How to start a mobile EV charging business? The electric vehicle revolution is accelerating, and with it comes a surging demand for convenient charging solutions. This burgeoning market presents a unique opportunity for entrepreneurs: establishing a mobile EV charging business offers a flexible, scalable, and potentially highly profitable venture. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and steps necessary to navigate the complexities of launching and growing a successful mobile EV charging operation, from market research and business planning to securing funding and managing daily operations.
Successfully launching a mobile EV charging business requires careful planning and execution across several key areas. Thorough market research is crucial to identify underserved areas and understand the competitive landscape. A robust business plan, including financial projections and a risk mitigation strategy, is essential for securing funding and attracting investors. Navigating legal and regulatory hurdles, procuring the right equipment, and implementing efficient operational procedures are also vital for long-term success. Finally, a strong marketing strategy is key to attracting and retaining customers in this rapidly evolving market.
Market Research and Analysis
Launching a successful mobile EV charging business requires a thorough understanding of your target market. This involves more than just identifying a general need; it demands a deep dive into the specific demographics, competitive landscape, and potential challenges within your chosen area. This section details the crucial steps involved in conducting effective market research and analysis.
Identifying Key Demographics
Understanding the demographics of EV owners and potential customers is paramount. This goes beyond simply knowing the total number of EVs in your area. Focus on identifying specific pockets of high EV adoption. For instance, affluent neighborhoods with higher-than-average household incomes often have a greater concentration of EV owners. Similarly, areas with robust public transportation infrastructure might attract individuals who use EVs as a supplemental mode of transport. Analyzing local census data, real estate records, and even social media trends can provide valuable insights into the distribution and characteristics of your potential customer base. Consider factors such as age, income levels, and proximity to workplaces or charging infrastructure. For example, a dense apartment complex with limited private parking spaces may present a greater need for public charging stations than a suburban neighborhood with predominantly single-family homes and garages.
Competitive Pricing Analysis
A comprehensive pricing strategy is essential for profitability. Before setting your rates, thoroughly research the pricing models of existing EV charging businesses in your region. Note the variations in pricing structures – per kilowatt-hour (kWh), per charging session, subscription models, or tiered pricing based on charging speed. Consider factors such as location (e.g., higher prices in prime locations), charging speed (faster charging typically commands higher prices), and additional services offered (e.g., membership programs or loyalty discounts). Analyze how these different approaches affect customer acquisition and retention. For instance, a competitor might offer lower kWh rates but charge a higher connection fee, while another might offer a subscription model with unlimited charging within a specific monthly allowance. Understanding these nuances allows you to develop a pricing strategy that is both competitive and profitable.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Local EV Charging Market
The EV charging market presents both significant opportunities and challenges. Opportunities include the growing adoption of EVs, government incentives supporting EV infrastructure development, and the increasing demand for convenient charging solutions. However, challenges include high upfront capital costs for installing charging stations, competition from established players, potential regulatory hurdles, and the need for robust maintenance and customer support. Furthermore, the reliability of the electricity grid and the availability of suitable locations for charging stations are critical factors. For instance, a location with limited grid capacity might require significant upgrades before it can support a high-powered charging station, increasing upfront investment costs. Similarly, securing permits and navigating local zoning regulations can prove time-consuming and complex. Identifying and mitigating these challenges proactively is key to long-term success.
Competitive Analysis Table
A competitive analysis is crucial for understanding the market landscape. The table below compares three hypothetical competitors in a given region. Remember to replace this with actual data for your specific target area.
| Location | Pricing (per kWh) | Services Offered | Customer Reviews (Average Rating) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Downtown Charging Hub | $0.35 | Fast charging, membership program, app-based payment | 4.2 stars |
| Suburban Charge Point | $0.28 | Level 2 charging, limited hours of operation | 3.8 stars |
| City Center Electrify | $0.40 | Fast and Level 2 charging, 24/7 access, premium customer support | 4.5 stars |
Business Plan Development
A robust business plan is crucial for securing funding, guiding operational decisions, and ensuring the long-term success of your mobile EV charging business. This document will serve as your roadmap, outlining your strategies for capturing market share and achieving profitability. It should be a living document, regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changing market conditions and business performance.
Target Market Definition and Segmentation
Defining your target market is the first step in developing a successful business plan. This involves identifying specific customer segments most likely to utilize your mobile EV charging services. For example, you might focus on businesses with large fleets of electric vehicles, residential areas with limited charging infrastructure, or event organizers requiring on-site charging solutions. Consider factors such as geographic location, demographics, charging needs (speed, frequency), and willingness to pay. Detailed market segmentation allows for tailored marketing and pricing strategies, maximizing efficiency and profitability. For instance, a premium service targeting high-net-worth individuals could command higher prices compared to a basic service offered to residential customers.
Revenue Projections and Expense Budget
Accurate revenue projections are essential for demonstrating the financial viability of your business. This involves estimating the number of charging sessions, average revenue per session, and overall revenue generated over a specific period (e.g., annually for the first three years). Consider factors like charging rates, subscription models (if any), and potential seasonal variations in demand. Your expense budget should include all operational costs, such as vehicle acquisition and maintenance, charging equipment, insurance, permits and licenses, marketing and advertising, salaries, and administrative expenses. A realistic budget should account for unexpected expenses and allow for contingency planning. For example, a projection might show an annual revenue of $200,000 in year one, increasing to $350,000 in year three, based on a projected growth in EV adoption and service utilization. Expenses should be detailed, itemized, and realistic based on market prices and industry benchmarks.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Your marketing and sales strategy will determine your ability to reach your target customers. This could involve online marketing (social media, search engine optimization, targeted advertising), partnerships with businesses or organizations (e.g., offering discounted rates to fleet operators), participation in EV-related events, and direct outreach to potential clients. Building strong relationships with key stakeholders, such as property managers and event organizers, can create a reliable stream of recurring business. A strong brand identity and customer service are also critical for building trust and loyalty. For example, a targeted social media campaign focused on eco-conscious consumers in specific geographic areas can effectively reach your desired audience. Strategic partnerships with local businesses could provide access to their customer base and generate referral business.
Financial Model and Profitability Analysis
A detailed financial model is crucial for assessing the financial health of your business over time. This model should project revenue, expenses, and profitability (net income) over a three-year period, providing a clear picture of the business’s financial performance. Key financial metrics, such as break-even point, return on investment (ROI), and cash flow, should be included. Sensitivity analysis, which examines the impact of changes in key assumptions (e.g., charging rates, operating costs), can provide insights into the business’s resilience to various scenarios. For example, a three-year projection might show a net income of $20,000 in year one, $60,000 in year two, and $120,000 in year three, indicating strong growth and profitability. This model should be supported by realistic assumptions and market data.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Plan
Identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies is critical for business success. Potential risks include competition, fluctuating energy prices, regulatory changes, technological advancements, and unexpected equipment failures. For each identified risk, develop a specific mitigation strategy. For example, to mitigate the risk of competition, you might focus on differentiation through superior customer service, faster charging speeds, or strategic partnerships. To mitigate the risk of fluctuating energy prices, you might explore hedging strategies or negotiate fixed-rate contracts with energy suppliers. A comprehensive risk assessment and mitigation plan demonstrates your preparedness for potential challenges and strengthens investor confidence.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance

Launching an EV charging business requires navigating a complex legal and regulatory landscape. Failure to comply with all applicable laws and regulations can result in significant penalties, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. This section Artikels the key legal and regulatory considerations for establishing and operating a successful EV charging business. Understanding these requirements is crucial for minimizing risk and ensuring long-term viability.
Necessary Permits and Licenses
Securing the necessary permits and licenses is the foundational step in establishing legal compliance. The specific requirements vary significantly depending on location (national, state/province, and local levels), the type of charging stations deployed (Level 2 vs. DC Fast Charging), and the business model (e.g., privately owned vs. franchise). Generally, permits and licenses might include business licenses, zoning permits, electrical permits, and potentially environmental permits. The process of obtaining these often involves submitting detailed applications, providing proof of insurance, demonstrating compliance with building codes and safety standards, and undergoing inspections. For example, in California, obtaining a business license involves registering with the California Secretary of State and the relevant county or city. Electrical permits require detailed plans reviewed and approved by the local utility company and fire marshal.
Permit and License Acquisition Process, How to start a mobile ev charging business
The process of obtaining permits and licenses is typically multi-stage and can be time-consuming. It begins with identifying the relevant authorities and obtaining application forms. Next, applicants must complete the forms accurately and comprehensively, often including detailed site plans, electrical schematics, and proof of insurance. Then, applications are reviewed by the respective agencies, which may involve site inspections to ensure compliance with building codes and safety regulations. Once approved, the necessary permits and licenses are issued. The timeline for this process can vary considerably, ranging from several weeks to several months, depending on the complexity of the project and the efficiency of the regulatory agencies. Delays are common, so proactive planning and communication with regulatory bodies are crucial.
Safety Regulations and Standards
Adhering to safety regulations and standards is paramount for protecting both employees and customers. These regulations cover various aspects of EV charging station operation, including electrical safety, fire prevention, and accessibility. Standards like those set by the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the US, or equivalent standards in other jurisdictions, must be meticulously followed. This involves using certified equipment, implementing proper grounding and bonding techniques, and installing adequate fire suppression systems. Regular inspections and maintenance are essential to ensure continued compliance and prevent potential hazards. For instance, the NEC specifies requirements for wiring, grounding, and overcurrent protection for EV charging stations. Failure to comply can lead to electrical fires or other serious incidents.
Checklist of Legal and Regulatory Requirements
A comprehensive checklist is essential for tracking compliance. This checklist should include:
- Business license
- Zoning permits
- Electrical permits
- Building permits
- Environmental permits (if applicable)
- Insurance (general liability, professional liability, etc.)
- Compliance with relevant safety standards (e.g., NEC)
- Data privacy compliance (depending on data collected)
- Accessibility compliance (ADA compliance in the US)
This checklist serves as a dynamic tool, requiring updates as regulations evolve and the business expands. Regular reviews and updates are necessary to maintain ongoing compliance.
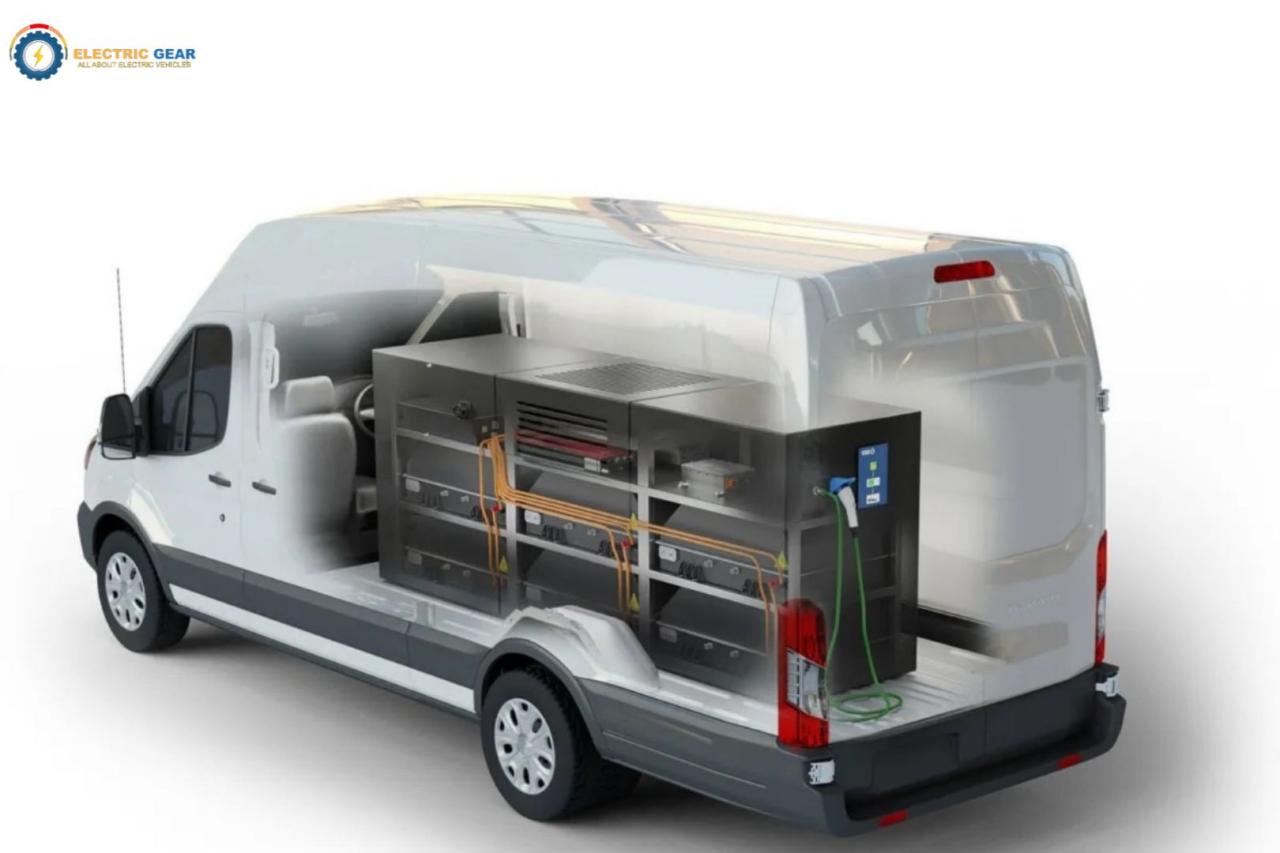
Infrastructure and Equipment
Setting up the physical infrastructure for your mobile EV charging business is crucial for success. This involves selecting the right charging stations, ensuring proper installation, and establishing a robust maintenance plan. The choices you make here will directly impact your operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
The core of your business lies in the charging stations themselves. You need to carefully consider the types of chargers you’ll offer, their capacity, and their suitability for your target market. This involves balancing initial investment costs with the potential revenue generated from different charging speeds and customer demands.
EV Charging Station Types and Market Suitability
Level 2 chargers and DC fast chargers represent the primary options for your mobile EV charging business. Level 2 chargers, providing a slower charging rate (typically 3-10 kW), are ideal for overnight or extended-duration charging, making them suitable for residential areas or locations with ample dwell time. DC fast chargers, on the other hand, offer significantly faster charging speeds (50 kW to 350 kW+), catering to customers needing a quick top-up. They are best suited for high-traffic areas like commercial centers, highway rest stops, or event venues where charging time is a critical factor. The choice depends on your target market’s charging needs and preferences. For example, a business focused on fleet charging might prioritize Level 2 chargers for overnight charging, while a business serving commuters might favor DC fast chargers.
EV Charging Station Installation Process
Installing EV charging stations involves several key steps. First, a thorough site assessment is necessary to determine the available power capacity, the proximity to existing electrical infrastructure, and the accessibility for both charging vehicles and maintenance personnel. This assessment should include a detailed evaluation of the electrical load capacity to ensure the chosen charger’s power draw doesn’t overload the existing system. Site preparation might involve groundworks, such as creating a level and stable surface for the charging station. Next, electrical work is required, which might include upgrading the existing electrical service, running new conduits and wiring, and installing a dedicated circuit breaker for the charger. Finally, the charging station itself is installed, tested, and commissioned, ensuring it meets all safety and performance standards. The entire process necessitates adherence to local building codes and electrical regulations. Failure to do so can result in significant delays and potential legal issues.
Charging Equipment Maintenance and Servicing Plan
A proactive maintenance plan is vital for ensuring the reliability and longevity of your charging equipment. This should include regular inspections, preventative maintenance tasks (such as cleaning connectors and checking for loose connections), and prompt repairs of any malfunctions. Developing a detailed maintenance schedule, perhaps utilizing a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS), will allow you to track maintenance activities, predict potential failures, and minimize downtime. Establishing relationships with qualified technicians or service providers is crucial for timely repairs and minimizing operational disruptions. This could involve signing service contracts or creating a network of trusted professionals across your service area. Consider implementing a system for remote monitoring of your charging stations, enabling early detection of potential issues.
Cost Breakdown for Charging Infrastructure
The cost of acquiring and installing EV charging infrastructure varies significantly depending on several factors, including the type of charger, the installation complexity, and any necessary electrical upgrades. For a Level 2 charger, the cost could range from $2,000 to $10,000 per unit, including the charger itself, installation labor, and any required electrical work. DC fast chargers are significantly more expensive, ranging from $50,000 to $200,000 or more per unit, due to their higher power capacity and more complex technology. Furthermore, the cost of site preparation, permitting, and inspections should also be factored into your budget. For instance, upgrading electrical service to accommodate multiple fast chargers at a busy location could easily add tens of thousands of dollars to the project cost. Consider securing financing options, such as loans or grants, to manage the substantial upfront investment required. A detailed cost analysis, broken down by component and location, is crucial for accurate budgeting and financial planning.
Operations and Management: How To Start A Mobile Ev Charging Business
Efficient daily operations are crucial for the success of any EV charging business. This involves a well-defined system for managing charging stations, handling customer interactions, and ensuring optimal energy usage. A robust operational plan will minimize downtime, maximize revenue, and cultivate customer loyalty.
Daily Operations of an EV Charging Station
Daily operations encompass a multifaceted approach, ensuring smooth functioning and customer satisfaction. This includes regular inspections, proactive maintenance, and prompt responses to any issues. A systematic checklist should be implemented to standardize procedures.
- Pre-opening Checks: Inspect all charging stations for any physical damage, malfunctioning equipment, or loose connections. Verify network connectivity and payment gateway functionality. Check for any reported issues from the previous day.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously monitor the charging stations’ status using a central management system. This allows for immediate identification of any errors or malfunctions.
- Customer Service: Provide prompt and helpful assistance to customers. This could involve guiding them through the charging process, addressing any technical issues, or answering billing inquiries. Consider offering multilingual support based on your target market.
- Maintenance and Cleaning: Regular cleaning of the charging stations and surrounding areas is essential for maintaining a positive customer experience. Preventive maintenance, including regular inspections and software updates, should be scheduled to minimize downtime and extend the lifespan of equipment.
- End-of-Day Procedures: Perform a final inspection of all charging stations. Generate daily reports on energy consumption, revenue, and any issues encountered. Address any outstanding customer inquiries or complaints.
Pricing Model and Payment Processing
A clear and competitive pricing strategy is essential for attracting and retaining customers. The chosen payment processing system must be secure, reliable, and user-friendly.
Pricing models can vary, ranging from a per-kilowatt-hour (kWh) rate to a flat-rate subscription service or a combination of both. Consider offering tiered pricing based on charging speed or time of day to incentivize off-peak charging and optimize grid usage. For example, a tiered system might offer a lower rate during off-peak hours (11 pm to 7 am) and a higher rate during peak hours. Payment processing can be integrated through various methods including credit/debit cards, mobile payment apps (Apple Pay, Google Pay), and RFID cards. The system should provide detailed transaction records for accounting and reporting purposes.
Customer Inquiry and Complaint Handling
Effective customer service is paramount for building a positive brand reputation. A streamlined process for handling inquiries and complaints is crucial.
Establish multiple channels for customer contact, including phone, email, and a dedicated mobile app or website portal. All inquiries and complaints should be documented, tracked, and resolved within a specified timeframe. For example, aim to respond to all inquiries within 24 hours and resolve complaints within 48-72 hours. Consider implementing a customer satisfaction survey to gather feedback and identify areas for improvement. A well-defined escalation process should be in place to handle complex or unresolved issues.
Energy Consumption Management and Charging Efficiency
Optimizing energy consumption and charging efficiency is critical for minimizing operational costs and maximizing profitability.
Implement a smart charging system that manages energy distribution and optimizes charging schedules based on grid demand and availability. This can help reduce peak demand charges and improve overall energy efficiency. Regularly monitor energy consumption data to identify potential areas for improvement. Consider using renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, to reduce reliance on the grid and lower operating costs. For instance, a company might install solar panels on the charging station canopy to power a portion of its operations. Invest in high-efficiency charging equipment to minimize energy loss during the charging process. This can lead to significant cost savings over the long term.
Marketing and Sales
A successful EV charging business requires a robust marketing and sales strategy to attract and retain customers. This involves identifying your target audience, crafting compelling messaging, and utilizing a diverse range of marketing channels to reach them effectively. Equally important is building a loyal customer base through rewarding programs and exceptional service.
Effective marketing hinges on understanding your customer’s needs and preferences. Consider factors such as location, charging habits, and vehicle types when designing your marketing campaigns. Tailoring your messaging to resonate with these specific demographics is crucial for maximizing impact and achieving a strong return on investment.
Marketing Campaign Design
A multi-faceted marketing campaign should be implemented to attract customers. This campaign will leverage both online and offline strategies to reach a broad audience and build brand awareness. The core message should highlight the convenience, speed, and reliability of your charging stations, emphasizing any unique selling propositions, such as competitive pricing, advanced technology, or convenient locations. Consider offering introductory discounts or promotions to incentivize initial adoption. For example, a “first charge free” offer could be very effective in driving initial traffic. A geographically targeted approach, using localized advertising within a radius of your charging stations, will also maximize efficiency.
Potential Marketing Channels
Several marketing channels offer significant potential for reaching your target audience.
- Online Advertising: Google Ads and other search engine marketing (SEM) campaigns can target users searching for EV charging stations in your area. This ensures your business appears prominently in search results. Retargeting campaigns can also be effective in reminding users who have previously visited your website or interacted with your ads.
- Social Media Marketing: Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter can be used to build brand awareness, engage with potential customers, and run targeted advertising campaigns. Sharing visually appealing content, such as photos of your charging stations and customer testimonials, can significantly enhance engagement.
- Partnerships: Collaborating with local businesses, such as car dealerships, coffee shops, or shopping malls, can provide access to a wider customer base. Offering bundled deals or cross-promotional opportunities can be mutually beneficial.
- Email Marketing: Building an email list allows for direct communication with customers and the promotion of special offers, updates, and loyalty programs. Targeted email campaigns can be highly effective in driving repeat business.
- Public Relations: Securing media coverage in local news outlets or industry publications can significantly increase brand visibility and credibility. Press releases announcing the launch of new charging stations or special initiatives can be particularly effective.
Customer Loyalty Program
A robust customer loyalty program is essential for retaining customers and encouraging repeat business.
- Rewards Program: Offer points or discounts for frequent charging sessions. These points can be redeemed for free charging, merchandise, or other incentives. Consider tiered rewards systems to incentivize higher levels of usage.
- Exclusive Offers: Provide loyalty members with access to exclusive deals and promotions not available to the general public. This creates a sense of exclusivity and appreciation.
- Personalized Communication: Regularly communicate with loyalty members through email or other channels, providing updates, special offers, and personalized recommendations.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Solicit feedback from loyalty members to improve your services and address any concerns promptly. This demonstrates a commitment to customer satisfaction and builds trust.
Promotional Materials Examples
Effective promotional materials are crucial for conveying your brand message and attracting customers.
- Website Content: A user-friendly website with clear information about your charging stations, pricing, and location is essential. High-quality images and customer testimonials can enhance credibility and engagement. For example, a section detailing the environmental benefits of using your charging stations can resonate with environmentally conscious consumers.
- Brochures: Printed brochures can be distributed at local businesses or events. They should include clear information about your services, pricing, and contact details. A visually appealing design is crucial to grab attention. For example, a brochure could highlight the convenience of charging while shopping or dining at nearby establishments.
- Social Media Posts: Visually appealing social media posts with engaging captions can increase brand awareness and drive traffic to your website. Using high-quality images and videos of your charging stations in action can be very effective.
Financial Projections and Funding

Securing funding and creating robust financial projections are crucial for the success of any mobile EV charging business. This involves a detailed understanding of potential revenue streams, operating costs, and a clear strategy for managing cash flow to ensure long-term financial stability. A well-defined financial plan will not only attract investors but also provide a roadmap for navigating the complexities of the business.
Funding Acquisition Strategies illustrate the various avenues available for securing capital. This section will Artikel potential funding sources and provide a framework for developing a compelling funding proposal.
Funding Acquisition Strategies
Several avenues exist for securing the necessary capital to launch and operate a mobile EV charging business. These options range from bootstrapping (using personal savings), to securing loans from financial institutions, to attracting investments from venture capitalists or angel investors. The optimal strategy will depend on factors such as the scale of the operation, the entrepreneur’s personal financial resources, and the overall market opportunity.
- Bootstrapping: This involves using personal savings and revenue generated from early operations to fund the business. This approach minimizes debt but may limit initial growth potential. A successful bootstrapping strategy requires meticulous financial management and a strong focus on profitability from the outset.
- Small Business Loans: Banks and credit unions offer loans specifically designed for small businesses. Securing a loan requires a comprehensive business plan, demonstrating the viability of the venture and the ability to repay the loan. Interest rates and repayment terms will vary depending on the lender and the borrower’s creditworthiness. For example, a business seeking $50,000 for equipment might secure a loan with a 7% interest rate over five years.
- Venture Capital/Angel Investors: These investors provide capital in exchange for equity in the business. Attracting these investors requires a compelling business plan, a strong management team, and a clear path to significant growth and profitability. Investors will typically conduct thorough due diligence before committing funds. A successful pitch might secure a $250,000 investment in exchange for a 20% stake in the company.
Financial Forecasting
A comprehensive financial forecast is essential for attracting funding and managing the business effectively. This forecast should project revenue, expenses, and profitability over a period of at least three to five years. The forecast should consider various scenarios, including best-case, worst-case, and most-likely outcomes. Detailed projections allow for proactive adjustments to the business strategy based on evolving market conditions.
For instance, a financial forecast might project annual revenue growth of 25% over the first three years, based on an estimated increase in EV adoption and the expansion of charging services to new areas. This would be accompanied by a detailed breakdown of operating expenses, including labor costs, equipment maintenance, insurance, and marketing. Profitability would be calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenue for each year.
Pricing Strategy
The pricing strategy must balance profitability with market competitiveness. Factors to consider include the cost of electricity, equipment maintenance, labor costs, and the competitive landscape. Different pricing models can be implemented, such as per-session charging, subscription plans, or tiered pricing based on charging speed. A thorough market analysis will inform the most effective pricing strategy to maximize revenue while attracting customers.
For example, a pricing model could involve a base rate per charging session, with additional charges based on the kilowatt-hours (kWh) consumed. This could be structured to incentivize off-peak charging by offering lower rates during periods of lower electricity demand. A subscription model might offer unlimited charging at a fixed monthly fee, appealing to high-usage customers.
Cash Flow Management
Effective cash flow management is vital for the long-term sustainability of the business. This involves accurately forecasting cash inflows and outflows, managing accounts receivable and payable efficiently, and maintaining sufficient working capital. A robust cash flow management system can help avoid financial difficulties and ensure the business can meet its operational obligations.
Strategies for managing cash flow include negotiating favorable payment terms with suppliers, implementing efficient billing systems, and securing lines of credit to cover unexpected expenses. Regular monitoring of cash flow, coupled with proactive adjustments to the business plan, is crucial for maintaining financial stability.
Technology and Software
Successfully operating a mobile EV charging business hinges on robust technology and software. Efficient management of charging stations, seamless billing processes, and insightful data analysis are all crucial for profitability and customer satisfaction. The right software solutions can automate many tasks, reduce operational costs, and enhance the overall user experience.
Choosing the appropriate software and integrating it effectively is a key decision that will impact your business’s scalability and efficiency. This section explores the various software options available, payment methods, and key features of a comprehensive charging station management system.
EV Charging Station Management Software Options
Several software solutions cater specifically to the needs of EV charging station operators. These range from cloud-based platforms offering comprehensive features to simpler, on-premise systems suitable for smaller operations. Key considerations when selecting software include scalability (ability to handle increasing numbers of chargers and users), integration capabilities (compatibility with various hardware and payment gateways), reporting and analytics (providing data on usage, revenue, and operational efficiency), and customer support. Examples of such software include ChargePoint, EVBox, and ABB Ability™. The specific choice will depend on the size and complexity of your business, as well as your budget and technical expertise.
Payment Options for EV Charging
Offering diverse payment options is essential for maximizing customer convenience and adoption. A robust system should seamlessly integrate with various payment gateways to support credit and debit cards (Visa, Mastercard, American Express), mobile payment systems (Apple Pay, Google Pay, PayPal), and potentially even subscription services for regular users or fleet operators. The ability to offer contactless payments is particularly important in the context of hygiene and convenience. Some systems may also support RFID cards or dedicated charging apps. Choosing the right payment options involves balancing the convenience offered to customers with the transaction fees and processing complexities involved.
Features of Robust Charging Station Management Software
A robust charging station management software package should include several key features. These features enable efficient operation, streamlined billing, and improved customer service. Real-time monitoring of charger status (available, in use, offline), remote diagnostics and troubleshooting, automated billing and invoicing, detailed reporting and analytics (energy consumption, revenue generated, peak usage times), user management and access control, and integration with third-party services (e.g., mapping applications, energy providers) are all essential aspects of a comprehensive system. The software should also provide a user-friendly interface for both administrators and end-users.
Potential Technology Partners for Software Integration
Successful integration of software and hardware requires collaboration with various technology partners. These partners may include payment gateway providers (Stripe, PayPal, Square), mapping services (Google Maps, HERE Technologies), hardware manufacturers (charging station providers), and telecommunications companies for reliable network connectivity. Establishing strong relationships with these partners is crucial for ensuring seamless operation and smooth integration of your charging infrastructure and software. Examples of potential partners could also include companies specializing in data analytics or customer relationship management (CRM) systems to enhance your business intelligence and customer engagement.






