How to start a wheelchair transportation business? This question unlocks a world of opportunity, blending entrepreneurial spirit with a vital social need. Starting this type of business requires meticulous planning, from comprehensive market research and securing the necessary licenses and insurance to acquiring and maintaining accessible vehicles and building a reliable team. Success hinges on understanding the specific regulatory landscape, crafting a robust operational plan, and implementing effective marketing strategies to reach your target clientele. This guide navigates the complexities, providing a step-by-step approach to launching a successful and impactful wheelchair transportation service.
The journey begins with a thorough market analysis to identify underserved communities and competitive pressures. A detailed business plan, including financial projections and a SWOT analysis, forms the bedrock of your venture. Legal compliance is paramount, encompassing securing the necessary permits and adhering to ADA regulations. Building a strong team of qualified and compassionate drivers is essential, as is implementing efficient operational procedures and customer service protocols. Finally, a multi-faceted marketing strategy will attract clients and establish your business as a reliable provider of vital transportation services.
Market Research and Business Planning

Launching a successful wheelchair transportation business requires meticulous planning and a deep understanding of the market. This involves comprehensive market research to identify opportunities and a robust business plan to guide operations and growth. Failing to conduct thorough research and develop a solid business plan significantly increases the risk of failure.
Market Research Steps
Effective market research is crucial for understanding the demand for wheelchair transportation services in your target area. This involves analyzing various factors to assess the viability and potential profitability of your business. The following steps Artikel a comprehensive approach.
- Demographic Analysis: Determine the size and characteristics of the potential customer base. This includes identifying the number of wheelchair users, their age distribution, income levels, and geographic location within your service area. For example, a city with a large senior population and limited public transportation options presents a strong market opportunity. Conversely, an area with robust public transit and a smaller elderly population may offer less potential.
- Competitive Analysis: Identify existing wheelchair transportation services in your area. Analyze their pricing strategies, service offerings, market share, and customer reviews. This helps determine your competitive advantage and inform your pricing and marketing strategies. A SWOT analysis (discussed later) will be particularly helpful here.
- Unmet Needs Assessment: Identify gaps in the current service offerings. Are there specific needs (e.g., 24/7 service, specialized equipment for certain medical conditions, transportation for specific events) not being adequately met by existing providers? Targeting these unmet needs can create a unique selling proposition and attract a loyal customer base.
- Regulatory Compliance Research: Understand all local, state, and federal regulations related to wheelchair transportation, including licensing, insurance, and safety standards. Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties and business closure.
Business Plan Development
A comprehensive business plan is essential for securing funding, guiding operations, and tracking progress. It should include the following key elements.
- Executive Summary: A concise overview of the business, its goals, and its market opportunity.
- Company Description: Details about the business structure (sole proprietorship, LLC, etc.), mission statement, and legal aspects.
- Market Analysis: A summary of the market research findings, including demographic data, competitive landscape, and unmet needs.
- Services Offered: A clear description of the transportation services provided, including pricing and service areas.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: Strategies to reach target customers, such as online advertising, partnerships with healthcare providers, and community outreach. Examples include online ads targeted to specific demographics or partnerships with local hospitals and nursing homes.
- Management Team: Information about the key personnel involved in the business, their experience, and qualifications.
- Financial Projections: This section is crucial and should include a projected income statement, cash flow analysis, and balance sheet. For example, a projected income statement might forecast revenue based on estimated ridership and pricing, while a cash flow analysis would project monthly cash inflows and outflows to ensure sufficient working capital.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis helps identify the internal strengths and weaknesses of the business, as well as external opportunities and threats.
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| Experienced drivers | High initial investment costs |
| Excellent customer service | Dependence on fuel prices |
| Specialized equipment | Competition from established players |
| Opportunities | Threats |
| Expanding service area | Economic downturn |
| Partnerships with healthcare providers | Changes in regulations |
| Technological advancements (e.g., ride-sharing apps) | Increased insurance costs |
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: How To Start A Wheelchair Transportation Business
Launching a wheelchair transportation business requires navigating a complex web of legal and regulatory requirements. Failure to comply can result in significant fines, legal action, and damage to your reputation. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is paramount for both operational success and ethical responsibility. This section Artikels the key legal and regulatory aspects to consider.
Licensing and Permits
Securing the necessary licenses and permits is a crucial first step. Requirements vary significantly depending on location, ranging from local business licenses to state-specific transportation permits. For example, in California, you might need a “Transportation Network Company (TNC)” permit alongside a business license from your city, while in Texas, the regulatory framework might involve different state agencies and a different set of permits. Some jurisdictions may also require specialized permits for transporting individuals with disabilities. It’s imperative to thoroughly research the specific requirements in your area of operation by consulting your state’s Department of Transportation, local government agencies, and potentially legal counsel specializing in transportation regulations. Failing to obtain all necessary permits can lead to operational shutdowns and legal penalties.
Insurance Coverage
Adequate insurance is non-negotiable. You’ll need comprehensive liability insurance to protect your business from claims arising from accidents or injuries. Commercial auto insurance, specifically tailored for transporting passengers, is also essential. This type of insurance covers damages to your vehicle and potential injuries to passengers. The amount of coverage required will depend on factors such as the number of vehicles in your fleet, the type of vehicles, and the specific risks involved. Obtaining insurance involves providing detailed information about your business operations, vehicles, and drivers to insurance providers. They will assess the risk profile and offer appropriate coverage options, potentially requiring safety inspections or driver background checks. Securing sufficient insurance protects your business from potentially devastating financial losses in case of accidents or incidents.
ADA Compliance
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) sets standards for accessibility in transportation. For wheelchair transportation businesses, this translates to ensuring your vehicles are equipped to safely and comfortably accommodate wheelchair users. This includes features like wheelchair ramps or lifts, secure wheelchair tie-downs, appropriate space for wheelchairs and passengers, and accessible vehicle interiors. Beyond vehicle modifications, ADA compliance also extends to your customer service practices. Your drivers should be trained to handle wheelchairs safely and assist passengers with boarding and disembarking. Your company should also have policies in place to address the needs of passengers with various disabilities. Non-compliance with ADA regulations can result in significant fines and legal challenges. Understanding and implementing ADA guidelines is vital for ethical operations and legal compliance.
Vehicle Acquisition and Maintenance
Starting a wheelchair transportation business requires careful consideration of vehicle acquisition and ongoing maintenance. The right vehicles are crucial for providing safe and reliable service, while a robust maintenance plan minimizes downtime and maximizes the lifespan of your fleet. This section details the process of selecting appropriate vehicles and implementing a comprehensive maintenance strategy.
Wheelchair Accessible Vehicle Comparison
Choosing the right wheelchair accessible vehicle (WAV) depends on several factors, including budget, passenger capacity, and the types of wheelchairs you’ll be transporting. Several options exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
| Vehicle Type | Cost (Estimate) | Capacity | Accessibility Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minivan Conversion (e.g., Chrysler Pacifica, Toyota Sienna) | $35,000 – $50,000 (new); $20,000 – $35,000 (used) | 1-2 wheelchairs + passengers | Ramp or lift, securement system for wheelchairs |
| Full-Size Van Conversion (e.g., Ford Transit, Ram ProMaster) | $50,000 – $80,000 (new); $30,000 – $50,000 (used) | 2-3 wheelchairs + passengers | Ramp or lift, multiple wheelchair securement points, potentially more spacious interior |
| Larger Passenger Van Conversion (e.g., Sprinter Van) | $70,000 – $120,000 (new); $40,000 – $70,000 (used) | 3+ wheelchairs + passengers | Multiple ramps or lifts, extensive securement systems, high passenger capacity |
Note that these cost estimates are approximate and can vary significantly based on the year, model, mileage, and specific conversion features. Used vehicles offer cost savings but may require more frequent maintenance. New vehicles offer warranties and potentially lower maintenance costs in the short term.
Vehicle Maintenance and Repair Plan
A proactive maintenance schedule is essential for preventing breakdowns and ensuring the safety of your passengers. This plan Artikels key tasks, their frequency, cost estimates, and responsible parties. Consistent adherence to this plan is vital for maintaining operational efficiency and minimizing unexpected expenses.
| Task | Frequency | Cost Estimate | Responsible Party |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil Change | Every 3,000-5,000 miles | $50 – $100 | Designated Mechanic/Maintenance Team |
| Tire Rotation and Inspection | Every 5,000-7,000 miles | $50 – $75 | Designated Mechanic/Maintenance Team |
| Brake Inspection and Service | Every 10,000-12,000 miles or as needed | $100 – $300 | Designated Mechanic/Maintenance Team |
| Lift/Ramp Inspection and Maintenance | Monthly | $50 – $150 (depending on complexity) | Certified Lift Technician |
| Wheelchair Securement System Inspection | Monthly | $25 – $50 | Designated Mechanic/Maintenance Team |
| Major Service (e.g., transmission fluid change) | Annually or as recommended by manufacturer | $300 – $500 | Designated Mechanic/Maintenance Team |
| Emergency Repairs | As needed | Varies | Roadside Assistance Provider/Designated Mechanic |
Vehicle Management System
Efficient vehicle management relies on a robust system for tracking mileage, maintenance records, and repair costs. A dedicated software program or spreadsheet can be used to record this information. This system should include fields for vehicle identification number (VIN), odometer readings, dates of service, descriptions of repairs, costs incurred, and the responsible party for each task. Regularly reviewing this data allows for proactive maintenance planning, identification of recurring issues, and accurate budgeting for vehicle-related expenses. For example, consistently high repair costs associated with a specific vehicle might indicate the need for replacement or more frequent maintenance. Data analysis can also reveal trends in maintenance needs, allowing for more effective preventative maintenance scheduling and optimized resource allocation.
Operations and Staffing
Efficient operations and a well-trained staff are crucial for the success of any wheelchair transportation business. This section details the processes involved in recruiting, training, and managing personnel, as well as establishing robust operational procedures to ensure smooth and reliable service delivery. Careful planning in these areas directly impacts customer satisfaction and the overall profitability of the enterprise.
Driver Recruitment, Hiring, and Training
The selection of qualified drivers is paramount. Potential drivers must undergo a rigorous screening process to ensure they possess the necessary skills, experience, and personality traits to provide safe and compassionate transportation. This involves a thorough review of driving records, background checks, and potentially, medical evaluations to confirm their physical and mental fitness for the job. The hiring process should also assess their interpersonal skills, as they will be interacting directly with vulnerable clients.
- Driver Selection Criteria: A clean driving record with minimal or no traffic violations is essential. Experience driving vehicles adapted for wheelchair users is highly desirable. Applicants should possess a valid driver’s license and appropriate endorsements. Successful candidates will demonstrate patience, empathy, and a commitment to providing excellent customer service. First aid and CPR certification is also strongly recommended.
- Training Curriculum: The training program should cover various aspects of wheelchair transportation. This includes safe wheelchair securement techniques, proper vehicle operation and maintenance, customer service protocols, emergency procedures, and knowledge of relevant regulations and accessibility guidelines. Practical driving exercises and simulations should be incorporated to reinforce learning. Regular refresher training should be provided to maintain competency and address any updates in regulations or best practices. The training should also include sensitivity training to handle passengers with diverse needs and disabilities.
Operational Plan: Daily Procedures, Dispatch Systems, and Customer Service
A well-defined operational plan ensures smooth daily operations and efficient service delivery. This plan should detail procedures for booking management, dispatching, driver assignments, and customer communication. A robust dispatch system, whether manual or software-based, is essential for tracking bookings, assigning drivers, monitoring vehicle locations, and managing real-time updates. Effective communication protocols are critical to ensure seamless coordination between dispatchers, drivers, and customers.
Example Dispatch System: A simple system could involve a phone line for booking requests, a whiteboard to track assignments, and a GPS tracking system for monitoring vehicles. More sophisticated systems might incorporate dispatch software with features like automated routing, real-time tracking, and customer communication portals.
Customer Service Protocols: Drivers should be trained to provide courteous and respectful service, maintaining professional conduct at all times. Clear communication with customers, punctuality, and addressing any concerns promptly are key aspects of excellent customer service. Regular feedback mechanisms should be in place to monitor customer satisfaction and identify areas for improvement.
Booking, Scheduling, and Dispatching System
Efficient management of customer bookings, scheduling, and dispatching is crucial for operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. This requires a reliable system capable of handling multiple bookings, optimizing routes, and assigning drivers effectively. Several software options exist, each with unique features and capabilities.
Software Options Comparison: Some popular scheduling software options include specialized transportation management systems (TMS) and general-purpose scheduling tools adaptable to transportation needs. TMS often offer features like route optimization, real-time tracking, automated billing, and integration with payment gateways. General-purpose scheduling tools may require more customization but offer flexibility in adapting to specific business requirements. Factors to consider when selecting software include cost, scalability, ease of use, and integration capabilities with other systems.
Workflow Flowchart (Booking to Completion):
A simplified flowchart could be represented as follows:
1. Customer Booking: Customer requests a ride via phone, online portal, or app.
2. Booking Confirmation: The system confirms availability and provides details to the customer.
3. Dispatch: The system assigns the closest available driver to the booking.
4. Driver Notification: The driver receives the booking details and customer information.
5. Pickup: The driver picks up the customer at the designated location.
6. Transportation: The driver safely transports the customer to their destination.
7. Drop-off: The driver assists the customer with exiting the vehicle at the destination.
8. Trip Completion: The system updates the booking status to complete.
9. Billing/Payment: The system generates an invoice and processes payment.
Marketing and Sales
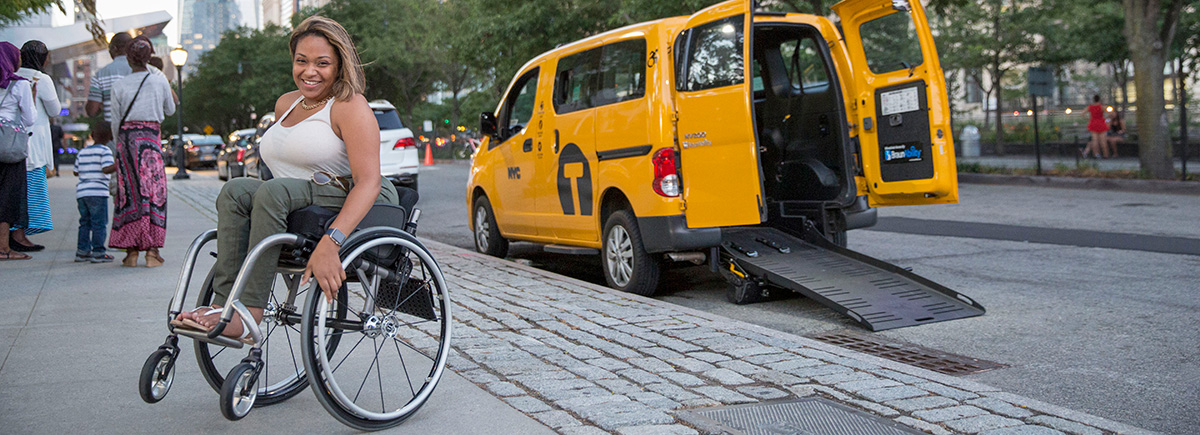
Successfully marketing a wheelchair transportation business requires a multi-pronged approach targeting diverse customer segments with tailored messaging and competitive pricing. This involves leveraging both online and offline channels to maximize reach and build brand awareness. A robust pricing strategy, reflective of operational costs and market conditions, is crucial for profitability.
Marketing Strategies for Target Customers
Effective marketing requires reaching healthcare providers, individuals, and families with distinct messaging tailored to their specific needs and preferences. For healthcare providers, highlighting efficiency, reliability, and compliance with HIPAA regulations is paramount. Direct mail marketing, targeted advertising in medical journals, and participation in healthcare industry events are effective strategies. For individuals and families, emphasizing compassionate care, personalized service, and convenience is key. Online marketing through social media, search engine optimization (), and targeted advertising campaigns on platforms like Google Ads and Facebook Ads can reach a wider audience. Offline strategies include local advertising in community newspapers and partnerships with local organizations serving the disabled community. Building relationships with referral sources, such as hospitals and rehabilitation centers, is also crucial.
Pricing Strategies and Revenue Impact
Several pricing models exist for wheelchair transportation services, each with implications for revenue and profitability. A per-trip pricing model, charging a fixed fee per trip, is straightforward but may not account for distance or service complexity. An hourly rate offers flexibility but can be less predictable in terms of revenue. Value-based pricing, which considers factors such as distance, travel time, and the level of care required, offers a more customized approach but necessitates a robust cost analysis. A subscription model, offering discounted rates for recurring transportation needs, can foster customer loyalty and provide a predictable revenue stream. The optimal pricing strategy depends on factors such as the target market, operational costs, and competitive landscape. For example, a business targeting high-income individuals might adopt a value-based pricing model, while one focusing on low-income clients may opt for a more affordable per-trip model. Careful analysis of market rates and competitor pricing is essential for developing a competitive and profitable strategy.
Marketing Materials and Value Proposition, How to start a wheelchair transportation business
Marketing materials should clearly communicate the business’s value proposition—reliable, safe, and compassionate wheelchair transportation services. Brochures should feature professional photography showcasing clean, well-maintained vehicles and friendly, compassionate staff. The messaging should emphasize key benefits such as timely pickup and drop-off, experienced drivers, and adherence to safety regulations. Website content should be informative, easy to navigate, and include clear contact information, service area details, and online booking capabilities. The website design should be visually appealing and user-friendly, ensuring accessibility for individuals with disabilities. For example, a brochure might feature a large, high-quality photograph of a driver assisting a passenger into a wheelchair-accessible vehicle, accompanied by a short, impactful headline such as “Your Journey, Our Priority.” The website could include testimonials from satisfied customers, further enhancing credibility and trust. Consistent branding across all marketing materials is crucial for building brand recognition and reinforcing the business’s image.
Technology and Customer Service

In today’s competitive landscape, a successful wheelchair transportation business requires a robust technological infrastructure and a commitment to exceptional customer service. Efficient operations, streamlined communication, and a positive customer experience are crucial for building a loyal clientele and achieving sustainable growth. Integrating technology and prioritizing customer satisfaction are not merely add-ons; they are fundamental pillars of a thriving business.
Technology plays a vital role in optimizing operations and enhancing the customer experience. From initial booking to final payment, technology streamlines the entire process, increasing efficiency and reducing administrative overhead. Simultaneously, a proactive and responsive approach to customer service fosters trust and loyalty, encouraging repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals. This section details how to effectively integrate technology and cultivate exceptional customer service.
Mobile App Integration for Booking and Dispatch
A dedicated mobile application offers significant advantages. Customers can easily request rides, view real-time vehicle locations, track their trips, and manage their accounts. For the business, the app streamlines dispatch, optimizes routes, and provides valuable data for operational improvements. Examples of suitable software include custom-developed apps or utilizing platforms like Uber’s API for white-labeling a solution. Hardware requirements are minimal, primarily focusing on reliable smartphones and tablets for drivers and dispatchers. Consider integrating features like real-time ride tracking for increased safety and transparency.
GPS Tracking and Communication Systems
Real-time GPS tracking is essential for monitoring vehicle locations, ensuring timely arrivals, and optimizing routes. This technology enhances operational efficiency and improves customer satisfaction by providing accurate ETAs. Software solutions like Samsara or Geotab provide comprehensive fleet management capabilities, including GPS tracking, driver behavior monitoring, and automated reporting. Hardware involves GPS tracking devices installed in each vehicle, communicating data to a central server. Furthermore, integrated communication systems, such as two-way radios or mobile messaging apps, facilitate seamless communication between dispatchers and drivers, ensuring efficient coordination and prompt responses to customer requests.
Customer Complaint Handling and Resolution
A well-defined procedure for handling customer complaints is critical. This should involve a prompt acknowledgment of the complaint, a thorough investigation, and a fair resolution. A dedicated customer service team should be trained to handle complaints professionally and empathetically. Effective strategies include actively soliciting feedback, offering apologies for any inconvenience, and providing timely updates on the resolution process. Documenting all complaints and resolutions is essential for identifying recurring issues and implementing corrective actions. Consider implementing a customer relationship management (CRM) system to manage customer interactions and track complaint resolution.
Accurate Record Keeping and Transparent Billing
Maintaining accurate records is crucial for financial management, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. This includes detailed trip records, driver logs, maintenance records, and customer information. Transparent billing is essential for building trust and ensuring customer satisfaction. A clear and concise invoice should detail all charges, including base fare, distance, waiting time, and any additional fees. Software solutions such as QuickBooks or Xero can automate invoice generation, payment processing, and financial reporting. Implement a system that allows customers to easily access their invoices and payment history online. This transparency fosters trust and reduces potential disputes.






