Parent PLUS Loan ASU: Navigating the complexities of financing your child’s education at Arizona State University can feel overwhelming. This comprehensive guide demystifies the Parent PLUS loan process, providing a clear understanding of eligibility requirements, the application process, repayment options, and potential pitfalls. We’ll explore the intricacies of this federal loan program, empowering you to make informed decisions and successfully manage your financial responsibilities.
From understanding eligibility criteria based on credit history to mastering the online application and navigating various repayment plans, we’ll cover every step. We’ll also compare Parent PLUS loans with other financial aid options available at ASU, helping you determine the best path for your family’s financial situation. This guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools to confidently manage the Parent PLUS loan process and ensure a smooth educational journey for your child.
ASU Parent PLUS Loan Eligibility Requirements
Securing financial aid for higher education is a crucial step for many families. The Parent PLUS Loan, offered through the federal government, can help parents cover their child’s educational expenses at Arizona State University (ASU). However, eligibility for this loan program is subject to specific criteria. Understanding these requirements is essential for parents seeking to utilize this financial aid option.
Student Eligibility for Parent PLUS Loan Consideration
For parents to be eligible for a Parent PLUS loan, their dependent student must first meet certain requirements. The student must be accepted for admission or already enrolled at ASU, be pursuing a degree or certificate program, and be registered for at least half-time enrollment. Furthermore, the student must meet the general eligibility requirements for federal student aid, including providing a valid Social Security number and being a U.S. citizen or eligible non-citizen. The student’s financial aid application must also be completed and processed through the ASU Office of Financial Aid and Scholarships.
Credit History Requirements for Parent PLUS Loan Applicants
The primary eligibility criterion for the Parent PLUS loan rests with the parent applicant’s credit history. The Department of Education will conduct a credit check on the parent applying for the loan. Adverse credit history, such as bankruptcies, foreclosures, or a history of late payments, may result in loan denial. While a perfect credit score isn’t required, a history of responsible credit management is crucial. Parents with a history of serious credit issues might be denied a Parent PLUS loan outright. In such cases, alternative options, such as an endorser, may be explored.
Step-by-Step Process for Determining Parent PLUS Loan Eligibility
Determining eligibility for a Parent PLUS Loan involves several steps. First, the student must complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). Next, the parent must complete the Parent PLUS Loan application through the National Student Loan Data System (NSLDS). The Department of Education will then conduct a credit check on the parent applicant. If approved, the loan funds will be disbursed to ASU to be applied towards the student’s tuition and fees. If denied, parents may be able to explore alternative options or appeal the decision. Finally, parents must understand the terms and conditions of the loan before accepting it.
Comparison of Parent PLUS Loan Eligibility with Other ASU Financial Aid Options
| Financial Aid Option | Credit Check Required? | Income-Based? | Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parent PLUS Loan | Yes | No | Parent’s creditworthiness, student enrollment status |
| Federal Direct Subsidized/Unsubsidized Loans | No | No | Student’s enrollment status, FAFSA completion |
| ASU Scholarships | No | May be income-based | Academic merit, financial need, specific program requirements |
| Grants (Federal Pell Grant) | No | Yes | Financial need, enrollment status, FAFSA completion |
Applying for an ASU Parent PLUS Loan: Parent Plus Loan Asu
Securing financial aid for your child’s education at Arizona State University (ASU) often involves exploring various loan options. The Parent PLUS Loan, a federal loan program, allows parents to borrow funds to cover their child’s educational expenses. Understanding the application process and potential challenges is crucial for a smooth borrowing experience.
The Parent PLUS loan application process involves several key steps, from initial eligibility verification to loan disbursement. Careful preparation and attention to detail are essential to ensure a successful application. Failure to provide accurate information or meet specific requirements can lead to delays or denial.
Parent PLUS Loan Application Process
The application process for a Parent PLUS loan is primarily conducted online through the Federal Student Aid website (studentaid.gov). Parents must first complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) and be deemed eligible for the loan. The FAFSA gathers information about your income and assets to determine your eligibility for federal student aid. Following this, the Parent PLUS loan application itself requires specific steps.
- Complete the FAFSA: This crucial first step provides the foundation for your eligibility determination. The FAFSA requires information about both the parent and student, including Social Security numbers, tax information, and assets.
- Apply for a Parent PLUS Loan: Once the FAFSA is processed, you’ll be able to access the Parent PLUS loan application through the Federal Student Aid website. This application requires additional information, such as your credit history and banking details.
- Credit Check and Approval: The Department of Education will perform a credit check as part of the application process. A negative credit history can result in loan denial. A co-signer may be an option in certain circumstances.
- Master Promissory Note (MPN): Upon approval, you’ll need to sign a Master Promissory Note (MPN), a legal agreement outlining your loan terms and responsibilities. This note signifies your commitment to repay the borrowed funds.
- Loan Disbursement: Once the MPN is signed, the loan funds will be disbursed directly to ASU. The disbursement schedule usually aligns with the academic calendar.
Required Documentation
The Parent PLUS loan application requires several documents to support your financial information and identity verification. Providing accurate and complete documentation is essential for a timely processing of your application. Failure to provide the necessary documentation can lead to delays or rejection.
- Social Security Number: Both the parent and student’s Social Security numbers are required.
- Tax Information: Tax returns (IRS 1040) or tax transcripts are needed to verify income and tax liability.
- Bank Information: Account details are required for loan disbursement and repayment.
- Student’s Financial Information: Information about the student’s enrollment and cost of attendance at ASU is required.
Parent PLUS Loan Denial and Appeal
A Parent PLUS loan application may be denied for several reasons, primarily due to adverse credit history. However, there are options for appealing a denial. Careful review of the denial reasons is crucial for constructing a successful appeal.
Parents denied a Parent PLUS loan can explore options such as finding a creditworthy co-signer or demonstrating improved financial circumstances. They can also request a review of the decision with the Department of Education, providing additional documentation or explanation to support their case. An appeal involves providing additional information or evidence to address the reasons for denial. This might include documentation demonstrating improvement in credit history or addressing any inaccuracies in the initial application. The appeal process has specific timelines and requirements that must be followed.
Understanding the Terms and Conditions of an ASU Parent PLUS Loan

Securing a Parent PLUS loan to support your child’s education at Arizona State University involves understanding the associated terms and conditions. This includes a thorough grasp of interest rates, repayment options, and the potential consequences of default. Failing to understand these aspects can significantly impact your financial well-being.
Interest Rates and Their Determination
Parent PLUS loan interest rates are variable and are determined by the U.S. Department of Education. The rate is set at the beginning of each federal fiscal year (July 1st) and remains fixed for the life of the loan. This means that while your rate won’t change after your loan is disbursed, it will differ from the rate offered to other borrowers who take out loans in subsequent years. The specific interest rate is dependent on the prevailing market conditions and the government’s cost of borrowing. Borrowers should check the official Federal Student Aid website for the most current interest rate information. Additionally, a loan origination fee is typically added to the principal loan amount. This fee is a percentage of the loan and is deducted upfront, increasing the total cost of borrowing.
Repayment Options and Deferment
Several repayment options are available to Parent PLUS loan borrowers, offering flexibility based on individual financial circumstances. These options typically include standard repayment plans (fixed monthly payments over a 10-year period), extended repayment plans (longer repayment terms resulting in lower monthly payments but higher total interest), and graduated repayment plans (lower payments initially that increase over time). The choice of repayment plan will influence the total amount of interest paid over the life of the loan. Deferment, which temporarily suspends loan payments, may be available under specific circumstances, such as unemployment or economic hardship. However, interest may still accrue during deferment periods, adding to the total loan amount. It’s crucial to contact your loan servicer to explore the available options and determine the most suitable repayment plan.
Consequences of Loan Default
Defaulting on a Parent PLUS loan has serious financial ramifications. A default occurs when a borrower fails to make payments for a specified period. This negatively impacts the borrower’s credit score, making it challenging to obtain future loans, credit cards, or even rent an apartment. The Department of Education may also pursue collection actions, including wage garnishment, tax refund offset, and referral to a collection agency. These actions can lead to significant financial hardship and legal consequences. It’s imperative to contact your loan servicer immediately if you anticipate difficulties making payments to explore available options such as forbearance or repayment plan modifications to avoid default.
Comparison of Repayment Plans
The following table compares different Parent PLUS loan repayment plans. Note that these are examples and specific terms may vary depending on the loan and the servicer.
| Repayment Plan | Repayment Period | Monthly Payment (Example) | Total Interest Paid (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | 10 years | $300 | $5,000 |
| Extended | 25 years | $150 | $15,000 |
| Graduated | 10 years | $200 (increasing annually) | $7,000 |
Managing and Repaying an ASU Parent PLUS Loan
Successfully managing and repaying your ASU Parent PLUS loan requires proactive planning and understanding of available resources. This section details the repayment process, budgeting strategies, and assistance options for borrowers facing financial hardship. Careful management can minimize stress and ensure timely repayment.
Making Loan Payments, Parent plus loan asu
ASU Parent PLUS loan payments can be made through several convenient methods. Borrowers can access their loan account online through the National Student Loan Data System (NSLDS) or the loan servicer’s website to make payments electronically. This often involves setting up automatic payments, providing a debit card or bank account information for recurring withdrawals. Alternatively, payments can be made by mail using a check or money order, though this method is generally slower and less efficient. Contacting the loan servicer directly is crucial to obtain the correct mailing address and payment instructions. Remember to always include your loan identification number on any payment sent by mail to ensure proper processing.
Budgeting and Managing Loan Repayments
Effective budgeting is crucial for avoiding loan default. Begin by creating a detailed monthly budget, outlining all income and expenses. Allocate a specific amount for your loan payment each month, ensuring it’s a manageable portion of your income. Consider using budgeting apps or spreadsheets to track expenses and monitor progress. If unexpected expenses arise, explore options like temporarily reducing non-essential spending or contacting your loan servicer to discuss potential repayment plan adjustments, such as deferment or forbearance (options explained below). Regularly reviewing your budget and making adjustments as needed will maintain financial stability and timely loan repayment.
Resources for Borrowers Facing Financial Hardship
Borrowers experiencing financial difficulty should proactively contact their loan servicer. Several options may be available to help manage repayment. Deferment temporarily postpones payments, often requiring documentation of financial hardship, such as unemployment. Forbearance allows for temporary suspension or reduction of payments but typically doesn’t stop interest accrual. Income-driven repayment plans adjust monthly payments based on income and family size, potentially lowering monthly obligations. The loan servicer can explain the eligibility requirements and implications of each option. Additionally, seeking guidance from a financial advisor or credit counselor can provide valuable support in navigating financial challenges and creating a sustainable repayment plan. Remember, proactive communication with your loan servicer is key to preventing delinquency and default.
Tips for Responsible Loan Management
Responsible loan management requires consistent effort and attention. The following tips can contribute to successful repayment:
- Understand your loan terms, including interest rates, repayment schedules, and fees.
- Set up automatic payments to ensure timely payments and avoid late fees.
- Budget carefully to ensure loan payments are consistently made.
- Monitor your loan account regularly online to track payments and identify any issues.
- Contact your loan servicer immediately if you anticipate difficulty making payments.
- Explore options like deferment, forbearance, or income-driven repayment plans if needed.
- Consider consolidating your loans to simplify repayment and potentially lower interest rates.
Comparing ASU Parent PLUS Loans with Other Loan Options
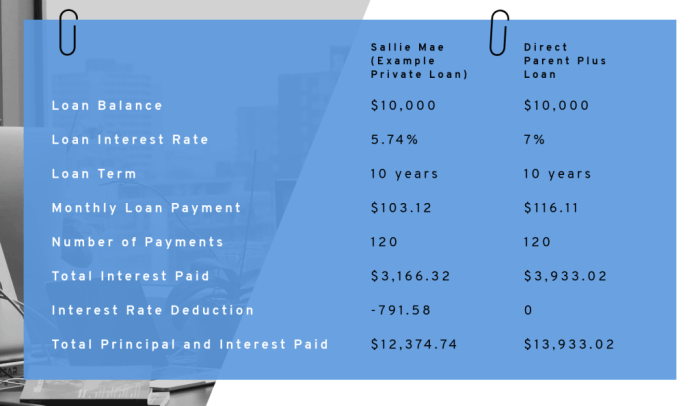
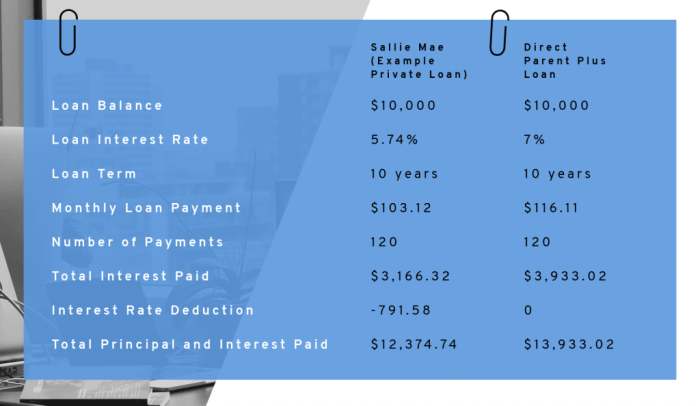
Choosing the right financing option for your child’s education at Arizona State University (ASU) is crucial. While Parent PLUS loans offer a significant amount, they aren’t the only option, and understanding the alternatives is key to making an informed financial decision. This section compares Parent PLUS loans with other federal student loan options available to ASU students, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each to help parents determine the best fit for their circumstances.
Federal Student Loan Options for ASU Students
Several federal student loan programs cater to undergraduate and graduate students attending ASU. These include Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, and Direct Graduate PLUS Loans. Understanding the nuances of each is essential for effective financial planning.
Parent PLUS Loans versus Direct Subsidized Loans
Direct Subsidized Loans are awarded based on financial need and are only available to undergraduate students. The government pays the interest while the student is enrolled at least half-time, during grace periods, and during deferment. Parent PLUS Loans, conversely, are not need-based and are available to parents of undergraduate and graduate students. Interest accrues from the time the loan is disbursed, regardless of the student’s enrollment status. Therefore, a Direct Subsidized Loan is preferable if the student qualifies, offering lower overall costs due to subsidized interest. However, the loan amount may be significantly less than what a Parent PLUS loan can provide.
Parent PLUS Loans versus Direct Unsubsidized Loans
Direct Unsubsidized Loans are available to both undergraduate and graduate students, regardless of financial need. Unlike Subsidized Loans, interest accrues from disbursement. Comparing this to Parent PLUS Loans, the key difference lies in the borrower. Parent PLUS Loans are for parents, while Unsubsidized Loans are for the student. Parents might choose a Parent PLUS Loan to consolidate borrowing and simplify repayment, while students may prefer an Unsubsidized Loan to build their credit history and manage their own debt. The interest rate is typically the same for both loan types in a given year, but the total cost could vary based on the interest capitalization during the loan term.
Parent PLUS Loans versus Direct Graduate PLUS Loans
Graduate students have access to Direct Graduate PLUS Loans, similar to Parent PLUS Loans, but with the student as the borrower. The decision between these two loan types hinges on creditworthiness. If a parent has poor or limited credit history, they may be denied a Parent PLUS Loan, making the Direct Graduate PLUS Loan (if the student qualifies) a viable alternative. Conversely, if the parent has good credit, a Parent PLUS Loan may offer more favorable terms.
Comparison of Key Features
| Loan Type | Borrower | Credit Check Required | Interest Rate (Example – Rates Vary Annually) | Repayment Terms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parent PLUS Loan | Parent | Yes | 7.54% (Example) | 10-25 years |
| Direct Subsidized Loan | Student | No | 5.04% (Example) | 10-25 years |
| Direct Unsubsidized Loan | Student | No | 7.54% (Example) | 10-25 years |
| Direct Graduate PLUS Loan | Graduate Student | Yes | 8.05% (Example) | 10-25 years |
Note: Interest rates are subject to change and are examples only. Refer to the official Federal Student Aid website for current rates.
Illustrative Example of Parent PLUS Loan Scenario
This example illustrates a hypothetical scenario of a family using a Parent PLUS loan to finance their child’s education at Arizona State University (ASU). We’ll Artikel the loan details, explore the financial implications for the family, and depict a sample repayment schedule. Remember that actual loan terms and interest rates can vary.
The Johnsons are financing their daughter Sarah’s four-year education at ASU. After factoring in scholarships and other financial aid, they need $40,000 to cover tuition, fees, and living expenses. They decide to take out a Parent PLUS loan for the full amount. The loan carries a fixed annual interest rate of 7.5%, a common rate for Parent PLUS loans, although this can fluctuate. The loan repayment period is 10 years, with a standard monthly repayment plan.
Loan Amount and Interest Rate
The Johnsons borrowed $40,000 at a 7.5% annual interest rate. This interest rate is applied to the principal balance each year. The interest accrues throughout the repayment period, meaning interest is added to the principal balance each month. The higher the interest rate, the greater the total cost of the loan. The fixed interest rate ensures that their monthly payments remain consistent throughout the loan term.
Repayment Schedule and Total Cost
The loan’s repayment schedule is amortized over 10 years (120 months). This means that each monthly payment includes both principal and interest. Early in the repayment period, a larger portion of the payment goes toward interest, while later, a larger portion goes toward principal. A detailed breakdown of the repayment schedule would show a gradual decrease in the principal balance over time. For example, the first few months might show payments where only a small amount of principal is paid off due to the large interest component. In contrast, the final months would show payments with a much larger portion going towards the principal balance as it shrinks. To illustrate, a sample repayment schedule (without precise figures which would require a loan amortization calculator) might look like this: Month 1: Payment $450 (high interest portion), Month 60: Payment $450 (roughly equal principal and interest), Month 120: Payment $450 (high principal portion). The total cost of the loan, including interest, would be significantly higher than the initial $40,000 borrowed. A loan calculator can provide the exact figures based on the interest rate and repayment period.
Financial Impact on the Family Budget
The $450 monthly payment represents a substantial commitment for the Johnsons. They need to factor this expense into their monthly budget, ensuring it doesn’t jeopardize their ability to meet other financial obligations such as housing, food, and transportation. They might need to adjust their spending habits or explore additional income streams to accommodate the loan payments. This loan significantly impacts their financial flexibility, potentially limiting their ability to save for other goals or handle unexpected expenses. They must diligently budget and track their spending to manage this added financial responsibility. Failing to make payments could result in negative credit impacts.
Final Thoughts
Securing a Parent PLUS Loan for your child’s ASU education requires careful planning and understanding. This guide has provided a roadmap through the complexities of the application process, repayment options, and financial management strategies. By understanding eligibility requirements, interest rates, and potential challenges, you can make informed decisions that align with your family’s financial goals. Remember to utilize available resources and seek professional advice when needed to ensure a successful and manageable loan experience. Ultimately, informed financial planning empowers you to support your child’s educational aspirations without undue financial strain.
Top FAQs
What happens if my Parent PLUS loan application is denied?
If denied, you can explore options like requesting a credit reconsideration or applying with a co-signer. You may also investigate alternative financing options.
Can I consolidate my Parent PLUS loan with other federal student loans?
Yes, you can consolidate your Parent PLUS loan with other eligible federal student loans through the Federal Direct Consolidation Loan program.
What are the tax implications of Parent PLUS loans?
Interest paid on Parent PLUS loans may be tax deductible, depending on your income and other factors. Consult a tax professional for personalized advice.
What if I lose my job and can’t make payments?
Contact your loan servicer immediately to explore options like deferment or forbearance to avoid default. They can provide guidance and explore solutions.