How do businesses help a country’s economy? This question lies at the heart of understanding national prosperity. Businesses aren’t just profit-making entities; they are the engines of economic growth, driving job creation, innovation, and overall societal well-being. From small local shops to multinational corporations, every business plays a vital role, contributing in ways both direct and indirect to the financial health of a nation. This exploration delves into the multifaceted ways businesses power economic advancement, revealing the intricate connections between private enterprise and national success.
The following sections detail how businesses contribute to a nation’s economy through job creation, tax revenue generation, technological advancements, investment, international trade, consumer spending, and community development. We’ll examine the impact of various business sizes and sectors, illustrating the significant role businesses play in shaping a nation’s economic landscape and future.
Job Creation and Employment
Businesses are fundamental drivers of economic growth, and their contribution extends significantly to job creation and overall employment levels within a nation. The impact varies across sectors and business sizes, with ripple effects felt throughout the economy. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for policymakers aiming to stimulate employment and reduce unemployment.
Businesses generate employment opportunities both directly and indirectly. Direct employment refers to jobs created within the business itself, such as hiring employees to manufacture products, provide services, or manage operations. Indirect employment encompasses jobs created in related industries or sectors as a result of the primary business’s activities. For example, a new manufacturing plant (direct employment for factory workers) will also create demand for transportation services, raw materials suppliers, and local businesses catering to the plant’s employees (indirect employment).
Direct and Indirect Job Creation Across Sectors
The creation of jobs varies significantly across different business sectors. In the manufacturing sector, a car manufacturer directly employs assembly line workers, engineers, and managers. Indirectly, it creates jobs in parts suppliers, logistics companies, and dealerships. The service sector, encompassing restaurants, hotels, and healthcare, directly employs waitstaff, chefs, nurses, and doctors, while indirectly supporting jobs in food production, cleaning services, and pharmaceutical companies. The technology sector, with its software developers and engineers, directly creates high-skilled jobs, and indirectly supports roles in marketing, sales, and customer service. The agricultural sector, while often employing fewer people directly compared to other sectors, still provides jobs for farmers, agricultural workers, and those involved in processing and distribution. The impact of each sector on employment is complex and interdependent.
The Role of SMEs in National Employment
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are particularly crucial for national employment rates. They are often more flexible and adaptable than larger corporations, enabling them to quickly respond to changing market demands and create jobs in niche areas. Their contribution is substantial, even exceeding that of larger firms in many countries.
| Business Size | Sector | Job Creation Method | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| SME | Retail | Direct employment of sales staff, managers; indirect employment in supply chain and logistics. | Increased consumer spending, local economic growth. |
| SME | Construction | Direct employment of builders, contractors, laborers; indirect employment in material supply and transportation. | Infrastructure development, regional economic stimulus. |
| Large Corporation | Manufacturing | Direct employment of factory workers, engineers, managers; indirect employment in supporting industries. | Mass production, export opportunities, potential for significant job creation but also susceptibility to automation. |
| SME | Technology | Direct employment of software developers, designers; indirect employment in marketing and customer support. | Innovation, high-skilled job creation, potential for rapid growth and significant economic impact. |
Hypothetical Scenario: Positive Impact of a New Business Venture
Imagine a new tech startup focusing on renewable energy solutions is established in a rural region with high unemployment. This startup directly hires engineers, software developers, and marketing personnel. Indirectly, it creates jobs in local construction firms building the startup’s facilities, transportation companies delivering equipment, and restaurants and cafes serving the employees. Increased local spending by employees stimulates further job creation in the retail and service sectors. Over time, the startup’s success attracts other businesses to the region, creating a positive feedback loop and significantly reducing the region’s unemployment rate, transforming the local economy. This illustrates how a single, innovative business can generate a substantial positive impact on a region’s employment landscape.
Tax Revenue Generation

Businesses are vital contributors to a nation’s tax revenue, forming a cornerstone of government funding for public services and infrastructure. The type and level of taxation significantly impact business decisions, influencing investment, hiring practices, and overall economic activity. Understanding this complex interplay is crucial for policymakers aiming to foster economic growth while ensuring equitable revenue generation.
Different tax systems influence business behavior and subsequent government revenue in various ways. For instance, a high corporate tax rate might incentivize businesses to shift profits to lower-tax jurisdictions, reducing the overall tax revenue collected by the high-tax country. Conversely, a simpler, more transparent tax system can encourage compliance and increase revenue collection. A value-added tax (VAT), for example, can be more efficient in collecting revenue compared to a reliance on corporate income tax alone, as it captures revenue at each stage of the production and distribution process. Conversely, a heavily regressive tax system, disproportionately affecting low-income earners, could stifle consumer spending and hinder overall economic growth, indirectly impacting business revenue and subsequent tax contributions.
Tax Contributions of Multinational Corporations Versus Small Businesses
The tax contributions of multinational corporations (MNCs) and small businesses differ significantly due to variations in size, structure, and tax planning capabilities. MNCs, with their complex global operations and access to sophisticated tax advisory services, often leverage international tax laws and regulations to minimize their tax liabilities. Small businesses, on the other hand, generally have simpler structures and fewer resources dedicated to tax optimization, leading to potentially higher effective tax rates.
| Tax Type | MNC Tax Rate (Example) | Small Business Tax Rate (Example) | Potential Economic Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corporate Income Tax | 15% (after aggressive tax planning) | 25% (standard rate) | MNCs may invest less domestically due to lower effective tax rates; Small businesses might face higher compliance costs and reduced profitability. |
| VAT/Sales Tax | Standard rate (e.g., 20%) | Standard rate (e.g., 20%) | Both contribute equally, though MNCs may have greater ability to offset input VAT. |
| Payroll Tax | Significant contributions, depending on employee numbers and wages | Lower contributions, generally correlated with fewer employees and lower wages | MNCs contribute substantially to employment-related taxes, while small businesses’ contributions are proportionately smaller. |
Note: These rates are illustrative examples and vary significantly across countries and jurisdictions. Effective tax rates can differ substantially from statutory rates due to deductions, credits, and other tax planning strategies.
The Role of Tax Incentives in Attracting Businesses and Boosting Economic Activity
Tax incentives, such as tax breaks, deductions, and credits, are frequently used by governments to attract businesses and stimulate economic activity within specific regions or sectors. These incentives can take various forms, including reduced corporate tax rates for businesses investing in specific industries (e.g., renewable energy), tax credits for research and development, or tax exemptions for businesses creating new jobs in designated areas. For example, a government might offer a tax holiday for new businesses setting up operations in a depressed economic area to stimulate job creation and local investment. Effectively designed tax incentives can lead to increased investment, job creation, and economic growth. However, poorly designed incentives can lead to inefficiencies, distort markets, and may not always result in the desired economic outcomes. A critical assessment of the costs and benefits of any tax incentive program is essential to ensure its effectiveness.
Innovation and Technological Advancement

Businesses are crucial drivers of innovation and technological advancement, contributing significantly to a nation’s economic growth. Their investment in research and development, coupled with the commercialization of new technologies, fuels productivity gains, creates new industries, and enhances global competitiveness. This section explores the key roles businesses play in this process.
Businesses spearhead technological innovation across various sectors, leading to substantial economic benefits. This innovation manifests in the development of new products, processes, and services, which in turn stimulate economic growth. The resulting increased efficiency, improved quality, and creation of new markets generate wealth and improve living standards.
Key Industries Driving Technological Innovation
The technology sector itself, encompassing software development, hardware manufacturing, and telecommunications, is a primary driver of innovation. However, technological advancements are not limited to this sector. The pharmaceutical industry, for instance, continuously invests in research and development, leading to the creation of life-saving drugs and treatments. The automotive industry is also a key player, constantly innovating with electric vehicles, autonomous driving systems, and advanced safety features. These advancements not only improve the quality of life but also generate substantial economic activity through job creation and export opportunities. Furthermore, the renewable energy sector is experiencing rapid innovation, with businesses developing more efficient and cost-effective solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage solutions. This innovation is crucial for addressing climate change and ensuring long-term economic sustainability.
Research and Development Spending and National Competitiveness
A strong correlation exists between a nation’s research and development (R&D) spending and its global competitiveness. Businesses that invest heavily in R&D are better positioned to develop cutting-edge technologies, improve existing products and services, and gain a competitive advantage in the global marketplace. This investment leads to increased productivity, higher profitability, and the creation of high-value jobs. Conversely, nations with low levels of business R&D spending often lag behind in technological advancement and struggle to compete in the global economy. Government policies that incentivize business R&D, such as tax breaks and grants, can significantly boost national competitiveness. For example, countries like South Korea and Israel have implemented successful policies to encourage R&D investment, resulting in strong economic growth and technological leadership in specific sectors.
Examples of Successful Commercialization of Innovative Technologies
Apple’s introduction of the iPhone revolutionized the mobile phone industry, creating a massive new market and generating substantial economic activity. The development and commercialization of the iPhone spurred innovation in related industries, such as app development and mobile content creation, further boosting economic growth. Similarly, the development and widespread adoption of the internet and related technologies have transformed numerous industries and significantly impacted global economic growth. The rise of e-commerce, for example, has created new business models and opportunities, while the development of social media platforms has revolutionized communication and marketing. Tesla’s success in commercializing electric vehicles and battery technology has not only disrupted the automotive industry but also stimulated innovation in related fields, such as renewable energy and battery storage. These examples illustrate the significant economic impact of successful technology commercialization.
Investment and Capital Formation
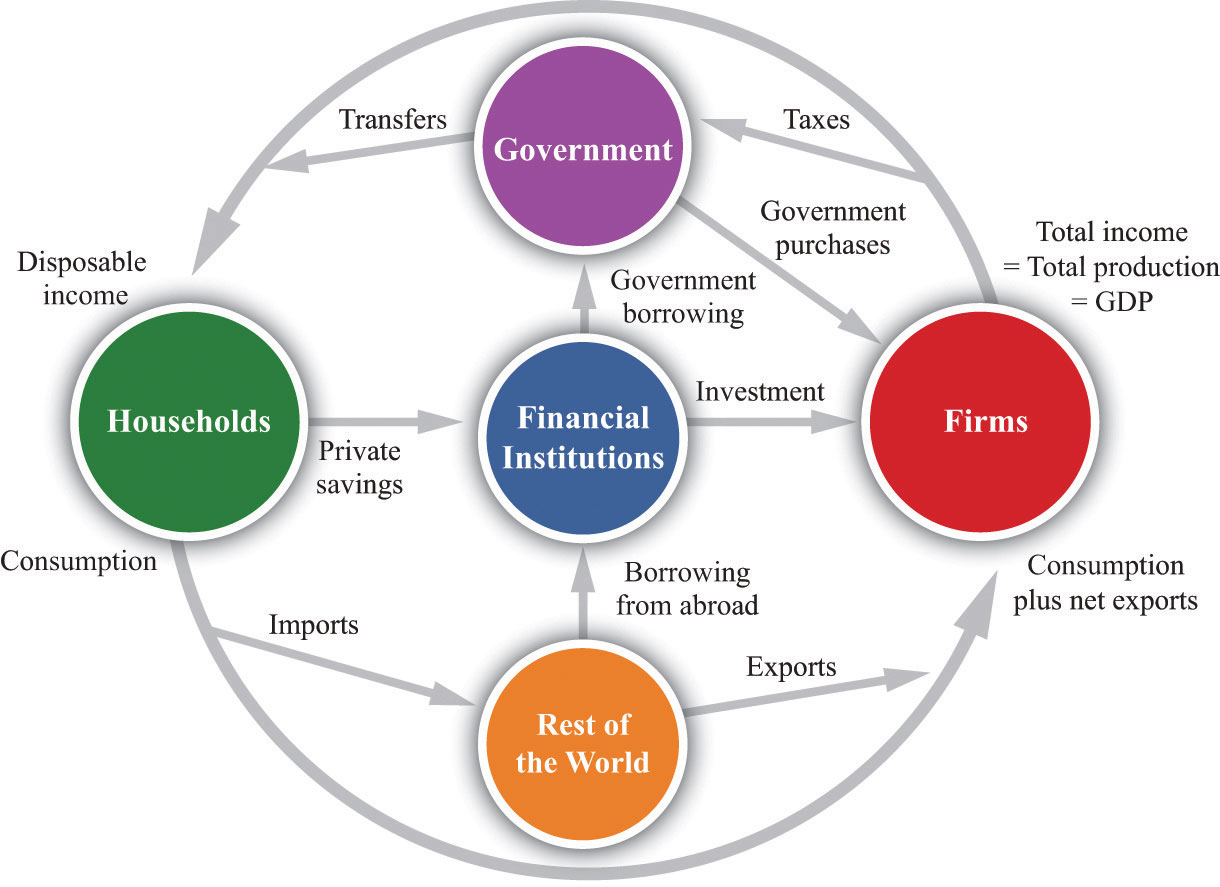
Business investment is a cornerstone of economic expansion, fueling growth and improving a nation’s overall standard of living. This investment, encompassing infrastructure development, acquisition of equipment, and technological advancements, directly contributes to increased productivity and competitiveness. A robust investment climate attracts both domestic and foreign capital, creating a virtuous cycle of economic development.
Businesses invest in infrastructure to improve the efficiency of their operations and access wider markets. This can include investments in transportation networks (roads, railways, ports), communication systems (internet infrastructure, telecommunications), and energy grids. Improved infrastructure reduces transportation costs, enhances communication, and ensures reliable energy supply, thereby boosting productivity and attracting further investment. For example, the construction of high-speed rail lines can significantly reduce travel time and transportation costs for businesses, facilitating trade and economic activity across wider geographical areas. Investment in equipment, such as machinery and technology, increases productivity and efficiency. Modern, efficient equipment allows businesses to produce more goods and services with fewer resources, leading to higher output and lower costs. This, in turn, enhances competitiveness and profitability, stimulating further investment. For instance, a factory investing in automated production lines can significantly increase its output while reducing labor costs. Technological advancements are critical for long-term economic growth. Businesses invest in research and development (R&D), software, and other technologies to improve their products, processes, and services. This leads to innovation, increased efficiency, and the creation of new markets, fostering economic dynamism and competitiveness. The development and adoption of cloud computing, for example, has revolutionized numerous industries, enabling businesses to operate more efficiently and reach wider audiences.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and its Impact
Foreign direct investment (FDI) significantly influences a nation’s economic growth. It involves the investment made by a company or individual in a foreign country to gain control or influence over an existing business or to create a new business. While FDI offers numerous benefits, it also presents potential drawbacks.
Positive impacts of FDI include increased capital inflow, technological transfer, job creation, and enhanced managerial expertise. Increased capital inflow boosts investment levels, expanding productive capacity and stimulating economic growth. FDI often involves the transfer of advanced technologies and managerial skills, upgrading domestic industries and enhancing productivity. The creation of new jobs and the training of local workforce further contributes to economic development. For example, the establishment of a multinational manufacturing plant in a developing country can bring in significant capital investment, create numerous jobs, and introduce advanced manufacturing techniques.
However, FDI can also lead to negative consequences. Potential downsides include increased economic dependence on foreign companies, potential exploitation of local resources, and possible negative impacts on domestic industries. Over-reliance on foreign investment can make a country vulnerable to global economic fluctuations. Concerns about environmental degradation or unfair labor practices associated with FDI projects can also arise. For instance, a foreign company might exploit cheap labor or deplete natural resources without adequate compensation or environmental protection measures.
Comparative Analysis of Business Investment Strategies
Businesses employ diverse investment strategies, each with its own risk-reward profile. Understanding these strategies is crucial for both businesses and policymakers.
| Investment Strategy | Potential Rewards | Potential Risks | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Growth | Increased market share, enhanced brand recognition, improved profitability through internal expansion. | Slower growth rate, limited access to new technologies or markets, increased financial strain during expansion. | A bakery expanding by opening new stores using its own capital and resources. |
| Mergers and Acquisitions | Rapid market expansion, access to new technologies and markets, elimination of competition. | High initial investment costs, integration challenges, potential for cultural clashes and conflicts. | A large pharmaceutical company acquiring a smaller biotech firm to gain access to its innovative drug pipeline. |
| Joint Ventures | Shared risks and resources, access to local expertise and markets, faster market entry. | Potential conflicts between partners, loss of control over certain aspects of the business, difficulties in coordinating operations. | Two car manufacturers collaborating to develop and produce a new electric vehicle model. |
| Franchise | Rapid expansion with lower risk, established brand recognition, passive income stream. | Limited control over individual franchisees, franchise fees and royalties, potential reputational damage from poorly performing franchises. | A fast-food chain expanding its network through franchising agreements. |
International Trade and Exports: How Do Businesses Help A Country’s Economy
Businesses are pivotal in driving a nation’s economic growth through international trade and exports. Their involvement extends beyond simply selling goods abroad; it encompasses strategic planning, logistical management, and navigating international regulations – all contributing significantly to a country’s balance of trade and overall economic health. Successful export strategies not only generate revenue but also foster innovation, create jobs, and enhance a nation’s global competitiveness.
Businesses play a direct role in exporting goods and services, acting as the primary agents responsible for transferring domestically produced products and services to international markets. This activity directly impacts a nation’s balance of trade, the difference between the value of its exports and imports. A positive balance of trade, where exports exceed imports, signifies a strong national economy, indicating robust domestic production and international demand. Conversely, a negative balance necessitates careful examination of import-export strategies and economic policies.
The Role of Businesses in Exporting Goods and Services and Their Contribution to the Balance of Trade
Exporting goods and services contributes directly to a nation’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by adding to national income. Businesses actively seek out foreign markets, adapting their products and services to meet the specific needs and preferences of international consumers. This process involves market research, product development, logistical planning, and managing international transactions, all of which stimulate economic activity within the country. Successful exporting creates jobs, both directly within the exporting businesses and indirectly in supporting industries such as logistics and transportation. Moreover, increased export revenue strengthens the national currency and improves the country’s overall balance of payments. For instance, a country heavily reliant on exporting agricultural products will experience economic benefits directly tied to global demand and prices for those products. Fluctuations in global demand will directly impact the exporting businesses, their employees, and the national economy.
Impact of Global Trade Agreements on Businesses and the National Economy
Global trade agreements, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) agreements or bilateral trade deals, significantly impact businesses and national economies. These agreements typically reduce or eliminate tariffs and other trade barriers, facilitating increased trade volumes. For businesses, this translates into expanded market access, potentially leading to increased sales and profits. The reduced trade barriers also encourage competition, driving innovation and efficiency improvements. On a national level, trade agreements can lead to economic growth by boosting exports, attracting foreign investment, and increasing consumer choice. However, trade agreements can also present challenges. Businesses may face increased competition from foreign companies, necessitating adaptation and innovation to remain competitive. Some sectors of the national economy might experience job losses due to increased imports, requiring government intervention such as retraining programs or support for affected industries.
Case Study: Export Success Boosting a Country’s Economic Standing
Consider “TechNova,” a fictional small technology company in the country of “Atheria.” TechNova specializes in developing and manufacturing advanced agricultural sensors. Their export strategy focused on targeting developing nations with a significant agricultural sector but lacking advanced technology. TechNova invested in building strong relationships with distributors in these target markets, offering customized training and technical support. Their innovative sensors increased crop yields, reducing waste and improving farming efficiency. As a result, TechNova’s exports increased dramatically, generating significant revenue for the company and contributing substantially to Atheria’s export earnings. This success led to job creation within TechNova, as well as in supporting industries like logistics and transportation. Increased tax revenue from TechNova’s profits also benefitted Atheria’s government, which in turn could be reinvested in infrastructure or other public services. The improved balance of trade strengthened Atheria’s currency and boosted its international reputation as a hub for technological innovation in the agricultural sector. This positive feedback loop showcased how a single business’s export success can significantly impact a nation’s overall economic standing.
Consumer Spending and Market Growth
Businesses are the lifeblood of a thriving consumer market. Their activities, from product conception to marketing and pricing, directly influence consumer spending, a key driver of economic growth. A strong relationship exists between business dynamism and consumer confidence, creating a positive feedback loop that fuels economic expansion.
Businesses stimulate consumer spending primarily through product development, marketing, and pricing strategies. Product development focuses on creating goods and services that meet evolving consumer needs and desires. This might involve improving existing products, introducing innovative features, or developing entirely new offerings. Effective marketing campaigns build brand awareness, highlight product benefits, and persuade consumers to make purchases. Pricing strategies, including discounts, promotions, and loyalty programs, incentivize consumer spending and manage demand.
The Influence of Product Development on Consumer Spending
Effective product development directly impacts consumer spending. Companies invest heavily in research and development to understand consumer preferences and create products that address unmet needs. For instance, the development of smartphones dramatically altered consumer behavior, leading to increased spending on mobile apps, data plans, and related accessories. Similarly, the evolution of streaming services has shifted entertainment consumption and increased spending on subscription-based content. Successful product development often creates entirely new markets and consumer spending patterns.
The Role of Marketing and Pricing in Driving Consumer Spending
Marketing plays a crucial role in influencing consumer perceptions and driving purchase decisions. Effective marketing campaigns, leveraging various channels like digital advertising, social media, and traditional media, build brand loyalty and create demand for products. Pricing strategies are equally important. Competitive pricing, coupled with promotions and discounts, can significantly boost sales volume and consumer spending. Conversely, premium pricing, often associated with luxury brands, relies on creating a perception of exclusivity and high value to justify higher prices.
Consumer Confidence and its Impact on Business Activity, How do businesses help a country’s economy
Consumer confidence, a measure of consumers’ optimism about the economy and their personal financial situation, significantly impacts business activity and overall economic growth. High consumer confidence leads to increased spending, boosting demand for goods and services. Businesses respond by increasing production, hiring more employees, and investing in expansion. Conversely, low consumer confidence results in decreased spending, forcing businesses to cut back on production, reduce employment, and postpone investments. This illustrates the direct correlation between consumer sentiment and business performance.
Examples of Businesses Influencing Consumer Behavior and Market Trends
Apple’s consistent innovation in consumer electronics has significantly shaped consumer behavior and market trends. The introduction of the iPod, iPhone, and iPad created entirely new markets and profoundly impacted how people consume media, communicate, and access information. Similarly, Amazon’s dominance in e-commerce has revolutionized retail, influencing consumer shopping habits and expectations regarding convenience, speed, and selection. These examples demonstrate how businesses, through innovative products and effective marketing, can not only drive consumer spending but also shape long-term market trends.
Community Development and Social Responsibility
Businesses play a crucial role in fostering community development and improving the overall well-being of society. Beyond their primary economic functions, companies increasingly recognize the importance of contributing to the social fabric of the communities in which they operate, leading to a symbiotic relationship where both the business and the community thrive. This contribution manifests through various avenues, including philanthropic activities, social initiatives, and the broader adoption of corporate social responsibility (CSR) principles.
Businesses contribute significantly to local community development through a range of philanthropic activities and social initiatives. These contributions often involve direct financial support for local charities, schools, and community centers, as well as in-kind donations of goods and services. Many businesses also sponsor local events and programs, fostering a sense of community pride and engagement. Furthermore, employee volunteer programs allow businesses to leverage their workforce’s skills and time to support local causes, strengthening the bond between the company and the community. For instance, a tech company might volunteer to provide digital literacy training to underprivileged youth, while a food manufacturer might donate surplus food to local food banks. Such actions not only benefit the community directly but also enhance the company’s image and build strong relationships with local stakeholders.
Corporate Social Responsibility and its Impact
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) encompasses a company’s commitment to operating ethically and sustainably, considering its impact on all stakeholders—employees, customers, communities, and the environment. Implementing effective CSR strategies demonstrates a business’s commitment to ethical conduct, environmental protection, and social justice. This commitment significantly impacts a business’s reputation, attracting customers who value ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. Studies have shown a positive correlation between strong CSR performance and improved financial performance, indicating that ethical and socially responsible businesses can attract investors and customers who are willing to pay a premium for their products and services. For example, companies with strong CSR profiles often experience increased brand loyalty, improved employee morale, and enhanced access to capital. Conversely, neglecting CSR can lead to reputational damage, boycotts, and ultimately, financial losses.
A Community Development Program Example
A hypothetical program designed to contribute to the social and economic well-being of a specific community, say, a low-income neighborhood facing high unemployment, could focus on skill development and job creation. The program might consist of three key components: (1) A vocational training program offering courses in high-demand skills such as coding, welding, or healthcare assistance. This would equip residents with the skills needed to secure better employment opportunities. (2) A job placement service connecting graduates of the training program with local businesses seeking employees. This ensures the program’s effectiveness in reducing unemployment. (3) Mentorship and entrepreneurial support, providing guidance and resources to residents interested in starting their own businesses. This would foster self-reliance and stimulate local economic activity. The program would also involve partnerships with local organizations, schools, and government agencies to maximize its impact and ensure sustainability. Successful implementation would require ongoing evaluation and adaptation to ensure it continues to meet the community’s evolving needs. The program’s success would be measured by factors such as the number of participants who complete the training, the employment rate among graduates, and the number of new businesses launched.






