borrowers plays a vital role, with individuals possessing higher credit scores generally securing more favorable rates. Competition among lenders also influences rates, as institutions strive to attract customers with competitive offers. Finally, the type of vehicle being financed (new versus used) and the loan term also affect the final interest rate.
Factors Influencing Auto Loan Rate Trends, Grow financial auto loan rates
The Federal Reserve’s actions regarding interest rates directly impact the cost of borrowing money. When the Fed raises interest rates to combat inflation, auto loan rates tend to follow suit. Conversely, rate cuts often lead to lower auto loan rates. Inflation, which measures the rate at which prices for goods and services are increasing, also plays a crucial role. High inflation generally pushes interest rates higher as lenders seek to protect their returns against the eroding purchasing power of money. Economic growth, or the lack thereof, significantly influences consumer demand and lender risk assessments. Strong economic growth usually leads to more favorable lending conditions, potentially lowering rates. Conversely, economic downturns can increase risk and thus lead to higher rates.
Comparison of Current Rates to Historical Averages
Currently, average auto loan rates are somewhat elevated compared to the historical lows seen in recent years. However, they remain within a reasonable range when considered against longer-term historical averages. For example, 36-month loan terms averaged around 4% in the early 2010s, significantly lower than the current average. The differences are primarily attributed to the economic conditions prevailing during those periods. Longer-term loans (e.g., 72 months) have historically carried higher interest rates to reflect the increased risk for lenders. These longer terms also often expose borrowers to a greater total interest paid over the life of the loan.
Average Auto Loan Interest Rates by Credit Score and Loan Term
The following table presents average auto loan interest rates for various credit scores and loan terms. These figures are estimates based on current market conditions and should be considered approximations. Individual rates may vary based on lender policies, the borrower’s specific financial profile, and the type of vehicle being financed.
| Credit Score | Loan Term (months) | Average Interest Rate | Rate Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| 660-679 (Fair) | 36 | 8.5% | 7.5% – 9.5% |
| 680-699 (Good) | 36 | 7.0% | 6.0% – 8.0% |
| 700-759 (Very Good) | 36 | 5.5% | 4.5% – 6.5% |
| 760-850 (Excellent) | 36 | 4.0% | 3.0% – 5.0% |
| 660-679 (Fair) | 60 | 9.5% | 8.5% – 10.5% |
| 680-699 (Good) | 60 | 8.0% | 7.0% – 9.0% |
| 700-759 (Very Good) | 60 | 6.5% | 5.5% – 7.5% |
| 760-850 (Excellent) | 60 | 5.0% | 4.0% – 6.0% |
Factors Affecting Auto Loan Rate Increases
Auto loan interest rates are dynamic, influenced by a complex interplay of macroeconomic factors and regulatory changes. Understanding these influences is crucial for borrowers seeking to secure favorable loan terms. Several key elements contribute to fluctuations in rates, impacting the overall cost of borrowing for new and used vehicles.
Inflation’s Impact on Auto Loan Interest Rates
Inflation, the persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services, directly impacts auto loan rates. When inflation rises, lenders increase interest rates to compensate for the decreased purchasing power of future repayments. Higher inflation erodes the real value of money, meaning lenders need a higher return to maintain profitability. For example, during periods of high inflation like the late 1970s or the current inflationary environment, we’ve seen a corresponding increase in auto loan interest rates to offset the risk of inflation eroding the lender’s return. The Federal Reserve’s actions to combat inflation, such as raising interest rates, further exacerbate this effect.
The Federal Reserve’s Monetary Policy and Auto Loan Rates
The Federal Reserve (the Fed) plays a pivotal role in influencing interest rates across the economy, including auto loans. The Fed’s monetary policy tools, primarily the federal funds rate (the target rate banks charge each other for overnight loans), directly impact the prime rate, a benchmark for other interest rates. When the Fed raises the federal funds rate to combat inflation, borrowing costs across the board, including auto loans, tend to increase. Conversely, a reduction in the federal funds rate typically leads to lower auto loan rates, stimulating borrowing and economic activity. For instance, the Fed’s aggressive interest rate hikes in 2022 to curb inflation resulted in a significant increase in auto loan rates throughout the year.
Economic Growth or Recession and Borrowing Costs
Economic conditions significantly influence auto loan rates. During periods of strong economic growth, lenders are more willing to offer lower rates due to increased consumer demand and lower perceived risk. Conversely, during economic downturns or recessions, lenders become more risk-averse, leading to higher rates to compensate for the increased likelihood of loan defaults. The 2008 financial crisis, for example, saw a sharp increase in auto loan rates as lenders tightened lending standards and demanded higher interest rates to offset increased risk.
The Used Car Market’s Influence on New Car Loan Rates
The used car market’s performance has a surprising impact on new car loan rates. A strong used car market, characterized by high prices and strong demand, can indirectly lead to higher new car loan rates. This occurs because the residual value of new cars, a key factor in determining loan terms, increases, potentially leading to higher interest rates as lenders perceive a lower risk in lending. Conversely, a weak used car market may lead to lower new car loan rates.
Changes in Lending Regulations and Their Effect on Rates
Government regulations significantly influence lending practices and, consequently, auto loan rates. Changes in lending regulations, such as stricter requirements for loan approvals or increased capital requirements for lenders, can lead to higher auto loan rates. This is because lenders pass on the increased costs associated with compliance to borrowers. For example, the Dodd-Frank Act, implemented after the 2008 financial crisis, introduced stricter regulations on lending practices, potentially impacting auto loan rates by increasing compliance costs for lenders.
Impact of Credit Scores on Auto Loan Rates
Your credit score is a crucial factor influencing the interest rate you’ll receive on an auto loan. Lenders use credit scores to assess your creditworthiness – essentially, your likelihood of repaying the loan on time. A higher credit score signals lower risk to the lender, resulting in more favorable loan terms. Conversely, a lower score indicates higher risk, leading to higher interest rates and potentially less favorable loan options.
Credit scores are typically calculated using a range of factors including payment history, amounts owed, length of credit history, credit mix, and new credit. These factors are weighted differently by various credit scoring models, such as FICO and VantageScore, but the overall principle remains consistent: a higher score reflects responsible credit management.
Credit Score Ranges and Corresponding Interest Rates
The interest rate you qualify for is directly tied to your credit score. While exact rates vary depending on the lender, the current economic climate, and the specific loan terms, a general range can illustrate the impact. Consider these approximate ranges, keeping in mind that individual rates may differ:
| Credit Score Range | Approximate Interest Rate Range (Example) |
|---|---|
| Excellent (750-850) | 3.0% – 5.0% |
| Good (670-749) | 5.5% – 7.5% |
| Fair (600-669) | 8.0% – 12.0% |
| Poor (Below 600) | 12.0% – 20% or higher |
*Note: These are example ranges and actual rates will vary based on lender, loan terms, and market conditions.*
Financial Implications of a Lower Credit Score
A lower credit score translates directly into a higher interest rate, significantly impacting the total cost of the loan over its lifetime. This increased cost is due to paying more in interest charges over the repayment period. The difference can be substantial, potentially amounting to thousands of dollars.
Scenario: Comparing Total Interest Paid
Let’s compare two borrowers, both seeking a $25,000 auto loan over 60 months:
Borrower A has an excellent credit score (780) and qualifies for a 4.5% interest rate.
Borrower B has a fair credit score (620) and qualifies for a 10% interest rate.
Using a standard loan amortization calculator (easily found online), we can see the stark difference:
Borrower A (4.5% interest): Total interest paid over 60 months would be approximately $2,870.
Borrower B (10% interest): Total interest paid over 60 months would be approximately $6,250.
The difference in total interest paid is approximately $3,380, solely due to the difference in credit scores. This highlights the significant financial advantage of maintaining a good credit history.
Strategies for Obtaining Lower Auto Loan Rates
Securing a favorable auto loan rate is crucial for minimizing the overall cost of your vehicle purchase. Several strategies can significantly impact the interest rate you receive, ultimately saving you thousands of dollars over the life of the loan. Understanding these strategies and implementing them effectively can make a substantial difference in your financial well-being.
Improving Credit Scores Before Applying for a Loan
A higher credit score is the single most significant factor influencing your auto loan rate. Lenders view individuals with higher credit scores as less risky borrowers. Improving your credit score before applying for a loan can translate into a substantially lower interest rate. This involves paying down existing debts, especially credit card balances, to reduce your credit utilization ratio. Consistent on-time payments on all credit accounts are also vital. Monitoring your credit report regularly for errors and disputing any inaccuracies can also positively impact your score. Consider using credit monitoring services or reviewing your credit reports from AnnualCreditReport.com to track your progress. Aiming for a score above 700 generally qualifies you for the best interest rates.
Comparison of Interest Rates Offered by Various Lenders
Different lenders offer varying interest rates, reflecting their risk assessments and business models. Banks typically offer a wide range of loan products but might have stricter lending criteria. Credit unions, often member-owned, may offer more competitive rates and personalized service to their members. Online lenders frequently provide convenient applications and potentially competitive rates, but it’s essential to thoroughly research their reputation and terms. Shopping around and comparing offers from multiple lenders – at least three to five – is crucial to finding the best rate. Use online comparison tools or visit lenders directly to gather quotes. Remember to factor in any associated fees when comparing offers. For example, a slightly higher interest rate with fewer fees might ultimately be more cost-effective.
Fixed-Rate vs. Variable-Rate Auto Loans
Fixed-rate loans offer predictable monthly payments throughout the loan term, providing financial stability. The interest rate remains constant, shielding you from potential rate increases. Variable-rate loans, on the other hand, have interest rates that fluctuate based on market conditions. While initially, they might offer lower rates, they expose you to the risk of higher payments if interest rates rise. The choice between a fixed and variable rate depends on your risk tolerance and financial outlook. If you prefer predictable payments and want to avoid the uncertainty of fluctuating rates, a fixed-rate loan is generally the safer option. However, if you anticipate interest rates remaining low or even declining, a variable-rate loan might offer short-term savings.
Negotiating with Lenders to Lower Interest Rates
Negotiating with lenders can sometimes lead to a lower interest rate. This involves presenting your strong financial standing, highlighting your excellent credit score, and demonstrating your commitment to repaying the loan. Having pre-approval from multiple lenders strengthens your negotiating position. You can use competing offers to leverage a better deal from your preferred lender. Politely and confidently express your desire for a lower rate, emphasizing your responsible financial history. Be prepared to walk away if the lender is unwilling to negotiate reasonably.
Steps to Secure a Favorable Interest Rate
Before applying for an auto loan, several steps can significantly increase your chances of securing a favorable interest rate.
- Check and improve your credit score.
- Shop around and compare rates from multiple lenders (banks, credit unions, online lenders).
- Choose a loan term that balances affordability with total interest paid.
- Make a substantial down payment to reduce the loan amount.
- Negotiate with lenders to secure a lower interest rate.
- Consider pre-approval from multiple lenders to strengthen your negotiating position.
- Carefully review all loan terms and conditions before signing.
Illustrative Examples of Loan Scenarios
Understanding the impact of interest rates on the total cost of an auto loan is crucial for informed financial decision-making. The following examples illustrate how even small differences in interest rates can significantly affect the overall repayment amount.
High-Interest Loan Scenario
Let’s consider a hypothetical loan of $25,000 with a high annual interest rate of 10%, amortized over 60 months (5 years). Using a standard loan amortization calculator, the monthly payment would be approximately $532.42. Over the life of the loan, the total interest paid would be approximately $6,745.20. This means that the borrower would pay a total of $31,745.20 to purchase a $25,000 vehicle. This scenario highlights the significant financial burden imposed by higher interest rates.
Low-Interest Loan Scenario
Now, let’s examine a similar loan scenario, but with a lower annual interest rate of 4%, also amortized over 60 months. The monthly payment in this case would be approximately $464.71. The total interest paid over the loan’s duration would be roughly $1,882.60. The total repayment amount would be $26,882.60. This represents a considerable cost savings compared to the high-interest scenario.
Comparison of Loan Scenarios
The difference between these two scenarios is stark. While both loans cover the same principal amount ($25,000) and have the same loan term (60 months), the higher interest rate (10%) results in a total interest payment almost four times greater ($6,745.20) than the lower interest rate (4%) scenario ($1,882.60). This difference translates to a total repayment amount that is almost $5,000 higher in the high-interest scenario. This example clearly demonstrates the importance of securing the lowest possible interest rate when financing a vehicle.
Cumulative Interest Paid: Bar Graph Illustration
A bar graph visually represents the cumulative interest paid over the life of each loan. The horizontal axis would represent the loan scenario (High Interest – 10% and Low Interest – 4%). The vertical axis would represent the total interest paid in dollars. The bar representing the high-interest loan (10%) would reach approximately $6,745.20, significantly taller than the bar representing the low-interest loan (4%), which would reach approximately $1,882.60. The clear difference in bar heights graphically illustrates the substantial cost savings associated with obtaining a lower interest rate. The graph title would be “Cumulative Interest Paid Over 60 Months,” and each bar would be clearly labeled with the corresponding interest rate and the dollar amount of interest paid. The graph would use a consistent scale on the vertical axis to accurately reflect the difference in interest payments.
Last Recap
Securing a favorable auto loan rate requires careful planning and understanding of the market dynamics. By proactively improving your credit score, comparing offers from different lenders, and negotiating effectively, you can significantly reduce the overall cost of your loan. Remember, a well-informed borrower is a powerful borrower. This guide has equipped you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of auto loan rates and achieve your financial goals. Now, take control and find the best financing for your next vehicle.
Expert Answers
What is the average processing time for a Grow Financial auto loan application?
Processing times vary, but generally range from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the completeness of your application and supporting documentation.
Can I refinance my existing auto loan with Grow Financial?
Yes, Grow Financial often offers auto loan refinancing options. Check their website or contact them directly for current eligibility criteria and rates.
What types of auto loans does Grow Financial offer?
They typically offer various loan types, including new and used car loans, with varying terms and interest rates. Specific offerings may change, so check their current offerings.
Does Grow Financial offer pre-approval for auto loans?
Yes, pre-approval can help you determine your borrowing power and shop for vehicles with confidence. Check their website for details on their pre-approval process.