How to give access to google my business account – How to give access to your Google My Business account is crucial for effective team management and efficient business operations. This guide unravels the intricacies of managing user permissions, offering a comprehensive walkthrough of adding, modifying, and removing user access. We’ll explore the different user roles, their associated permissions, and the best practices for securing your GMB account. Mastering these techniques ensures seamless collaboration and protects your business information.
From understanding the nuances of Owner, Manager, and Analyst roles to troubleshooting common access issues, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to navigate the Google My Business interface confidently. We’ll also cover managing access for multi-location businesses and implementing robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access. This guide serves as your complete resource for efficiently managing your GMB account’s user access.
Understanding Google My Business Account Roles and Permissions: How To Give Access To Google My Business Account
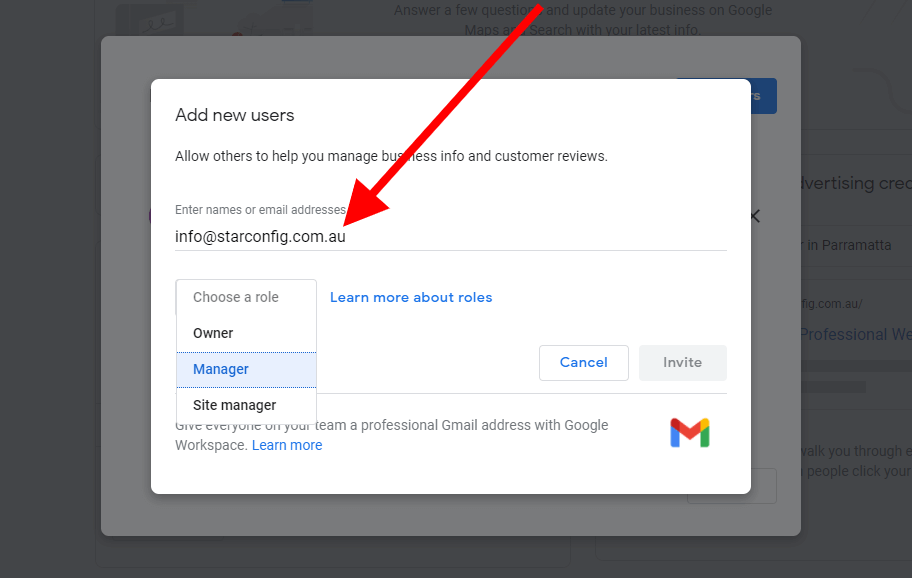
Effective management of your Google My Business (GMB) profile requires a clear understanding of user roles and their associated permissions. Assigning the correct roles ensures that each team member has the necessary access to contribute effectively while maintaining the security and integrity of your business information. This section details the different roles, their permissions, and the process of adding new users.
Google My Business User Roles
Google My Business offers three primary user roles: Owner, Manager, and Analyst. Each role grants distinct levels of access and control over the GMB profile. Understanding these differences is crucial for efficient team collaboration and secure account management. Improperly assigning roles can lead to unintended consequences, such as unauthorized edits or accidental deletion of important information.
Permissions Associated with Each Role
The Owner role holds the highest level of authority within a GMB account. Owners have complete control over all aspects of the profile, including adding and removing other users, making changes to business information, and managing all aspects of the listing. Managers possess significant control, enabling them to make most changes to the business profile, but they cannot add or remove other users. Analysts have the most limited access, primarily focused on viewing data and generating reports; they cannot make changes to the business information.
Adding a New User to a Google My Business Account
Adding a new user to your GMB account is a straightforward process. First, log in to your Google My Business account. Then, navigate to the “Manage users” section, typically found within the account settings. Next, click the “Add user” button. You will be prompted to enter the email address of the person you want to add. Finally, select the appropriate user role (Owner, Manager, or Analyst) and click “Invite.” The invited user will receive an email notification and will need to accept the invitation before gaining access.
Comparison of User Role Capabilities
| Role | Add/Remove Users | Edit Business Information | View Reports & Analytics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Owner | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Manager | No | Yes | Yes |
| Analyst | No | No | Yes |
Methods for Granting Access
Managing user access to your Google My Business (GMB) account is crucial for maintaining control and ensuring your business information is updated accurately. This section details the various methods for granting, managing, and revoking access, ensuring a smooth workflow for your team. Understanding these processes is key to effective GMB management.
Inviting Users via Email
Adding new users to your GMB account is straightforward through the platform’s built-in invitation system. This method uses email addresses to identify and grant permissions to specific individuals. The process involves navigating to the user management section within your GMB dashboard, entering the email address of the intended user, and selecting the appropriate permission level. Once the invitation is sent, the recipient will receive an email containing a link to accept the invitation and gain access to the account. This ensures a secure and controlled method for onboarding new team members.
Managing Existing User Permissions
After inviting users, you can adjust their permission levels as needed. This allows you to control which actions each user can perform within your GMB profile. For example, you might grant one user full administrative access, while another user only has permission to update posts. This granular control ensures that sensitive information remains protected while empowering team members to perform their designated tasks. To manage permissions, locate the user in the user management section and select their assigned role. You can then modify their permissions to reflect their current responsibilities.
Alternative Access Management When the Primary Account Owner is Unavailable
Situations may arise where the primary account owner is temporarily unavailable. In such cases, it’s crucial to have a designated alternate user with sufficient permissions to manage the account. This can prevent disruptions to your business’s online presence. Beforehand, designate a secondary user with administrative privileges. This ensures that critical tasks, such as responding to reviews or updating business information, can still be performed. Consider adding multiple users with administrative access as a further safeguard against potential account access issues. Regularly review and update these designated users to reflect changes in your team’s structure.
Revoking User Access
It’s essential to have a clear process for removing users from your GMB account when necessary. This might be due to employee departures, security concerns, or changes in team responsibilities. Following these steps ensures a smooth and secure removal process.
- Log in to your Google My Business account.
- Navigate to the “Users” or “Manage users” section within the settings.
- Locate the user whose access you want to revoke.
- Select the user’s entry to access their profile and permission settings.
- Select the option to remove or delete the user from your GMB account.
- Confirm the removal to finalize the process.
Troubleshooting Access Issues
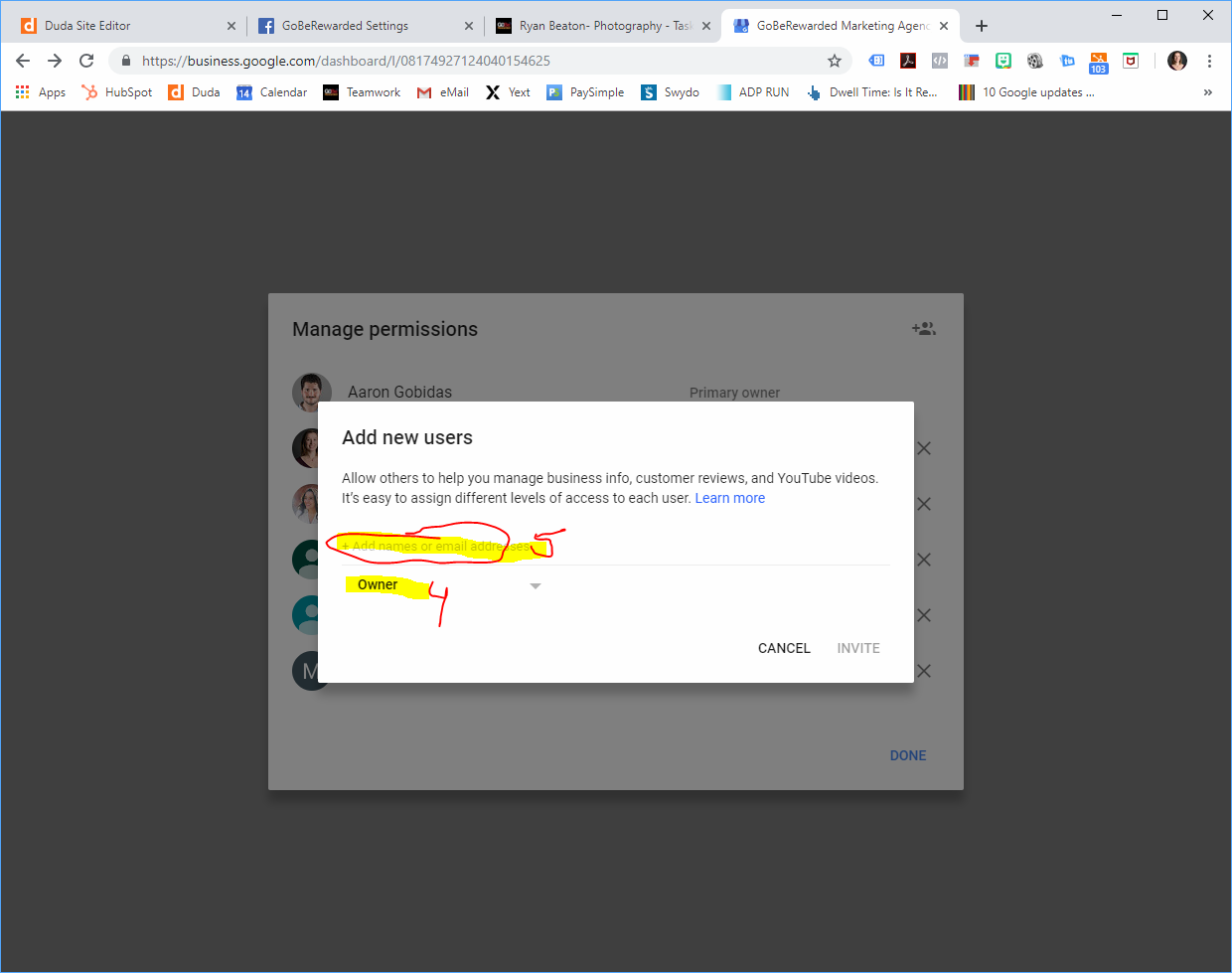
Gaining seamless access to your Google My Business (GMB) account is crucial for managing your online presence. However, various issues can prevent you from logging in or making necessary changes. This section details common problems and their solutions, enabling you to swiftly resolve access-related challenges and maintain control over your business profile.
Login Issues
Troubleshooting login problems involves systematically checking common culprits. Incorrect passwords, typos in email addresses, and browser-related issues are frequent causes of failed login attempts. Furthermore, account suspension due to policy violations or security concerns can also prevent access.
- Incorrect Password: If you’ve forgotten your password, use the “Forgot password” option on the Google login page. Google will guide you through resetting it via email or phone verification.
- Incorrect Email Address: Double-check the email address associated with your GMB account. A simple typo can prevent login. Try logging in using the email address used to create the GMB profile.
- Browser Issues: Clear your browser’s cache and cookies. Try logging in using a different browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari) to rule out browser-specific problems. Disable any browser extensions that might interfere with Google’s authentication process.
- Account Suspension: If you suspect your account is suspended, check for any notification emails from Google regarding policy violations. Address the issue highlighted in the email and contact Google My Business support for assistance. Examples of policy violations include inaccurate business information or engaging in prohibited activities.
Permission Errors
Permission errors arise when a user lacks the necessary authorization to access or modify specific aspects of the GMB account. This often occurs when attempting to manage aspects of the business profile for which a user hasn’t been granted the correct permissions.
- Insufficient Permissions: The error message might indicate that the user lacks the required permissions to perform the requested action. For example, an employee might not be able to post updates if they only have “viewer” access. The account owner needs to adjust user permissions within the GMB settings.
- Role Mismatch: Verify that the user’s assigned role (e.g., owner, manager, analyst) aligns with the actions they’re trying to perform. The owner role grants complete access, while other roles have more restricted permissions. If a user needs broader access, the owner must adjust their role within the GMB account settings.
- Example Error Message: “You do not have permission to edit this listing.” This indicates insufficient privileges. The solution is to contact the account owner to request elevated permissions.
Account Recovery
Account recovery procedures are in place to help regain access to GMB profiles after password loss or account compromise. This involves verifying ownership through various methods provided by Google.
- Google Account Recovery: If you’ve forgotten your password, Google’s account recovery process will guide you through verification methods such as email, phone, or security questions. Follow the prompts carefully and provide accurate information to regain access.
- Ownership Verification: Google might require you to verify ownership of the business through methods like phone verification, postcard verification, or other means. Respond promptly to any verification requests from Google to restore access to your GMB account.
- Contacting Google Support: If you encounter difficulties during the recovery process, contact Google My Business support directly. Provide them with all relevant information to expedite the recovery process. They can help you troubleshoot problems and verify your identity.
Best Practices for Account Management
Protecting your Google My Business (GMB) account is crucial for maintaining your online presence and safeguarding your business information. A compromised GMB account can lead to reputational damage, lost customers, and difficulty reclaiming control. Implementing robust security measures is therefore essential for any business relying on GMB for online visibility. This section Artikels best practices to ensure your GMB account remains secure and accessible only to authorized personnel.
Strong security practices go beyond simply choosing a password; they encompass a multi-layered approach that minimizes vulnerabilities and maximizes protection. This includes proactive measures to prevent unauthorized access and reactive steps to address any potential breaches. Regular review and updates of user permissions are equally vital in maintaining control and accountability within your GMB account.
Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication
Utilizing strong, unique passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly enhances GMB account security. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long, combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information such as your name, birthdate, or common words. Consider using a password manager to generate and securely store complex passwords for all your online accounts. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method, such as a code sent to your phone or email, in addition to your password. This makes it considerably more difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access, even if they obtain your password. Enabling MFA is a highly recommended security practice for all Google accounts, including GMB.
Regular Review and Update of User Permissions
Periodically reviewing and updating user permissions is essential for maintaining control and preventing unauthorized access to your GMB account. Regular audits ensure that only authorized individuals retain access and that permissions align with their roles and responsibilities. Removing access for employees who no longer require it minimizes potential security risks. When granting access, always assign the least privilege necessary; for example, give an employee only the permissions needed to perform their specific tasks. This limits the potential damage from a compromised account. Document all access grants and removals for accountability and auditing purposes. A log of these changes can be invaluable in case of security incidents.
Security Measures Checklist
Implementing a comprehensive security strategy involves multiple steps. The following checklist summarizes key measures to ensure optimal GMB account protection:
A proactive approach to GMB account security significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and potential damage. This checklist serves as a guide to help businesses establish and maintain a secure online presence.
- Create and use strong, unique passwords for your GMB account.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
- Regularly review and update user permissions, removing access for former employees.
- Grant only the minimum necessary permissions to each user.
- Keep your Google account information up-to-date, including recovery email and phone number.
- Be wary of phishing emails or suspicious links that may attempt to steal your credentials.
- Monitor your GMB account activity for any unusual or unauthorized changes.
- Implement a robust password management system.
- Regularly back up important GMB data.
- Familiarize yourself with Google’s security best practices and account recovery procedures.
Illustrating the User Interface
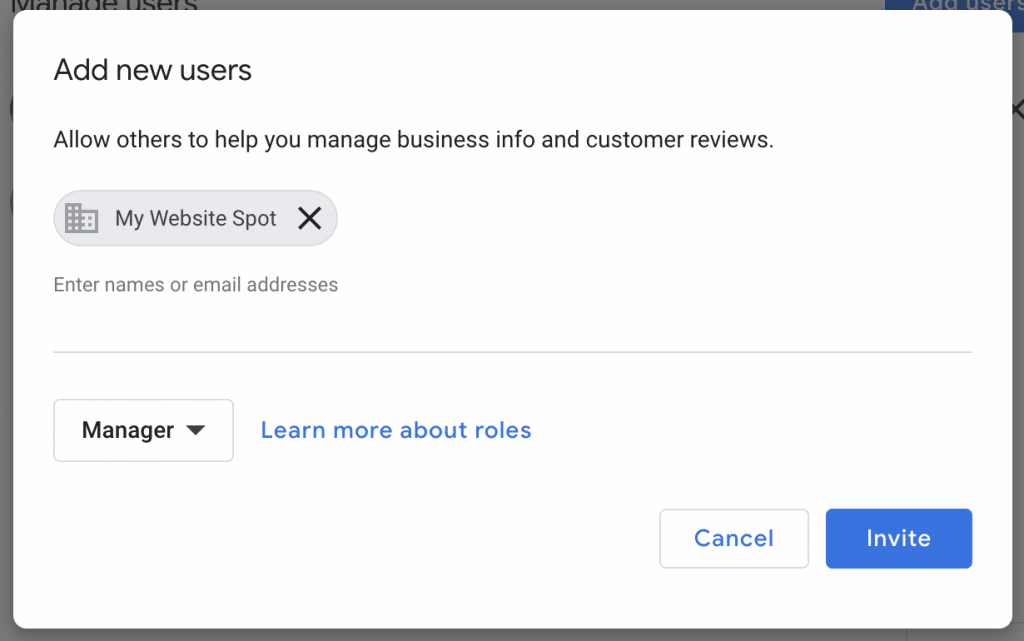
Navigating the Google My Business (GMB) interface to manage user access requires understanding its structure and key elements. The user interface is designed to be relatively intuitive, guiding users through the process of adding, modifying, and removing user permissions. The visual layout prioritizes clear labeling and straightforward navigation.
The main GMB dashboard provides access to various management features. To manage user access, you typically need to locate the “Users” or “Manage users” section, often found within the main settings menu. This menu is usually represented by a gear icon or a similar symbol. The exact location might vary slightly depending on the current GMB interface version, but it’s consistently placed in a prominent location within the main dashboard. The user management section itself is usually a dedicated page with a clean and organized layout.
Adding a New User to Google My Business, How to give access to google my business account
Adding a new user involves a straightforward process. First, navigate to the user management section as described above. You’ll then encounter a button or link clearly labeled as “Add user” or a similar phrase. Clicking this will open a new window or section within the existing page. This new area will prompt you to enter the email address of the person you wish to grant access to.
A typical interface would include a text field specifically labeled “Email address” where you would input the email address. Below this field, you’ll find a dropdown menu or a series of checkboxes allowing you to select the specific permissions you want to grant to the new user. These permissions might include options like “Owner,” “Manager,” “Analyst,” or other roles with varying levels of access. Each role is usually clearly defined with a brief description outlining its capabilities. For example, an “Owner” would have complete control, while a “Manager” might have limited access to specific aspects of the GMB profile.
After selecting the appropriate permissions, you typically need to click a “Save” or “Add user” button to finalize the process. The system will then send an invitation email to the designated email address. The email will contain a link allowing the new user to accept the invitation and gain access to the GMB account. Upon accepting, the new user will be visible within the GMB user management section, reflecting their assigned role and permissions. The interface will typically display a list of all current users, along with their assigned roles, providing a clear overview of account access. This list might include options to edit or remove user permissions as needed. Any changes made will be reflected instantly, or with a short delay, ensuring real-time updates to the account’s access control.
Managing Multiple Locations
Managing multiple Google My Business (GMB) locations requires a strategic approach to access control. Efficiently assigning permissions ensures each user has the necessary authority to manage their designated locations without compromising overall account security. This section details how to grant location-specific access and maintain control across your business network.
Location-Specific Access Granting
Granting access to specific locations within a multi-location GMB account involves leveraging the account’s hierarchical structure. The process begins with identifying the individual or team needing access and determining the precise locations they require permission for. Access is not granted to the entire account at once; instead, permissions are assigned on a location-by-location basis. This granular control prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data associated with other business locations. The process typically involves navigating to the “Manage locations” section within the GMB dashboard, selecting the relevant location, and then inviting the user, specifying their role and the location they will manage.
Assigning Differentiated Location Permissions
Different users may require varying levels of access depending on their roles and responsibilities. For instance, a location manager might need full control over their specific location’s profile, including posting updates, responding to reviews, and managing messaging. In contrast, a regional marketing manager might only need access to view performance metrics across several locations but not modify their individual profiles. GMB allows for the assignment of different roles (e.g., owner, manager, etc.) with varying permission levels. This ensures that only authorized individuals can perform specific actions, maintaining data integrity and security. This level of control is vital for large organizations with many locations and diverse teams.
Comparative Analysis of Multi-Location Access Management Methods
Managing access across multiple locations can be achieved through various methods, each with its strengths and weaknesses. One method is to individually invite users and assign permissions for each location, offering maximum control. However, this can be time-consuming for a large number of locations. Alternatively, user groups can be created to streamline the process, allowing administrators to assign permissions to an entire group at once, saving time and effort. However, this approach may be less granular in terms of control. The optimal method depends on the size and complexity of the business and its organizational structure. A large enterprise with numerous locations and complex reporting structures may benefit from a more structured group-based approach, while a smaller business with a few locations may find individual assignment sufficient.
Flowchart: Assigning Location-Specific Permissions
The following flowchart illustrates the process of assigning location-specific permissions in a multi-location GMB account:
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with “Start,” then branch to “Identify User and Location,” followed by “Navigate to GMB Manage Locations,” then “Select Location,” then “Invite User,” then “Assign Role and Permissions,” then “Confirm and Save,” finally ending with “End.” Each step would be represented by a box, and the arrows would indicate the flow of the process. Decision points could be included, such as “User already exists?” or “Permissions sufficient?”]






