How to start a wholesale clothing business is a question many aspiring entrepreneurs grapple with. This guide unravels the complexities, from meticulous market research and strategic sourcing to building a compelling brand and scaling your operations. We’ll navigate the legal and financial hurdles, explore effective marketing strategies, and delve into efficient inventory management and logistics. Prepare to transform your passion for fashion into a thriving enterprise.
Launching a successful wholesale clothing business requires a blend of creativity, business acumen, and a solid understanding of the industry. This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step roadmap, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to navigate each stage of the process, from identifying profitable niches to managing your growing business. We’ll cover everything from finding reliable suppliers and negotiating favorable terms to building a strong online presence and cultivating lasting customer relationships.
Market Research and Niche Selection: How To Start A Wholesale Clothing Business
Successfully launching a wholesale clothing business hinges on identifying a profitable niche and understanding your target market. Thorough market research is crucial for minimizing risk and maximizing your chances of success. This involves identifying underserved markets with high demand and relatively low competition. Ignoring this step can lead to significant financial losses and wasted effort.
Three Underserved Clothing Niches with High Profitability Potential
Three promising niches with potential for high profitability are sustainable and ethically sourced clothing, plus-size activewear, and gender-neutral children’s clothing. These areas demonstrate growing consumer demand and present opportunities for businesses that cater to specific needs and preferences often overlooked by larger retailers.
Target Customer Characteristics for Each Niche
Understanding your target customer is paramount. Detailed customer profiles allow for focused marketing and product development.
- Sustainable and Ethically Sourced Clothing: The target customer is typically environmentally conscious, aged 25-45, with a higher-than-average disposable income. They value transparency in the supply chain and are willing to pay a premium for ethically produced garments made from sustainable materials like organic cotton or recycled fabrics. They are often digitally savvy and engage with brands that align with their values through social media and online platforms.
- Plus-Size Activewear: The target customer is a woman (predominantly), aged 25-55, actively seeking inclusive and functional activewear. She is looking for comfortable, stylish, and supportive clothing that caters to her body type. This customer is often active on social media, seeking inspiration and community from fitness influencers and brands that represent body positivity.
- Gender-Neutral Children’s Clothing: The target customer is a parent (or guardian) aged 25-45, who values inclusivity and avoids gender stereotypes. They are seeking high-quality, durable clothing that transcends traditional gender norms. These parents are often digitally engaged and research products thoroughly, valuing reviews and brand transparency.
Competitive Landscape Comparison
Analyzing the competitive landscape for each niche helps identify opportunities and potential challenges. A strong understanding of existing competitors, their strengths and weaknesses, allows for strategic differentiation.
- Sustainable and Ethically Sourced Clothing: Competition is growing, but there’s still room for new entrants who can offer unique selling propositions (USPs), such as specializing in a particular material or focusing on a specific ethical certification. Existing players often focus on a limited range of products or price points.
- Plus-Size Activewear: While the market is expanding rapidly, there’s still a significant gap in the market for high-quality, stylish, and affordable options. Many existing brands focus on specific activities or body types, leaving opportunities for broader appeal.
- Gender-Neutral Children’s Clothing: This niche is relatively less saturated compared to others. However, success depends on effectively communicating the brand’s values and creating appealing designs that resonate with parents who prioritize inclusivity.
Pros and Cons of Each Niche
| Niche | Pros | Cons | Market Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainable & Ethical Clothing | Growing consumer demand, higher profit margins, strong brand loyalty potential | Higher production costs, sourcing challenges, need for transparent supply chain | High, with potential for significant growth |
| Plus-Size Activewear | Large underserved market, high demand for inclusive options, potential for strong brand community | Design complexities, need for specialized sizing and fitting expertise, competition increasing | Very High, rapid expansion expected |
| Gender-Neutral Children’s Clothing | Growing demand for inclusive options, less saturated market, opportunity for unique branding | Potential for slower initial growth, need for creative designs that appeal to a broad audience | High, with potential for steady growth |
Legal and Financial Aspects
Launching a wholesale clothing business requires careful consideration of both legal and financial factors. Navigating these aspects effectively is crucial for establishing a sustainable and profitable enterprise. Failure to comply with regulations can lead to significant penalties, while inadequate financial planning can result in business failure. This section Artikels the key legal and financial steps necessary to build a solid foundation for your wholesale clothing business.
Legal Requirements for a Wholesale Clothing Business
The legal requirements for starting a wholesale clothing business vary depending on your location. Generally, this includes registering your business, obtaining the necessary licenses and permits, and understanding relevant tax obligations. For example, in the United States, you’ll likely need to register your business as a sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation with your state. This registration process typically involves filing paperwork with the Secretary of State or a similar agency. Beyond state-level registration, you may also need to register with the IRS to obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN) if you plan to hire employees or operate as anything other than a sole proprietorship. Additionally, depending on your business activities and location, you may need permits related to sales tax collection, zoning regulations, and potentially industry-specific licenses, such as those concerning textile manufacturing or importing. Always consult with a legal professional or your local government agencies to ensure full compliance with all applicable regulations.
Securing Necessary Business Licenses and Permits
The process of securing necessary licenses and permits involves researching the specific requirements for your location and business type. This typically begins with identifying the relevant government agencies at the local, state, and potentially federal levels. You will need to gather the required documentation, complete application forms, and pay any associated fees. For example, a sales tax permit allows you to collect sales tax from your customers and remit it to the appropriate tax authority. A business license is a general permit granting you the right to operate your business legally within your jurisdiction. Specific permits might be needed depending on your location and business activities, such as zoning permits for operating from a specific location or permits for handling hazardous materials if you are dealing with certain types of dyes or chemicals in your clothing production or processing. Thorough research and timely application are key to avoid delays in launching your business.
Business Plan: Startup Costs, Projected Revenue, and Profit Margins
A comprehensive business plan is essential for securing funding and guiding your business decisions. It should include a detailed breakdown of startup costs, projected revenue, and profit margins. Startup costs can include expenses such as purchasing inventory, renting or buying a warehouse or office space, acquiring equipment (e.g., computers, sewing machines, packaging materials), marketing and advertising expenses, and legal and professional fees. Projected revenue should be based on realistic sales forecasts, considering market demand, pricing strategies, and sales channels. Profit margins are calculated by subtracting costs of goods sold and operating expenses from revenue. For example, if your total revenue is $100,000, your cost of goods sold is $50,000, and your operating expenses are $20,000, your profit margin is 30% ($100,000 – $50,000 – $20,000 = $30,000; $30,000/$100,000 = 0.30). A well-structured business plan demonstrates your understanding of the market and your ability to manage your business effectively. This plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the market and your business performance.
Funding Options for New Businesses
Several funding options are available for new businesses, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. These include bootstrapping (using personal savings), small business loans from banks or credit unions, crowdfunding platforms, angel investors, venture capital, and government grants. Bootstrapping offers complete control but may limit growth potential. Small business loans provide capital but require repayment with interest. Crowdfunding allows you to raise funds from a large number of individuals but can be time-consuming. Angel investors and venture capital firms offer significant investment but often require equity in your company. Government grants provide funding with less stringent repayment requirements but are often highly competitive. The choice of funding will depend on your business needs, risk tolerance, and the availability of funding sources. For example, a small business loan might be suitable for covering initial inventory purchases, while crowdfunding could be used for marketing and product development.
Building Your Brand and Online Presence
Establishing a strong brand identity and a compelling online presence is crucial for success in the competitive wholesale clothing market. Your brand needs to resonate with your target buyers, conveying professionalism, quality, and style. A well-designed website acts as your virtual storefront, showcasing your collection and facilitating seamless interactions with potential clients. Effective online marketing strategies are then essential to reach your ideal customer base and drive sales.
A cohesive brand identity provides a recognizable and memorable experience for your customers. This goes beyond simply having a logo; it encompasses a complete visual and communication strategy.
Brand Identity Design
Developing a strong brand identity involves crafting a unique logo, selecting a consistent color palette, and defining a clear brand voice. Your logo should be visually appealing, easily recognizable, and representative of your brand’s aesthetic. The color palette should evoke the desired emotions and align with your brand’s personality – for example, a vibrant palette might suit a youthful, trendy brand, while muted tones could reflect a more sophisticated, classic style. Your brand voice should be consistent across all communication channels, reflecting your brand’s personality and values. For example, a brand targeting eco-conscious buyers might adopt a friendly, informative, and sustainable tone.
Website Development
Your website serves as your primary sales channel and brand ambassador. It should be professional, user-friendly, and optimized for mobile devices. Essential features include high-quality product photography, detailed product descriptions, clear wholesale pricing, a secure checkout process, and contact information. Consider using a platform like Shopify or WooCommerce, which offer e-commerce functionalities and various customization options. A well-structured website with intuitive navigation will ensure a positive customer experience and encourage repeat business. Imagine a website with stunning visuals of your clothing line, organized by category and size, with easily accessible order forms and a FAQ section addressing common wholesale inquiries.
Online Marketing Strategies
Effective online marketing is key to reaching your target audience and driving wholesale orders.
Three effective strategies are:
- Search Engine Optimization (): Optimizing your website and content for relevant s will improve your search engine rankings, making it easier for potential buyers to find you. This involves using relevant s in your website content, product descriptions, and meta descriptions, as well as building high-quality backlinks from reputable sources.
- Social Media Marketing: Utilize platforms like Instagram and Pinterest to showcase your clothing line visually. Share high-quality images and videos, engage with potential customers, and run targeted advertising campaigns to reach your ideal audience. Consider collaborating with fashion influencers to increase brand awareness and reach a wider audience. For instance, partnering with a relevant influencer could result in a significant boost in brand visibility and engagement.
- Email Marketing: Build an email list and send targeted email campaigns to promote new collections, special offers, and industry news. Personalized email marketing can nurture relationships with potential clients and drive repeat business. For example, you could segment your email list based on buyer preferences and send tailored promotions accordingly.
Compelling Product Descriptions
Compelling product descriptions are essential for converting website visitors into customers. They should highlight key features and benefits, using persuasive language to showcase the value proposition of your clothing line. Instead of simply stating “red dress,” describe it as “a vibrant red midi dress, crafted from luxurious silk, perfect for evening events.” Include details such as fabric composition, sizing information, care instructions, and any unique selling points. Use strong action verbs and focus on the benefits the product offers to the customer. For example, instead of “durable fabric,” you could say “this fabric is built to last, ensuring your investment pays off.” High-quality product photography is also crucial, showcasing the clothing from multiple angles and in different settings.
Sales and Customer Relationship Management

Effective sales and customer relationship management (CRM) are crucial for the long-term success of any wholesale clothing business. Building strong relationships with your clients, understanding their needs, and streamlining your order fulfillment process are key to driving repeat business and maximizing profitability. This section Artikels strategies to achieve this.
Key Metrics for Wholesale Clothing Business Success
Tracking the right metrics provides invaluable insights into your business performance and areas for improvement. Three essential metrics to monitor include average order value (AOV), customer lifetime value (CLTV), and customer churn rate. AOV reveals the average amount spent per order, indicating the effectiveness of your pricing and upselling strategies. CLTV represents the total revenue expected from a customer throughout their relationship with your business, highlighting the importance of customer retention. The customer churn rate measures the percentage of customers lost over a specific period, indicating potential issues with customer satisfaction or your overall business model. Analyzing these metrics allows for data-driven decision-making, leading to optimized sales strategies and improved profitability.
Managing Customer Orders and Inquiries
Efficient order management is paramount for maintaining customer satisfaction and avoiding costly errors. A well-defined process is crucial. First, upon receiving an order (whether via email, online portal, or phone), immediately acknowledge its receipt and provide an estimated delivery timeframe. Second, verify order details, including quantities, sizes, and colors, and confirm availability. Third, process the order, ensuring accurate picking, packing, and shipping. Finally, provide tracking information to the customer and follow up to confirm receipt and address any potential issues. For inquiries, a prompt and helpful response is essential. Designate a specific point of contact or team to handle customer inquiries, ensuring consistency and efficiency. Utilize a ticketing system to track and manage inquiries, ensuring no request is overlooked.
Building Strong Relationships with Wholesale Clients
Strong client relationships are the cornerstone of a thriving wholesale business. Personalized communication, proactive engagement, and exceptional customer service are vital. Regular communication, beyond order updates, strengthens bonds. This might involve sharing new product information, offering exclusive deals, or simply checking in to see how things are going. Addressing concerns promptly and professionally builds trust and loyalty. Consider offering personalized service based on client history and preferences, showing that you value their business. Regular feedback requests help you understand their needs and improve your offerings. By actively fostering these relationships, you build a loyal customer base that drives repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) System Flowchart
A visual representation of a CRM system flowchart would depict a series of interconnected boxes and arrows. The process would begin with “Order Received” (box 1), followed by “Order Verification” (box 2), then “Inventory Check” (box 3). If inventory is sufficient, the flow proceeds to “Order Processing” (box 4), then “Shipping and Tracking” (box 5), and finally “Customer Confirmation” (box 6). If inventory is insufficient, a “Backorder Notification” (box 7) is sent to the customer, with a follow-up “Inventory Update” (box 8) once the item is available. Parallel to the order processing, “Inquiry Received” (box 9) would feed into “Inquiry Response” (box 10), with the response tracked in the system. All boxes are connected with arrows indicating the flow of information and actions. The flowchart clearly illustrates the steps involved in managing orders and inquiries, ensuring efficiency and transparency.
Inventory Management and Logistics

Efficient inventory management and streamlined logistics are crucial for the success of any wholesale clothing business. Balancing supply and demand, minimizing storage costs, and ensuring timely delivery to your clients are all key factors influencing profitability and customer satisfaction. A well-defined system encompassing inventory tracking, warehousing, and shipping is essential for scaling your operations and maintaining a competitive edge.
Inventory Level Management Systems
Effective inventory management prevents both overstocking, leading to wasted storage space and potential markdowns, and stockouts, which can damage customer relationships and lose sales opportunities. A robust system combines forecasting, tracking, and analysis. Forecasting uses historical sales data, seasonal trends, and market analysis to predict future demand. Accurate tracking, often facilitated by inventory management software, provides real-time visibility into stock levels. Regular analysis compares forecasts to actual sales, revealing areas for improvement in forecasting accuracy and identifying potential slow-moving or obsolete items. This data-driven approach allows for proactive adjustments to purchasing and minimizes risk. For example, a business might use a Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory system for fast-moving items, minimizing storage costs while ensuring sufficient stock, while employing a more traditional system for slower-moving items to avoid frequent reordering.
Fulfillment Methods: In-House vs. Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Choosing between in-house fulfillment and outsourcing to a 3PL depends on several factors, including order volume, budget, available space, and technical expertise. In-house fulfillment provides greater control over the process but requires significant investment in warehousing, staff, and technology. 3PLs offer scalability and flexibility, handling warehousing, picking, packing, and shipping, but at a cost. A small business starting out might opt for a 3PL to focus on sales and marketing, while a larger, established business might find in-house fulfillment more cost-effective in the long run. Consider the break-even point between the costs of in-house operations and 3PL fees when making this crucial decision. For example, a business experiencing rapid growth might initially use a 3PL to manage its inventory and shipping until its order volume justifies the investment in an in-house system.
Efficient Shipping and Handling Procedures
Efficient shipping and handling directly impact customer satisfaction and brand perception. Streamlined processes, including accurate order picking, careful packaging to prevent damage, and timely shipping, are vital. Investing in appropriate technology, such as barcode scanners and warehouse management systems (WMS), can significantly improve efficiency. Clear labeling, accurate shipping information, and prompt communication with customers regarding order status are essential elements of a positive customer experience. For instance, implementing a system for tracking packages and providing customers with real-time updates can significantly enhance their experience and reduce inquiries about order status. Furthermore, offering multiple shipping options, such as expedited delivery, allows customers to choose the level of service that best suits their needs.
Shipping Carrier Comparison
| Carrier | Cost (Average) | Transit Time (Average) | Tracking Capabilities | Insurance Options | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UPS | Medium-High | Fast | Excellent | Available | Reliable, wide network, various service options | Can be expensive, especially for international shipping |
| FedEx | Medium-High | Fast | Excellent | Available | Reliable, wide network, various service options, strong international presence | Can be expensive, especially for international shipping |
| USPS | Low | Slower | Good | Available | Cost-effective for smaller packages, extensive reach | Slower transit times, limited tracking information for some services |
| DHL | Medium-High | Fast | Excellent | Available | Reliable international shipping, strong global network | Can be expensive, especially for domestic shipping |
Scaling Your Business
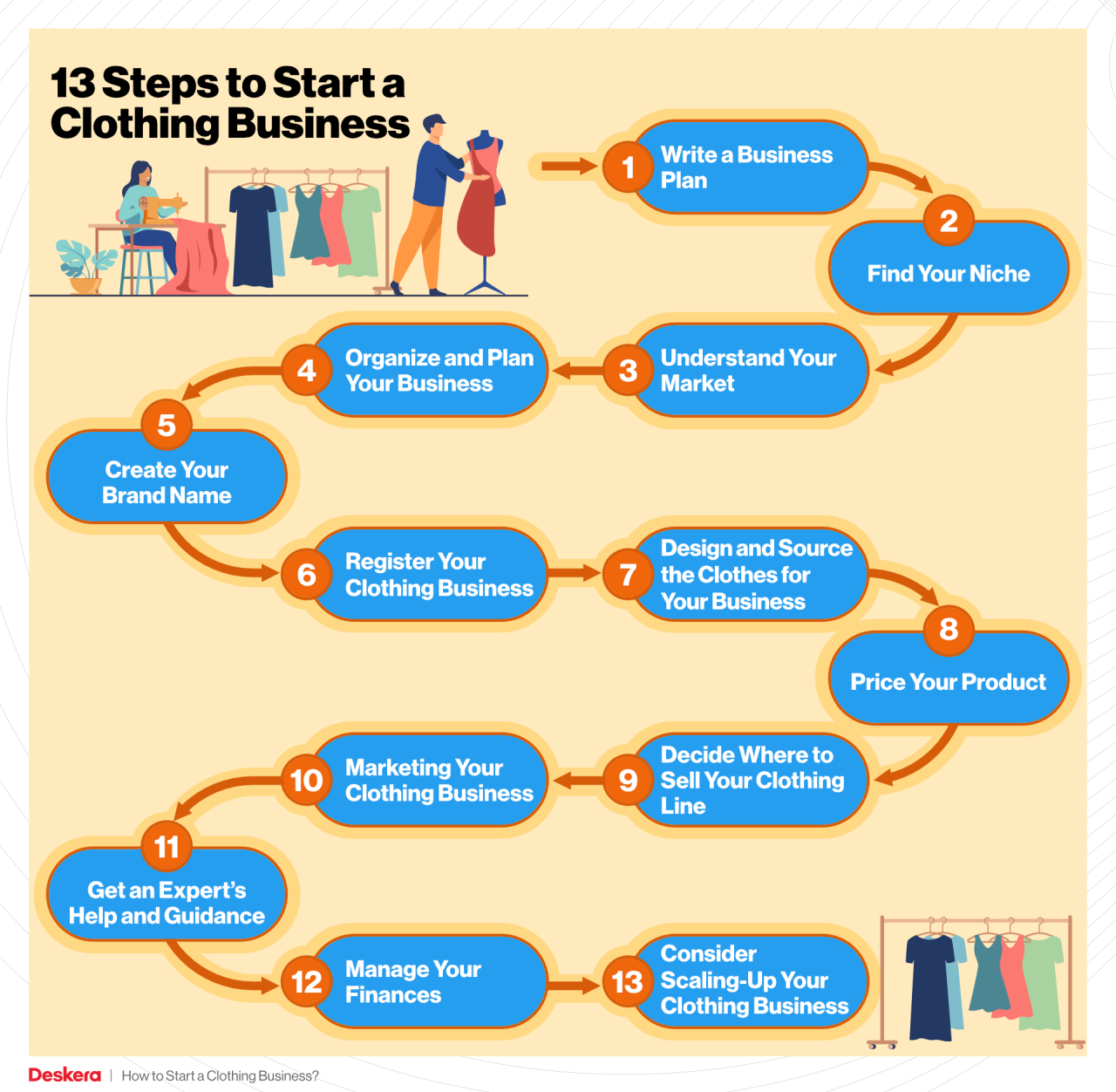
Scaling a wholesale clothing business requires a strategic approach that balances controlled growth with maintaining profitability and brand quality. Successful expansion involves carefully selecting new product lines, targeting appropriate markets, and efficiently managing resources. Ignoring these factors can lead to overextension and ultimately, failure.
Strategies for Expanding Product Line and Reaching New Markets
Expanding your product line and reaching new markets are crucial for sustained growth. Three effective strategies include diversification, geographic expansion, and targeted marketing to new customer segments. Diversification reduces reliance on a single product category, minimizing risk and maximizing revenue streams. Geographic expansion opens access to larger markets, increasing sales potential. Targeted marketing allows you to reach specific customer demographics, improving marketing ROI.
- Diversification: Introduce complementary product lines, such as accessories (jewelry, bags, scarves) or different clothing styles (e.g., adding sportswear to an existing formal wear line). This can leverage existing customer relationships and brand recognition while attracting new customers interested in the expanded offerings.
- Geographic Expansion: Explore new markets within your country or internationally. This could involve partnering with distributors in new regions or establishing online sales channels targeting international customers. Thorough market research is crucial to assess the viability of each new market.
- Targeted Marketing: Identify new customer segments with unmet needs and tailor your marketing efforts accordingly. This might involve partnering with influencers who reach a specific demographic or running targeted advertising campaigns on social media platforms.
Challenges of Scaling a Wholesale Clothing Business and Their Solutions
Scaling a wholesale clothing business presents several challenges, primarily related to logistics, finance, and maintaining quality. Overcoming these hurdles requires proactive planning and effective resource management.
- Increased Inventory Management Complexity: As your product line and sales volume grow, managing inventory becomes more complex. Solutions include implementing robust inventory management software, optimizing warehouse space, and establishing efficient supply chain processes. Failure to do so can lead to stockouts or excess inventory, both impacting profitability.
- Financial Strain: Rapid expansion often requires significant upfront investment in inventory, marketing, and potentially new facilities. Securing sufficient funding through loans, investors, or strategic partnerships is crucial. Careful financial planning and budgeting are essential to avoid cash flow problems.
- Maintaining Brand Consistency and Quality: As your business grows, maintaining consistent product quality and brand image across all sales channels becomes challenging. Implementing strict quality control measures, providing thorough training to employees, and establishing clear brand guidelines are vital to preserve brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Examples of Successful Wholesale Clothing Businesses and Their Growth Strategies
Several successful wholesale clothing businesses have demonstrated effective scaling strategies. These examples highlight the importance of strategic planning, adaptation, and a focus on customer needs.
- Fashion Nova: Fashion Nova’s success is attributed to its agile approach to trend forecasting and rapid product development, allowing them to quickly capitalize on popular styles. Their extensive use of social media marketing and influencer collaborations has also played a key role in their rapid growth.
- Shein: Shein’s massive scale is a result of its efficient supply chain, leveraging technology and direct-to-consumer sales. Their ability to offer trendy clothing at incredibly low prices has made them a major player in the fast fashion market.
- American Apparel (prior to bankruptcy): While ultimately facing financial difficulties, American Apparel’s early success stemmed from its focus on ethical manufacturing and high-quality, basic apparel. Their strong brand identity and commitment to sustainability resonated with a particular segment of consumers.
Three-Year Scaling Timeline, How to start a wholesale clothing business
A well-defined timeline is crucial for achieving ambitious growth goals. This timeline Artikels key milestones for a wholesale clothing business over three years. Remember, this is a sample and needs to be adapted to your specific circumstances.
| Year | Milestone | Action Items |
|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | Establish a strong online presence and secure initial wholesale clients. | Develop a professional website, optimize for , attend trade shows, build relationships with key retailers. |
| Year 2 | Expand product line and target new market segments. | Introduce complementary product lines, explore new geographic markets, implement targeted marketing campaigns. |
| Year 3 | Optimize operations for efficiency and scalability. | Implement advanced inventory management systems, streamline logistics, explore automation opportunities, and potentially secure additional funding. |






