Securing a 586 credit score car loan can feel daunting, but it’s achievable. This guide navigates the complexities of obtaining financing with a less-than-perfect credit score, exploring various loan options, strategies to improve your chances, and crucial financial considerations. We’ll delve into the factors influencing your credit score, explain how lenders view a 586 score, and offer practical steps to strengthen your application. Understanding your options is the first step towards driving away in your dream car.
From comparing interest rates and loan terms from different lenders to outlining the benefits and drawbacks of secured versus unsecured loans, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions. We’ll also cover alternative financing options, budgeting strategies, and the importance of understanding APR and hidden fees. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap for navigating the car loan process with confidence, even with a 586 credit score.
Understanding a 586 Credit Score
A credit score of 586 falls within the subprime range, signifying a higher-than-average risk to lenders. This score significantly impacts loan applications, potentially resulting in higher interest rates, stricter loan terms, or even loan denials. Understanding the factors contributing to this score and implementing strategies for improvement is crucial for securing favorable loan terms in the future.
Implications of a 586 Credit Score for Loan Applications
A 586 credit score presents challenges when applying for a car loan. Lenders view this score as indicative of a higher risk of default. This increased risk translates into less favorable loan options. Expect higher interest rates compared to borrowers with higher credit scores, resulting in significantly increased overall loan costs. Lenders may also impose stricter terms, such as requiring a larger down payment or a shorter loan term. In some cases, a 586 credit score may even lead to loan applications being denied outright. Securing a loan with a 586 credit score might necessitate exploring options with specialized lenders who cater to borrowers with subprime credit, although these lenders often charge even higher interest rates to compensate for the added risk.
Factors Contributing to a 586 Credit Score
Several factors contribute to a credit score. A 586 score suggests a history of missed or late payments, high credit utilization (the amount of credit used compared to the total available credit), and potentially a shorter credit history. A significant negative mark, such as a bankruptcy or foreclosure, can also substantially depress a credit score. The specific weighting of these factors varies depending on the scoring model used (e.g., FICO, VantageScore), but generally, payment history carries the most weight. High levels of debt relative to income also negatively impact credit scores. For example, consistently carrying balances close to or exceeding credit limits can significantly lower a score.
Strategies for Improving a 586 Credit Score
Improving a 586 credit score requires consistent effort and responsible financial management. First, prioritize paying all bills on time. Even a single missed payment can have a negative impact. Next, reduce credit utilization by paying down existing debts. Aim to keep credit utilization below 30% of available credit. Consider consolidating high-interest debt into a lower-interest loan to manage payments more effectively. Regularly monitoring credit reports for errors and disputing any inaccuracies is also crucial. Building a longer credit history by responsibly using credit accounts (credit cards, installment loans) can positively impact the score over time. Avoid applying for multiple loans or credit cards within a short period, as this can negatively affect the score.
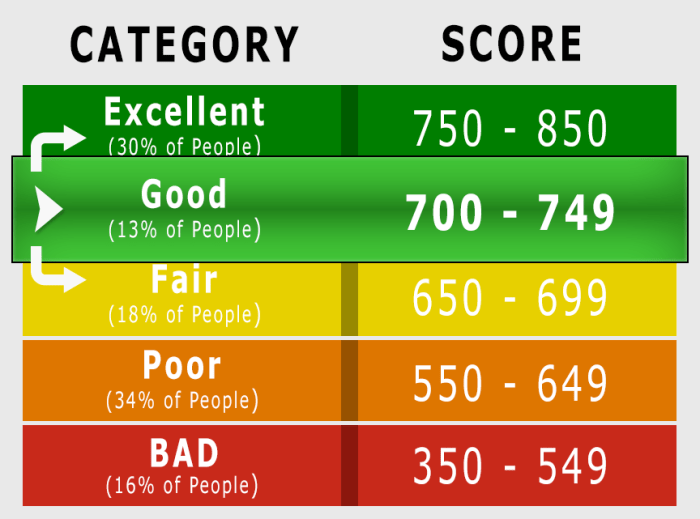
Examples of Credit Score Ranges and Their Associated Lending Risks
Credit scores are typically categorized into ranges, each associated with a different level of risk for lenders. Generally:
| Credit Score Range | Credit Category | Lending Risk |
|---|---|---|
| 800-850 | Excellent | Very Low |
| 740-799 | Very Good | Low |
| 670-739 | Good | Moderate |
| 580-669 | Fair | High |
| 300-579 | Poor | Very High |
A 586 score falls within the “Fair” category, representing a high risk to lenders. Borrowers with scores in this range typically face higher interest rates and stricter lending requirements. Conversely, those with excellent credit scores (800 and above) qualify for the most favorable loan terms. For instance, a borrower with an 800 credit score might qualify for a car loan with a significantly lower interest rate compared to someone with a 586 score, potentially saving thousands of dollars over the life of the loan.
Car Loan Options with a 586 Credit Score
Securing a car loan with a 586 credit score presents unique challenges and opportunities. While not considered excellent credit, it’s still possible to obtain financing, though likely at higher interest rates and with stricter lending criteria than borrowers with higher scores. Understanding the available options and their implications is crucial for making an informed decision.
Types of Car Loans Available
Individuals with a 586 credit score typically have access to several types of car loans, though their eligibility for specific options may vary depending on their income, debt-to-income ratio, and the lender’s policies. These generally include loans from banks and credit unions, online lenders, and buy-here-pay-here dealerships. Banks and credit unions often offer more competitive rates for qualified borrowers, while online lenders provide a broader reach and potentially more flexible terms. Buy-here-pay-here dealerships cater specifically to borrowers with poor credit but usually charge significantly higher interest rates.
Comparison of Lenders and Loan Terms
The interest rates and loan terms offered to borrowers with a 586 credit score can fluctuate widely based on the lender and the individual’s financial profile. The following table provides a general comparison, keeping in mind that these are estimates and actual rates and terms may vary:
| Lender Name | Interest Rate (Estimate) | Loan Term Options (Years) | Typical Fees |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Bank | 10-14% | 36, 48, 60 | Origination fee (1-3% of loan amount), late payment fees |
| Example Credit Union | 9-13% | 48, 60, 72 | Application fee (potential), late payment fees |
| Example Online Lender | 12-18% | 36, 48 | Origination fee (variable), prepayment penalties (potential) |
Note: These interest rates are estimates and can vary greatly depending on the lender, the borrower’s creditworthiness, the vehicle’s value, and the loan amount. Always check with individual lenders for current rates and terms.
Challenges of Securing a Car Loan with a 586 Credit Score
Obtaining a car loan with a 586 credit score presents several challenges. Higher interest rates are almost guaranteed, leading to significantly higher overall loan costs. Lenders may require a larger down payment to mitigate their risk. Loan terms may be shorter, resulting in higher monthly payments. The approval process may be more rigorous, requiring extensive documentation and potentially leading to loan denials. Finding a lender willing to work with borrowers in this credit score range might also take more time and effort.
Secured vs. Unsecured Car Loans
A secured car loan uses the vehicle itself as collateral. If the borrower defaults, the lender can repossess the car. Secured loans typically offer lower interest rates than unsecured loans because they present less risk to the lender. However, the risk of losing the car is a significant drawback. An unsecured car loan does not require collateral. While offering greater protection for the borrower, it usually comes with higher interest rates because of the increased risk for the lender. For a borrower with a 586 credit score, a secured loan might be more accessible, but carefully weighing the risks and benefits is essential.
Improving Loan Approval Chances
Securing a car loan with a 586 credit score can be challenging, but it’s not impossible. By taking proactive steps to improve your application and demonstrate financial responsibility, you significantly increase your chances of approval and potentially even negotiate favorable loan terms. This section Artikels strategies to strengthen your application and improve your odds of securing the financing you need.
Strategies for Increasing Loan Approval Likelihood
A 586 credit score falls within the “fair” range, indicating some credit history issues. Lenders view this score as moderately risky, making it crucial to present a compelling case for loan approval. This involves demonstrating your capacity to repay the loan responsibly. This can be achieved through several key strategies. Improving your credit score before applying is ideal, but not always feasible. Focusing on other aspects of your application can still yield positive results.
Preparing a Strong Loan Application
A well-prepared loan application significantly impacts approval chances. Follow these steps to maximize your chances of success:
- Gather Necessary Documentation: Compile all required documents beforehand. This includes proof of income (pay stubs, tax returns), employment verification, bank statements demonstrating sufficient savings, and your driver’s license.
- Complete the Application Accurately: Ensure all information provided is accurate and complete. Inaccuracies or omissions can lead to application rejection.
- Highlight Positive Financial Aspects: Emphasize positive aspects of your financial situation, such as consistent employment history, steady income, and responsible debt management (even if your credit score isn’t perfect).
- Choose the Right Lender: Research lenders who specialize in subprime loans or have more lenient credit score requirements. Credit unions often offer more flexible terms than larger banks.
- Consider a Co-signer: If possible, securing a co-signer with excellent credit can significantly boost your approval odds. The co-signer assumes responsibility for repayment if you default.
Negotiating Favorable Loan Terms, 586 credit score car loan
While a 586 credit score might limit your options, effective negotiation can still yield favorable loan terms.
- Shop Around: Compare offers from multiple lenders to find the most competitive interest rates and terms. Don’t settle for the first offer you receive.
- Highlight Your Strengths: Emphasize your positive financial attributes during negotiations, such as your stable employment and consistent income. This demonstrates your commitment to repayment.
- Negotiate the Down Payment: A larger down payment can significantly reduce the loan amount and improve your chances of approval. It also demonstrates your financial commitment.
- Explore Loan Term Options: A shorter loan term generally results in higher monthly payments but lower overall interest paid. Conversely, a longer term results in lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid. Consider your financial capabilities and choose a term that balances affordability and overall cost.
Supporting Documentation for Loan Applications
Providing comprehensive supporting documentation strengthens your application and builds lender confidence.
- Proof of Income: Pay stubs from the last three months, W-2 forms, or tax returns.
- Bank Statements: Statements showing consistent deposits and sufficient savings to cover potential unexpected expenses.
- Employment Verification: A letter from your employer confirming your employment status, income, and tenure.
- Rental or Mortgage Agreements: Proof of stable housing situation.
- Utility Bills: Demonstrates your established residency.
Financial Implications and Budgeting: 586 Credit Score Car Loan
Securing a car loan with a 586 credit score often means facing higher interest rates and potentially less favorable loan terms compared to borrowers with higher credit scores. This translates to a more expensive loan overall, impacting your long-term financial health. Careful budgeting and understanding the full cost of the loan are crucial to avoid financial strain.
Understanding the long-term financial implications of a car loan with a 586 credit score requires a realistic assessment of your income, expenses, and the total cost of borrowing. A higher interest rate directly increases the total amount you repay over the life of the loan. This can significantly impact your ability to save for other financial goals, such as a down payment on a house or investing for retirement. Furthermore, missing payments due to financial hardship can further damage your credit score, leading to a vicious cycle of higher interest rates and increased borrowing costs in the future.
Monthly Budget Incorporating a Car Loan Payment
Creating a realistic monthly budget is essential for successfully managing a car loan. This involves meticulously tracking all income and expenses to ensure sufficient funds are available for the loan payment each month. Failing to account for the car loan payment can lead to missed payments and negative consequences.
| Income | Amount | Expenses | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gross Monthly Salary | $4000 | Rent/Mortgage | $1200 |
| Other Income (e.g., part-time job) | $500 | Utilities (Electricity, Water, Gas) | $300 |
| Groceries | $400 | ||
| Transportation (excluding car payment) | $150 | ||
| Car Loan Payment | $400 | ||
| Health Insurance | $200 | ||
| Credit Card Payments | $150 | ||
| Savings | $200 | ||
| Total Income | $4500 | Total Expenses | $2700 |
| Remaining Amount | $1800 |
This sample budget demonstrates responsible financial management by allocating sufficient funds for the car loan payment while still allowing for savings and other essential expenses. Adjusting this budget to reflect your specific income and expenses is crucial for accurate financial planning.
Annual Percentage Rate (APR) and Interest Capitalization
The Annual Percentage Rate (APR) represents the total cost of borrowing, including interest and other fees, expressed as a yearly percentage. Understanding your APR is vital, as a higher APR will significantly increase the total amount you repay over the loan’s life.
Interest capitalization occurs when accrued interest is added to the principal loan amount, increasing the total amount owed. This process can quickly escalate the total cost of the loan, especially if payments are missed or if the loan has a high APR. For example, a $15,000 loan with a 15% APR will cost significantly more than the same loan with a 7% APR. The difference in total repayment could be thousands of dollars over the loan term. This illustrates the importance of shopping around for the best possible interest rate.
Potential Hidden Fees Associated with Car Loans
Several hidden fees can significantly impact the total cost of a car loan. It is crucial to be aware of these potential costs before signing any loan agreement.
Understanding these fees is essential for accurately budgeting and avoiding unexpected financial burdens. Failing to account for these additional costs can lead to financial strain and difficulty managing the loan.
- Origination Fee: A fee charged by the lender for processing the loan application.
- Prepayment Penalty: A fee charged for paying off the loan early.
- Late Payment Fee: A penalty for missing a loan payment.
- Document Preparation Fee: A fee for preparing the necessary loan documents.
- Gap Insurance: Insurance that covers the difference between the value of your car and the amount you owe on the loan if your car is totaled.
Alternative Financing Options

Securing a car loan with a 586 credit score can be challenging, but several alternative financing options exist. Understanding these options and their implications is crucial for making an informed decision. This section explores various avenues, including leasing versus buying, the role of co-signers, and the impact of down payment size.
Leasing Versus Buying a Car
Leasing and buying represent distinct approaches to car ownership, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Choosing between them depends heavily on individual financial circumstances and driving habits. A person with a 586 credit score might find leasing more accessible initially due to lower upfront costs, but long-term financial implications should be carefully considered.
Buying a car involves securing a loan to pay the full purchase price, gradually paying off the debt over several years. Leasing, on the other hand, involves paying for the use of the vehicle over a shorter term (typically 2-3 years), after which the lease ends, and the vehicle is returned. With a lower credit score, securing a loan to buy might require a larger down payment or result in higher interest rates compared to a lease. However, buying offers ownership and equity building, unlike leasing.
Using a Co-Signer for a Car Loan
A co-signer is an individual with a strong credit history who agrees to share responsibility for the loan repayment. Their excellent credit profile can significantly improve the chances of loan approval and secure a lower interest rate. For someone with a 586 credit score, a co-signer can be a valuable asset in obtaining favorable loan terms.
However, using a co-signer involves shared responsibility. If the primary borrower defaults on payments, the co-signer becomes liable for the remaining debt. This can severely impact the co-signer’s credit score and financial standing. Therefore, it’s crucial to have an open and honest discussion with the potential co-signer about the risks and responsibilities involved before proceeding. Choosing a reliable co-signer who understands and accepts the potential risks is paramount.
Impact of Down Payment Size on Loan Approval and Interest Rates
The size of the down payment plays a significant role in the loan approval process and the interest rate offered. A larger down payment reduces the loan amount, lowering the lender’s risk. This makes loan approval more likely, especially for individuals with lower credit scores. Furthermore, a substantial down payment can lead to a lower interest rate, as it demonstrates the borrower’s financial commitment and reduces the lender’s risk of default.
For example, a borrower with a 586 credit score might find it easier to secure a loan with a 20% down payment compared to a 5% or no down payment. The larger down payment might result in a significantly lower interest rate, saving thousands of dollars over the life of the loan. While a larger down payment requires a more substantial upfront investment, it can significantly improve the overall cost and approval chances of the loan.
Illustrative Scenarios
Understanding the realities of securing a car loan with a 586 credit score requires examining both successful and unsuccessful applications. These scenarios illustrate the factors influencing loan approval and the potential outcomes.
Successful Car Loan Application with a 586 Credit Score
Sarah, a 30-year-old with a 586 credit score, needed a reliable vehicle for her new job. She had a stable income, demonstrating consistent employment for the past three years. Before applying, Sarah diligently improved her credit profile by paying down existing debts and correcting minor errors on her credit report. She researched different lenders, comparing interest rates and loan terms. She opted for a slightly used car, reducing the loan amount needed. Sarah meticulously prepared all the necessary documentation, including proof of income, employment history, and a down payment. By presenting a strong financial profile and a well-prepared application, she successfully secured a car loan with a manageable interest rate. Her consistent payments further improved her credit score over time.
Challenging Car Loan Application with a 586 Credit Score
Mark, also 30, had a similar credit score of 586 but faced significant challenges securing a car loan. His income was inconsistent, with periods of unemployment affecting his credit history. He had several outstanding debts, limiting his borrowing capacity. Mark applied to several lenders without success, receiving rejections due to his financial instability. He lacked a substantial down payment and had not taken steps to improve his credit score before applying. The high interest rates quoted by the few lenders willing to consider him made the loan unaffordable. Mark’s situation highlights the importance of financial stability and proactive credit management when seeking a car loan. He ultimately had to delay his car purchase until he could significantly improve his financial standing.
Credit Score, Interest Rate, and Monthly Payment Relationship
The relationship between credit score, interest rate, and monthly payment is directly proportional. A higher credit score typically translates to a lower interest rate and, consequently, a lower monthly payment for the same loan amount. Conversely, a lower credit score results in a higher interest rate and a higher monthly payment. The following example illustrates this relationship for a $20,000 car loan over 60 months:
- Scenario 1: Credit Score 750, Interest Rate 4%, Monthly Payment: $366
- Scenario 2: Credit Score 680, Interest Rate 6%, Monthly Payment: $390
- Scenario 3: Credit Score 586, Interest Rate 10%, Monthly Payment: $423
Note: These are illustrative examples and actual rates and payments will vary depending on the lender, loan term, and other factors. The higher interest rate associated with a 586 credit score significantly increases the total cost of the loan over its lifetime.
Ending Remarks

Obtaining a car loan with a 586 credit score presents unique challenges, but it’s not insurmountable. By understanding your credit score, exploring various financing options, and diligently preparing your application, you can significantly increase your chances of approval. Remember to carefully compare interest rates, loan terms, and potential hidden fees to find the best deal. Proactive financial planning and responsible budgeting are key to managing your car loan successfully and building a stronger financial future. Take control of your financial situation, and drive confidently towards your goals.
Helpful Answers
What documents do I need to apply for a car loan with a 586 credit score?
Typically, lenders require proof of income (pay stubs, tax returns), identification (driver’s license), and proof of residence (utility bill). They may also request bank statements and employment verification.
Can I get pre-approved for a car loan with a 586 credit score?
Yes, many lenders offer pre-approval, which gives you an idea of your potential interest rate and loan amount before you start shopping for a car. This can strengthen your negotiating position.
How long does it take to improve my credit score from 586?
Improving your credit score takes time and consistent effort. Focusing on responsible credit card usage, paying bills on time, and keeping credit utilization low can yield results within several months, but significant improvement may take longer.
What is the difference between a secured and unsecured car loan?
A secured loan uses collateral (like the car itself) to secure the loan, often resulting in lower interest rates. An unsecured loan doesn’t require collateral but usually comes with higher interest rates.






