Where you can find tcs process for business continuity management – Find TCS Business Continuity Management Processes: Ensuring business continuity is paramount for any large organization, and Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) is no exception. This guide delves into the specifics of TCS’s robust Business Continuity Management (BCM) framework, outlining where to locate crucial documentation, understand its implementation across various business units, and grasp the key strategies employed for recovery and incident management. We’ll explore the technological underpinnings, legal compliance aspects, and the comprehensive training programs designed to equip TCS employees with the knowledge and skills to navigate disruptions effectively. Understanding TCS’s approach provides valuable insights into best practices for BCM implementation in large-scale organizations.
We will cover key aspects of TCS’s BCM, from its core principles and the roles and responsibilities involved to the specific processes used for different business units and critical functions. We’ll also examine the technological tools and strategies implemented to support business continuity, including data backup and recovery procedures, and the rigorous testing and auditing processes in place to ensure the effectiveness of the plan. Finally, we’ll discuss the legal and regulatory compliance considerations that shape TCS’s BCM framework.
TCS Business Continuity Management (BCM) Overview
Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) employs a robust Business Continuity Management (BCM) framework designed to ensure the organization’s continued operation during disruptive events. This framework prioritizes minimizing disruption, protecting critical assets, and facilitating swift recovery. The approach is proactive, preventative, and built upon industry best practices and regulatory compliance.
TCS’s BCM approach is founded on several core principles. These include a strong risk assessment methodology, comprehensive planning and preparedness activities, rigorous testing and exercising of plans, and a commitment to continuous improvement and adaptation based on lessons learned from incidents and changing business needs. The framework is also deeply integrated into TCS’s overall risk management strategy, ensuring alignment and synergy across various organizational functions.
Key Components of a TCS BCM Plan
A typical TCS BCM plan comprises several key components, each crucial for effective business continuity. These components are interconnected and work synergistically to mitigate risks and ensure operational resilience. The plan is not a static document; it’s a living, breathing entity, regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the business environment and emerging threats.
- Business Impact Analysis (BIA): This critical step identifies critical business functions, assesses their dependencies, and determines the potential impact of disruptions on the organization. The BIA informs the prioritization of recovery efforts and resource allocation.
- Recovery Strategies: Based on the BIA, recovery strategies are developed for critical business functions. These strategies Artikel the steps required to restore operations to acceptable levels within predefined recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs).
- Recovery Resources: This section details the resources required to execute the recovery strategies, including IT infrastructure, personnel, data backups, and alternative work locations. It ensures that necessary resources are identified and secured in advance.
- Communication Plan: Effective communication is vital during a disruption. This plan Artikels communication channels, procedures, and responsibilities for keeping stakeholders informed and coordinating recovery efforts.
- Testing and Exercises: Regular testing and exercises are conducted to validate the BCM plan’s effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. These exercises involve simulating various disruption scenarios to assess preparedness and response capabilities.
Roles and Responsibilities within a TCS BCM Framework
A well-defined structure of roles and responsibilities is crucial for the successful implementation and execution of the TCS BCM framework. Clear accountability ensures that tasks are completed efficiently and effectively, contributing to a robust and responsive BCM program. This structure is often hierarchical, with clearly defined reporting lines and escalation procedures.
- BCM Manager/Coordinator: This individual is responsible for the overall management and oversight of the BCM program, including plan development, maintenance, testing, and continuous improvement.
- Business Unit BCM Representatives: These individuals are responsible for the development and maintenance of BCM plans for their respective business units, ensuring alignment with the overall organizational strategy.
- IT Support Teams: IT teams play a crucial role in supporting the recovery of IT systems and infrastructure, ensuring data availability and system functionality.
- Crisis Management Team: This team is responsible for managing the organization’s response to a disruptive event, coordinating recovery efforts, and communicating with stakeholders.
- Senior Management: Senior management provides overall direction, support, and resources for the BCM program, ensuring its strategic alignment with organizational objectives.
Locating TCS BCM Documentation and Resources
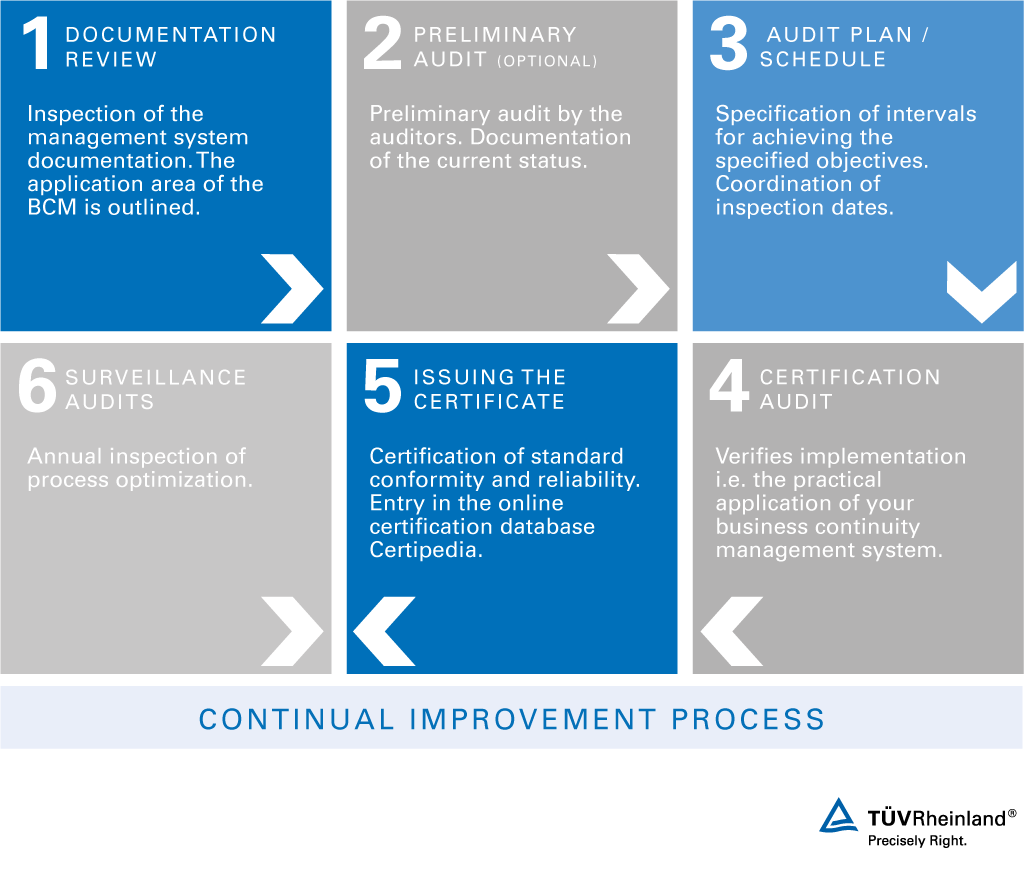
Accessing TCS Business Continuity Management (BCM) documentation and resources is crucial for ensuring business resilience and preparedness. This section details the internal TCS systems and procedures for locating and accessing relevant BCM materials. Understanding these processes is essential for all TCS employees involved in BCM activities or those needing to consult BCM plans and procedures.
The location of TCS BCM documentation varies depending on the specific document and its intended audience. However, several key internal portals and websites serve as central repositories for this critical information. Access permissions are typically role-based, ensuring only authorized personnel can view sensitive or confidential materials.
Internal TCS Websites and Portals for BCM Documentation
Access to TCS BCM documentation is primarily managed through the company’s internal intranet and dedicated portals. These systems often require specific login credentials and may have tiered access levels based on an employee’s role and responsibilities within the BCM framework. Examples of potential locations include, but are not limited to, the TCS Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, which might house policy documents, or a dedicated BCM SharePoint site containing detailed plans and procedures. Furthermore, specific departmental intranet sites might also host relevant BCM information tailored to the needs of that particular department. It is advisable to consult with your line manager or the designated BCM contact person within your department for guidance on the specific locations and access procedures applicable to your role.
Accessing Relevant BCM Documentation for Employees
Employees can access relevant BCM documentation through a combination of internal websites and designated portals. The specific access methods will depend on the employee’s role and responsibilities. Typically, access is granted through the employee’s company network login credentials. Once logged in, employees will be able to navigate to the relevant sections of the intranet or portal containing the BCM documentation. Some materials might require additional authorization or approval before access is granted, particularly those containing sensitive information. These access restrictions are in place to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the BCM plans and procedures.
Requesting Access to Specific BCM Materials
For materials requiring specific authorization, employees should follow the established internal request process. This typically involves submitting a formal request through the designated channels, such as an internal help desk ticket or a request form submitted to the BCM team. The request should clearly state the specific document or information required, the reason for the request, and the employee’s role and responsibilities. Once the request is received, it will be reviewed by the appropriate authorities to ensure the requester has the necessary authorization to access the requested material. The approval or rejection of the request will then be communicated to the employee. The process ensures responsible access control and maintains the integrity of the BCM documentation.
TCS BCM Process for Different Business Units
TCS, being a global IT services and consulting giant, employs a robust Business Continuity Management (BCM) framework. However, the specific implementation and emphasis of this framework vary across its diverse business units, influenced by factors such as industry sector, geographical location, and the criticality of the functions performed. This variation ensures a tailored approach to risk mitigation and business resilience across the organization.
The core principles of TCS’s BCM framework remain consistent across all units, focusing on risk assessment, business impact analysis, recovery planning, and regular testing and exercises. However, the specific processes and procedures implemented to achieve these objectives are adapted to the unique needs and challenges faced by each business unit.
Variations in BCM Implementation Based on Industry Sector
The BCM processes within TCS are tailored to the specific risks and regulatory requirements of the industry sectors served. For example, a business unit providing services to the financial sector will have a more stringent and regulated BCM plan compared to a unit focused on retail or manufacturing. Financial services require stricter adherence to regulatory compliance like SOX and GDPR, leading to more comprehensive documentation, frequent testing, and higher levels of recovery time objective (RTO) and recovery point objective (RPO) targets. In contrast, a business unit serving the retail sector might focus on maintaining operational continuity during peak seasons, prioritizing inventory management and supply chain resilience. These variations reflect the different levels of risk and the unique challenges presented by each industry.
Variations in BCM Implementation Based on Geographical Location
Geographical location also plays a significant role in shaping the specifics of TCS’s BCM processes. Business units operating in regions prone to natural disasters, such as earthquakes or hurricanes, will incorporate specific disaster recovery plans and procedures. These plans might involve geographically dispersed data centers, robust backup and recovery systems, and well-defined escalation procedures for crisis management. Furthermore, differences in local regulations and legal frameworks across various countries necessitate adaptations in the BCM framework to ensure compliance. For instance, data privacy regulations vary significantly globally, requiring different approaches to data protection and recovery.
BCM Procedures for Critical Business Functions within TCS
Critical business functions within TCS, such as application development and maintenance, infrastructure management, and client support, have dedicated BCM procedures. These procedures Artikel the steps to be taken to ensure the continued operation of these functions during disruptions. For instance, application development and maintenance might involve redundant development environments, version control systems, and automated deployment processes to minimize downtime. Infrastructure management would include redundant hardware, geographically dispersed data centers, and robust network security measures to protect against cyberattacks and other disruptions. Client support would involve multiple communication channels, escalation procedures, and a comprehensive knowledge base to ensure continuous service availability. These procedures are regularly tested and updated to reflect evolving threats and vulnerabilities.
Incident Management within TCS BCM
Effective incident management is crucial for minimizing disruption and ensuring business continuity within TCS’s BCM framework. This involves a structured process for identifying, responding to, and resolving incidents that threaten business operations, ranging from minor IT glitches to major disasters. A robust incident management system allows TCS to maintain operational resilience and protect its reputation.
The TCS BCM incident management process follows a clearly defined lifecycle, encompassing identification, escalation, resolution, and post-incident review. This systematic approach ensures consistent responses to diverse incidents, regardless of their scale or complexity. The process is underpinned by established escalation paths, communication protocols, and detailed documentation, all designed to optimize response times and minimize business impact.
Incident Management Process Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates the stages involved in managing incidents within the TCS BCM framework. It emphasizes the iterative nature of the process, highlighting the potential for feedback loops and continuous improvement.
| Stage | Action | Responsibility | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Incident Identification | Detection of an event impacting business operations. This may involve automated alerts, user reports, or monitoring systems. | IT Support, Business Units, Security Operations | Incident logged in the incident management system. |
| Incident Categorization & Prioritization | Assessment of the incident’s impact (severity and urgency) based on pre-defined criteria. | Incident Management Team | Assignment of severity level (e.g., Critical, Major, Minor) and priority level. |
| Initial Response & Containment | Implementation of immediate actions to contain the incident and prevent further damage. | Incident Response Team | Stabilization of the situation and prevention of escalation. |
| Investigation & Diagnosis | Thorough analysis to identify the root cause of the incident. | Technical Specialists, Subject Matter Experts | Identification of root cause and contributing factors. |
| Resolution & Recovery | Implementation of corrective actions to resolve the incident and restore normal operations. | Incident Response Team, Technical Specialists | Restoration of services and functionality. |
| Post-Incident Review | Analysis of the incident to identify areas for improvement in processes and procedures. | Incident Management Team, Business Units | Documentation of lessons learned and implementation of corrective actions. |
Incident Escalation Procedures
Escalation procedures are critical for ensuring timely and effective responses to incidents. The severity level of an incident determines the escalation path and the speed of response.
For example, a Critical incident, such as a major system outage affecting core business functions, would immediately escalate to the highest levels of management, involving the BCM leadership team and potentially external stakeholders. Major incidents, while significant, might follow a slightly less urgent path, potentially involving departmental managers and specialized technical teams. Minor incidents are handled within the relevant team, with escalation only if resolution proves difficult.
Communication Protocols During Business Disruption
Effective communication is paramount during a business disruption. TCS utilizes a multi-channel communication strategy to keep stakeholders informed and coordinated. This involves pre-defined communication plans and regularly tested communication channels.
This might include automated email alerts, SMS notifications, dedicated communication portals, and regular conference calls with key personnel. The specific communication channels and frequency depend on the severity of the incident and the stakeholders involved. Transparency and timely updates are prioritized to minimize anxiety and maintain stakeholder confidence.
Recovery Strategies and Procedures
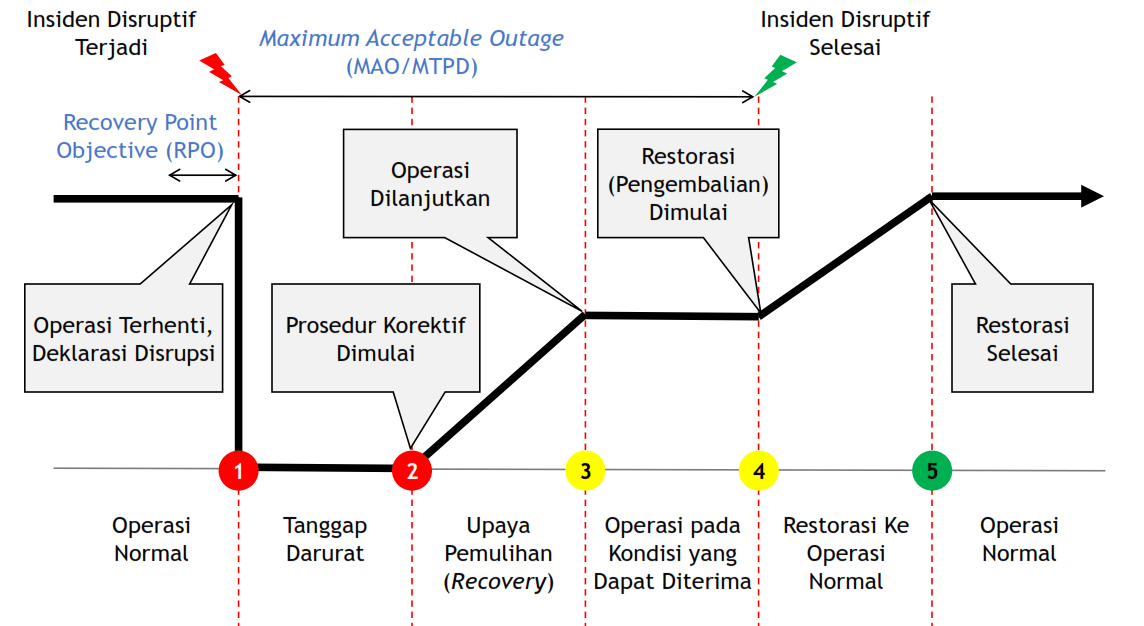
Effective recovery strategies are paramount to TCS’s Business Continuity Management (BCM) plan, ensuring minimal disruption to operations following unforeseen incidents. These strategies encompass a range of approaches tailored to different IT systems and business processes, prioritizing data protection and swift restoration of services. The plan Artikels detailed procedures for data backup and recovery, along with comprehensive steps for restoring business operations.
TCS employs a multi-layered approach to recovery, prioritizing the criticality of systems and processes. This approach considers factors such as recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) to ensure business resilience. The recovery strategies are regularly tested and updated to reflect evolving threats and technological advancements.
IT System Recovery Strategies
The selection of recovery strategies for TCS’s IT systems depends heavily on the criticality of the system and its associated business processes. The strategies employed include:
- Hot Site: A fully equipped and operational facility mirroring the primary data center, enabling immediate failover with minimal downtime. This strategy is typically employed for mission-critical systems requiring immediate recovery.
- Warm Site: A facility with essential infrastructure and some pre-configured systems, requiring minimal setup time before becoming operational. This is a cost-effective alternative to hot sites, suitable for systems with slightly higher RTOs.
- Cold Site: A facility with basic infrastructure, requiring significant setup time before becoming operational. This is a cost-effective option for non-critical systems with longer acceptable RTOs.
- Cloud-Based Recovery: Leveraging cloud infrastructure for disaster recovery, providing scalability and flexibility. This strategy allows for rapid recovery and potentially reduces the need for physical infrastructure.
- Data Replication: Real-time or near real-time replication of data to a secondary location, minimizing data loss in the event of a primary site failure. This is often integrated with other strategies for enhanced resilience.
Data Backup and Recovery Procedures
Data backup and recovery are fundamental components of TCS’s BCM plan. Regular backups are performed, using a combination of techniques to ensure data integrity and availability. The procedures are meticulously documented and regularly tested to validate their effectiveness.
The process involves:
- Scheduled Backups: Automated backups are performed at regular intervals (daily, weekly, etc.) using various technologies like tape backups, cloud storage, and disk-based solutions. Backup frequency is determined by the criticality of the data.
- Backup Verification: Regular checks are conducted to verify the integrity and accessibility of backups. This includes testing the restoration process to ensure data can be recovered successfully.
- Offsite Storage: Backups are stored offsite in secure locations to protect against physical damage or destruction of the primary site.
- Recovery Procedures: Detailed recovery procedures are documented, outlining the steps required to restore data from backups in the event of a disaster. These procedures are regularly reviewed and updated.
- Data Recovery Testing: Regular testing is performed to validate the effectiveness of the backup and recovery procedures. This ensures that the recovery process functions as intended and that RPOs and RTOs are met.
Restoring Business Operations After a Disruption
The restoration of business operations following a disruption is a phased approach, prioritizing critical functions and ensuring a smooth transition back to normal operations. The process includes:
- Incident Assessment: A thorough assessment of the impact of the disruption, identifying critical systems and processes affected.
- Activation of BCM Plan: The appropriate sections of the BCM plan are activated, outlining the recovery strategies and procedures to be followed.
- Resource Mobilization: Necessary resources, including personnel, equipment, and facilities, are mobilized to support the recovery effort.
- System Restoration: Affected systems are restored using the predefined recovery strategies, prioritizing critical systems based on business impact.
- Data Restoration: Data is restored from backups, ensuring data integrity and consistency.
- Business Process Restoration: Business processes are restored, ensuring continuity of operations.
- Post-Incident Review: A thorough review of the incident, identifying areas for improvement in the BCM plan and procedures.
Testing and Auditing of TCS BCM: Where You Can Find Tcs Process For Business Continuity Management
Regular testing and auditing are crucial for ensuring the effectiveness and readiness of TCS’s Business Continuity Management (BCM) plan. These activities identify weaknesses, validate recovery strategies, and ultimately safeguard business operations during disruptions. A robust testing and auditing program ensures the plan remains relevant and aligned with evolving business needs and technological advancements.
TCS employs a comprehensive approach to testing and auditing its BCM framework, encompassing various methods and frequencies to ensure thorough coverage and continuous improvement. This involves regular testing of recovery strategies, audits of the BCM plan’s effectiveness, and ongoing gap analysis to address any weaknesses identified in the process.
Testing Schedule and Types
TCS’s BCM testing schedule is designed to cover a range of scenarios and components, ensuring comprehensive evaluation of the plan’s effectiveness. The frequency and types of tests are determined based on risk assessments, regulatory requirements, and business criticality.
| Test Type | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Desktop Exercise | Annually for all critical business units; more frequently for high-risk areas | A walkthrough of the BCM plan involving key personnel to identify potential gaps and improve understanding of procedures. |
| Functional Exercise | Every 2-3 years for critical systems and processes | Partial activation of the BCM plan, testing specific recovery procedures and systems. |
| Full-Scale Simulation | Every 3-5 years, or as needed following significant changes | A comprehensive test involving full activation of the BCM plan, simulating a real-world disruption. This allows for a complete end-to-end test of all recovery procedures and systems. |
BCM Plan Audit Process
Auditing the TCS BCM plan involves a systematic review to assess its completeness, accuracy, and effectiveness. The audit process follows a structured methodology, using established checklists and standards.
The audit process typically involves:
- Document Review: Examining the BCM plan documentation for completeness, accuracy, and alignment with organizational policies and standards.
- Interviewing Key Personnel: Gathering feedback from individuals responsible for implementing and maintaining the BCM plan.
- Testing Review: Assessing the results of previous tests and exercises to identify areas for improvement.
- Gap Analysis: Identifying any gaps or weaknesses in the BCM plan based on the findings of the document review, interviews, and testing review.
- Reporting and Remediation: Documenting the audit findings, identifying areas for improvement, and developing a plan to address any identified gaps or weaknesses.
Gap Identification and Remediation
Identifying and addressing gaps or weaknesses in the BCM framework is an ongoing process. TCS utilizes several methods to proactively identify and remediate these issues. These methods include regular reviews of the plan, feedback from testing and exercises, and continuous monitoring of the business environment.
Examples of methods used to identify gaps include:
- Regular Reviews: The BCM plan is reviewed and updated at least annually to ensure it remains current and relevant.
- Post-Incident Reviews: Following any significant incident, a thorough review is conducted to identify areas for improvement in the BCM plan.
- Stakeholder Feedback: Feedback is gathered from stakeholders, including employees, customers, and vendors, to identify potential areas for improvement.
- Technology Updates: The BCM plan is updated to reflect changes in technology and infrastructure.
Remediation involves developing and implementing corrective actions to address identified gaps. This might involve updating the plan, conducting additional training, or implementing new technologies.
Training and Awareness Programs
TCS’s commitment to robust Business Continuity Management (BCM) extends beyond documentation and procedures; it encompasses a comprehensive training and awareness program designed to equip employees at all levels with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively contribute to business resilience. This program ensures consistent understanding and application of BCM principles across the organization, fostering a culture of preparedness and proactive risk mitigation.
TCS employs a multi-faceted approach to training and awareness, leveraging various methods to reach employees across different roles and locations. The program’s effectiveness is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect evolving business needs and technological advancements in the field of BCM.
New Employee Onboarding Training Module
This module introduces new TCS employees to the fundamental concepts of BCM and their role within the company’s overall resilience strategy. The training uses a blended learning approach combining online modules, interactive exercises, and facilitated workshops.
The module begins with an overview of TCS’s BCM policy and its importance in maintaining business operations during disruptions. It then explains the various types of incidents that could impact the organization, ranging from natural disasters to cyberattacks. Key concepts such as risk assessment, business impact analysis, and recovery strategies are introduced using real-world examples relevant to TCS’s operations.
Participants learn about their responsibilities within the BCM framework, including their roles in incident reporting, response, and recovery. They are also introduced to the company’s communication protocols and escalation procedures. The module concludes with a practical exercise simulating a minor incident scenario, allowing participants to apply the knowledge gained and practice their response skills. This practical application reinforces the learning and provides immediate feedback on their understanding. Successful completion of the module is a requirement for all new employees.
Awareness Campaigns and Communication
TCS utilizes various communication channels to raise awareness about BCM amongst its employees. Regular email updates, internal newsletters, and intranet articles keep employees informed about BCM initiatives, updates to procedures, and upcoming training opportunities. These communications highlight the importance of BCM and encourage proactive participation in exercises and training programs. Interactive online modules and quizzes are also utilized to reinforce key concepts and encourage employee engagement. The company also conducts regular awareness campaigns during key periods, such as disaster preparedness weeks, emphasizing specific aspects of BCM relevant to the current season or threat landscape. For example, during hurricane season, communications might focus on disaster preparedness plans and emergency contact procedures. These targeted campaigns ensure that BCM remains top-of-mind and that employees are equipped with the knowledge to respond effectively to specific threats.
Advanced BCM Training for Specific Roles
Beyond the new employee onboarding module, TCS offers advanced training programs tailored to specific roles and responsibilities within the BCM framework. These programs delve deeper into specific areas, such as incident management, recovery strategy development, and business impact analysis. For instance, employees responsible for data recovery receive specialized training on data backup and restoration procedures, while those involved in crisis communication undergo training on effective communication strategies during critical incidents. This specialized training ensures that employees have the advanced skills and knowledge needed to perform their roles effectively during a business disruption. Regular refresher courses are provided to keep employees updated on the latest best practices and technological advancements in BCM.
Technological Aspects of TCS BCM
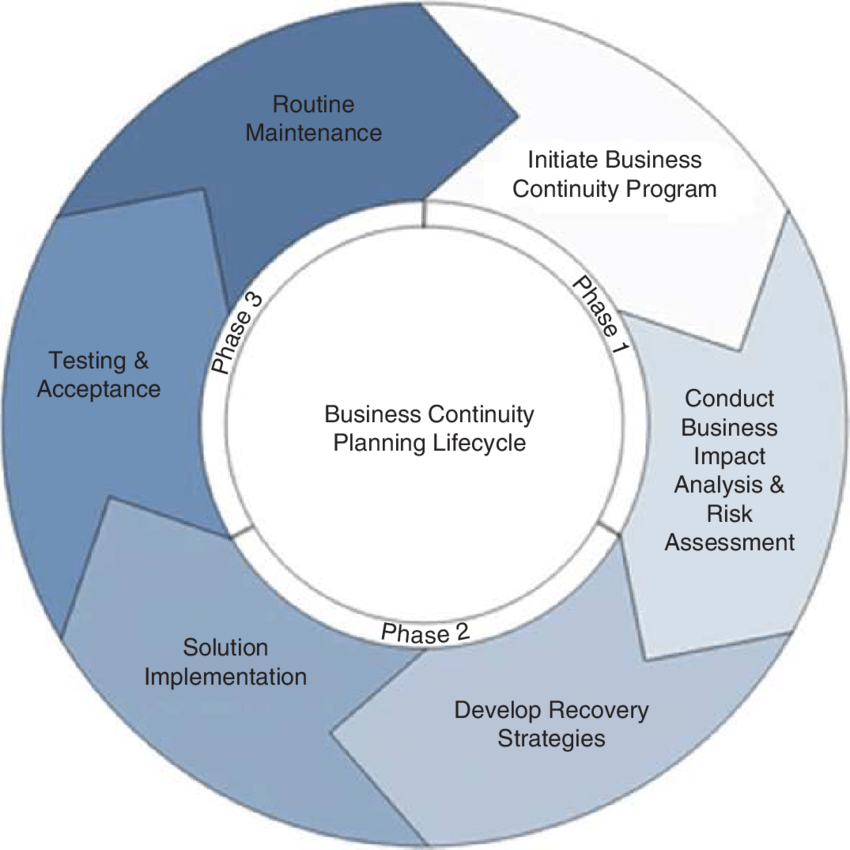
Technology plays a crucial role in enabling and enhancing TCS’s Business Continuity Management (BCM) capabilities, providing the infrastructure and tools necessary for effective response and recovery from disruptive events. A robust technological foundation is essential for monitoring, managing, and mitigating risks, ensuring the seamless continuation of critical business operations.
The effective implementation of TCS’s BCM strategy relies heavily on a sophisticated technological ecosystem. This encompasses various software and hardware solutions designed to facilitate communication, data backup and recovery, remote access, and real-time monitoring of critical systems. The selection and implementation of these technologies are guided by a risk assessment that considers the potential impact of various disruptions on different business units.
Data Backup and Recovery Systems
TCS employs advanced data backup and recovery systems, including both on-site and off-site storage solutions. These systems ensure data redundancy and accessibility even in the event of a major disruption such as a natural disaster or cyberattack. Regular data backups are scheduled and rigorously tested to ensure their integrity and recoverability. The systems incorporate features like data deduplication and compression to optimize storage space and bandwidth utilization. Recovery procedures are well-defined and regularly practiced to minimize downtime during restoration. Specific technologies employed might include enterprise-grade backup software, cloud-based storage solutions, and tape libraries for long-term archival.
Communication and Collaboration Platforms, Where you can find tcs process for business continuity management
Effective communication is paramount during a business disruption. TCS utilizes a range of communication and collaboration platforms to ensure seamless information flow among employees, clients, and stakeholders. These platforms include secure messaging systems, video conferencing tools, and collaborative workspaces that allow teams to continue working effectively even when geographically dispersed. These technologies enable rapid dissemination of critical information, coordination of recovery efforts, and maintenance of business operations. Examples of such platforms include secure internal messaging systems, video conferencing software, and project management tools integrated with disaster recovery plans.
Monitoring and Alerting Systems
TCS utilizes sophisticated monitoring and alerting systems to proactively identify and respond to potential threats and disruptions. These systems continuously monitor critical infrastructure, applications, and services, generating alerts in case of anomalies or performance degradation. This proactive approach enables early detection of potential problems, allowing for timely intervention and mitigation of their impact. The systems integrate various monitoring tools, including network monitoring software, application performance management (APM) tools, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems, providing a comprehensive view of the IT landscape.
Remote Access and Virtualization Technologies
TCS leverages remote access and virtualization technologies to ensure business continuity by enabling employees to access critical systems and data remotely. This capability is crucial during disruptions that prevent employees from accessing their physical workplaces. Virtualization technologies allow for rapid provisioning of resources and enable failover to backup systems, minimizing downtime. Specific technologies used might include virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) solutions, secure remote access gateways, and cloud-based virtual machines.
Cybersecurity Measures
Robust cybersecurity measures are integral to TCS’s BCM strategy. These measures include intrusion detection and prevention systems, data encryption, and regular security audits to protect against cyber threats that could disrupt business operations. The organization utilizes multi-factor authentication, access control lists, and regular security awareness training to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. The implementation of these measures is regularly reviewed and updated to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
TCS’s Business Continuity Management (BCM) framework is designed to ensure compliance with a wide range of legal and regulatory requirements, industry standards, and best practices. This commitment to compliance is integral to maintaining operational resilience and protecting the company’s reputation and client relationships. The framework proactively addresses potential legal liabilities and minimizes disruption caused by unforeseen events.
The process for ensuring compliance involves a multi-faceted approach that incorporates ongoing monitoring, regular audits, and continuous improvement initiatives. This includes the development and implementation of policies and procedures that are aligned with relevant legislation and regulatory frameworks, as well as industry-recognized best practices. Furthermore, TCS employs a system of regular reviews and updates to its BCM framework to reflect evolving legal landscapes and technological advancements.
Legal and Regulatory Requirements Addressed by TCS BCM
TCS’s BCM framework addresses a wide spectrum of legal and regulatory requirements, varying depending on the specific industry sector, geographic location, and the nature of TCS’s operations. Examples include data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, financial regulations such as those governing banking and financial services, and industry-specific compliance standards related to healthcare or telecommunications. The framework ensures that business continuity plans account for the specific legal and regulatory obligations relevant to each business unit and client engagement. This is achieved through a rigorous process of risk assessment and impact analysis that identifies potential legal ramifications of disruptions and incorporates appropriate mitigation strategies into the BCM plans. For example, data backup and recovery procedures are designed to meet the stringent requirements of data privacy regulations, ensuring business continuity while maintaining data security and integrity.
Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards and Best Practices
TCS leverages industry-recognized standards and best practices to guide the development and implementation of its BCM framework. These include frameworks such as ISO 22301 (Business Continuity Management Systems), NIST Cybersecurity Framework, and ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library). Adherence to these standards provides a structured approach to BCM, ensuring a consistent and comprehensive system across the organization. Regular audits and reviews are conducted to assess compliance with these standards and identify areas for improvement. The framework also incorporates industry best practices related to crisis management, communication, and stakeholder engagement, ensuring a coordinated and effective response to disruptive events. This commitment to best practices ensures that TCS’s BCM framework remains robust, adaptable, and effective in mitigating risks and ensuring business continuity.
Key Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Business Continuity Planning
Several key legal and regulatory considerations are paramount in developing effective business continuity plans. These include data protection and privacy laws, which mandate the secure storage, processing, and transmission of sensitive information. Compliance with these laws is critical, as data breaches can result in significant financial penalties and reputational damage. Furthermore, regulatory requirements related to financial reporting and disclosure demand that organizations maintain accurate and reliable financial records, even during disruptive events. Failure to comply can lead to legal sanctions and financial losses. Finally, industry-specific regulations, such as those governing healthcare or financial services, impose specific requirements on business continuity planning, emphasizing the need for tailored approaches to address sector-specific risks and vulnerabilities. TCS’s BCM framework addresses these considerations by integrating them into the risk assessment process and incorporating specific procedures to ensure compliance. For instance, data backup and recovery procedures are designed to meet data privacy requirements, while financial reporting procedures ensure the continued accuracy and availability of financial information during a disruption.






