How to start a cabinet business? This question marks the beginning of a potentially lucrative journey, one requiring careful planning, execution, and a keen eye for detail. From market research and crafting a solid business plan to navigating legal requirements and mastering the art of cabinet production, success hinges on a strategic approach. This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap, guiding you through each crucial step to establish and grow your cabinet making enterprise.
Building a thriving cabinet business demands more than just carpentry skills; it necessitates a strong understanding of business principles, marketing strategies, and financial management. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to successfully navigate the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities within this rewarding industry. We’ll delve into the specifics of market analysis, legal compliance, production processes, sales strategies, and financial planning, providing actionable steps to turn your vision into reality.
Market Research & Business Planning
Launching a successful cabinet business requires meticulous planning and a deep understanding of the market. A robust business plan, informed by comprehensive market research, is crucial for navigating the complexities of this industry and achieving long-term profitability. This section Artikels the key steps involved in conducting thorough market research and developing a comprehensive business plan.
Target Customer Demographics and Cabinet Style Preferences
Understanding your target customer is paramount. This involves identifying specific demographics—age, income level, location, lifestyle—and correlating these with preferred cabinet styles. For example, a high-end custom cabinet maker might target affluent homeowners in upscale neighborhoods, focusing on bespoke designs using exotic woods and intricate detailing. Conversely, a business specializing in budget-friendly cabinets might target first-time homebuyers or rental property owners, emphasizing affordability and functionality over elaborate designs. Market research techniques such as surveys, focus groups, and competitor analysis can help refine this understanding. Analyzing online searches for cabinet styles in your target area can also reveal valuable trends. For instance, a high volume of searches for “modern shaker cabinets” suggests a strong demand for that particular style in your region.
Business Plan Development: Financial Projections, Marketing, and Operations
A detailed business plan serves as a roadmap for your cabinet business. It should include comprehensive financial projections encompassing startup costs (equipment, materials, rent), operating expenses (labor, utilities, marketing), and revenue forecasts based on projected sales volume and pricing. The plan should also detail your marketing strategies, outlining how you will reach potential customers (e.g., online advertising, local partnerships, participation in home shows). Finally, it should cover operational procedures, including sourcing materials, production processes, quality control, and delivery/installation logistics. A well-structured business plan is essential for securing funding from lenders or investors. For instance, a detailed financial model showing a positive cash flow within three years could be crucial in obtaining a bank loan.
Competitor Analysis: Pricing, Product Offerings, and Target Markets
Identifying and analyzing your key competitors is vital. Let’s assume three competitors exist: “Artisan Cabinets,” specializing in high-end custom designs; “Budget Cabinets,” focusing on affordable, pre-fabricated options; and “Modern Designs,” specializing in contemporary styles. Artisan Cabinets commands premium pricing due to their bespoke offerings and target affluent clientele. Budget Cabinets offers lower prices with a standardized product line, targeting budget-conscious customers. Modern Designs occupies a niche market, offering stylish contemporary cabinets at a mid-range price point. Comparing these competitors allows you to identify opportunities in the market—perhaps a gap exists for eco-friendly cabinets or a specific style not well-served by existing businesses.
Marketing Plan: Online and Offline Strategies
A comprehensive marketing plan should encompass both online and offline strategies. Online strategies could include creating a professional website with high-quality images of your work, running targeted social media advertising campaigns (e.g., Facebook, Instagram), and utilizing search engine optimization () to improve your online visibility. Offline strategies might involve networking with local contractors, builders, and interior designers, participating in home shows and trade fairs, and distributing flyers or brochures in your target area. Consider a tiered marketing approach, starting with low-cost strategies (e.g., social media marketing) and gradually scaling up to more expensive methods (e.g., print advertising) as your business grows. For example, collaborating with local interior designers can generate significant referrals and build brand credibility.
Legal & Regulatory Requirements

Launching a cabinet business requires navigating a complex legal landscape. Understanding and fulfilling these requirements is crucial for operational legality, minimizing risk, and building a sustainable enterprise. Failure to comply can lead to significant fines, legal battles, and reputational damage. This section details the essential legal and regulatory steps involved in establishing and operating a successful cabinet business.
Business Registration and Name Selection
Registering your business name is the foundational legal step. This involves checking for name availability with your state’s Secretary of State or equivalent agency. You’ll need to choose a business structure (sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, etc.), which impacts liability and taxation. Following registration, obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS if you plan to hire employees or operate as anything other than a sole proprietorship. Simultaneously, consider trademarking your business name and logo to protect your brand identity and prevent others from using similar branding. This involves filing an application with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). Thorough research into existing trademarks is vital to avoid conflicts. For example, a cabinet maker intending to use “Artisan Woodworks” should first search the USPTO database to ensure no similar names are already registered.
Licensing and Permits
Securing the necessary licenses and permits varies depending on your location and business operations. This typically involves contacting your local government agencies, such as the city and county, to determine the specific requirements. These may include a business license, a general contractor’s license (if you’ll be installing cabinets), and potentially permits related to zoning and environmental regulations, especially if you’ll be manufacturing cabinets on-site. For instance, a cabinet shop operating in a residential zone might require a variance or special permit to operate commercially. Failure to obtain the required permits could result in hefty fines and potential business closure.
Insurance Requirements
Comprehensive insurance is vital to protect your business from various risks. General liability insurance is essential to cover potential injuries or property damage occurring on your premises or during installations. Workers’ compensation insurance is required in most states if you employ others, protecting your employees in case of workplace accidents. Product liability insurance protects you against claims related to defects in your manufactured cabinets. Commercial property insurance safeguards your business assets against damage from fire, theft, or other unforeseen events. The specific coverage and amount of insurance needed will depend on factors such as the size of your business, the number of employees, and the complexity of your operations. Consider consulting with an insurance broker to determine the appropriate coverage for your specific needs.
Compliance Standards and Certifications
Depending on your operations, you might need to adhere to specific industry standards and obtain relevant certifications. For example, if you use specific materials or manufacturing processes, certifications demonstrating compliance with safety and environmental regulations might be required. These certifications can enhance your credibility with clients and demonstrate your commitment to quality and safety. Furthermore, adherence to safety regulations, such as those concerning the use of power tools and handling of hazardous materials, is crucial for preventing workplace accidents and ensuring compliance with OSHA standards. Failure to comply can lead to significant penalties.
Production & Operations
Efficient production and operations are crucial for the success of any cabinet business. This section details the key aspects of establishing a robust and scalable production process, from material sourcing to inventory management. Careful planning in these areas will directly impact profitability and customer satisfaction.
Material Sourcing Plan
Sourcing high-quality materials at competitive prices is paramount. This involves selecting appropriate wood types, hardware, and finishes, considering factors like cost, durability, and aesthetic appeal. The following table compares three common wood types:
| Wood Type | Cost | Durability | Appearance | Workability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oak | High | High | Classic, strong grain | Moderate, can be difficult to work with |
| Pine | Medium | Medium | Soft, light grain | Easy to work with |
| MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard) | Low | Low | Smooth, uniform surface | Easy to work with, but prone to damage |
Beyond wood, sourcing reliable suppliers for hinges, drawer slides, knobs, and finishes is essential. Negotiating bulk discounts and establishing strong supplier relationships can significantly reduce costs. Consider exploring various finish options, including paint, stain, and lacquer, to cater to diverse customer preferences. Regularly evaluate supplier performance based on factors such as delivery times, quality consistency, and pricing.
Cabinet Manufacturing Process Flowchart
A well-defined production process is vital for efficiency and quality control. The following flowchart Artikels a typical cabinet manufacturing process:
1. Design & Planning: Client consultation, design creation, material selection, and detailed drawings.
2. Cutting & Shaping: Using CNC routers or other woodworking machinery to cut and shape the wood components according to the design specifications.
3. Assembly: Assembling the cabinet components, including doors, drawers, and shelves, using appropriate joinery techniques and hardware.
4. Finishing: Applying the chosen finish (paint, stain, lacquer) to protect and enhance the cabinet’s appearance.
5. Hardware Installation: Installing hinges, drawer slides, knobs, and other hardware.
6. Quality Control: Inspecting the finished cabinet for any defects or imperfections before packaging.
7. Packaging & Delivery: Packaging the cabinet securely for transport and arranging delivery to the client.
8. Installation: Installing the cabinet at the client’s location (if applicable).
Equipment and Tool Requirements
Investing in the right equipment and tools is critical for efficient and high-quality cabinet production. The initial investment can be significant, but the right tools will improve productivity and reduce errors.
| Equipment/Tool | Cost (Estimate) | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Router | $10,000 – $50,000 | Regular lubrication, blade changes, periodic servicing |
| Table Saw | $500 – $2,000 | Blade sharpening, regular cleaning |
| Planer | $300 – $1,500 | Blade sharpening, regular cleaning |
| Hand Tools (Chisels, Screwdrivers, etc.) | $200 – $500 | Regular sharpening and maintenance |
| Spray Gun | $100 – $500 | Regular cleaning and maintenance |
Note that these are estimates, and actual costs may vary depending on the brand, features, and location. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and accuracy of these tools.
Inventory Management Plan
Effective inventory management minimizes waste, ensures timely production, and avoids stockouts. This involves tracking both raw materials and finished goods. A robust inventory management system, whether manual or software-based, is crucial. This system should track material quantities, usage rates, and reorder points. Regular inventory audits should be conducted to identify discrepancies and adjust ordering strategies as needed. Consider using a FIFO (First-In, First-Out) method to manage inventory, ensuring that older materials are used before newer ones to minimize spoilage. Implementing a barcoding or RFID system can automate the tracking process and enhance accuracy. Regularly reviewing sales data and projecting future demand will help optimize inventory levels and minimize holding costs.
Sales & Marketing
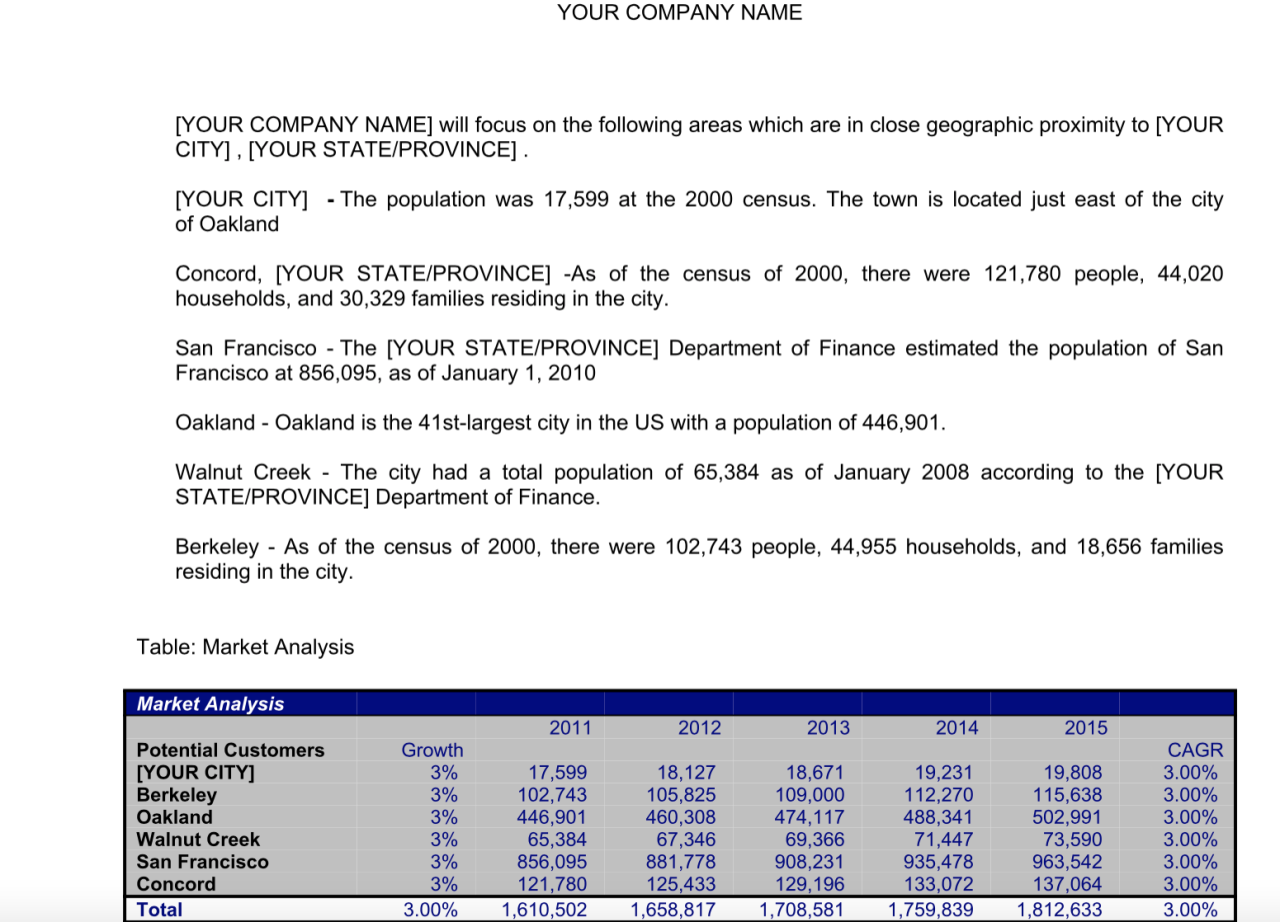
A robust sales and marketing strategy is crucial for the success of any cabinet business. This involves not only attracting customers but also nurturing relationships to ensure repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals. Effective pricing, targeted marketing, and a streamlined customer relationship management system are all key components.
Developing a comprehensive sales and marketing plan requires a deep understanding of your target market, your competition, and your unique selling proposition. This plan will guide your efforts in reaching potential clients and converting them into loyal customers.
Pricing Strategy
A well-defined pricing strategy is essential for profitability. It should balance production costs, market competitiveness, and desired profit margins. Several pricing models can be employed, including cost-plus pricing (calculating costs and adding a markup), value-based pricing (setting prices based on perceived value to the customer), and competitive pricing (aligning prices with competitors). Consider factors like material costs, labor, overhead, and the perceived value of custom cabinetry compared to mass-produced options. For example, a high-end custom cabinet business might use value-based pricing, emphasizing the quality of materials and craftsmanship, while a business focusing on budget-friendly options might employ competitive pricing. Regularly reviewing and adjusting prices based on market fluctuations and business performance is crucial.
Marketing Materials
High-quality marketing materials are vital for showcasing your business and attracting clients. A professional website is essential, showcasing your portfolio of work, testimonials, and contact information. The website should be visually appealing, easy to navigate, and optimized for search engines (). Brochures and other printed materials can supplement the website, providing potential clients with a tangible representation of your work and capabilities. Consider including high-resolution images of completed projects, highlighting unique features and design elements. For example, a brochure might showcase a specific project that demonstrates your expertise in a particular style, like modern minimalist cabinetry.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) System, How to start a cabinet business
Implementing a CRM system allows for efficient tracking of leads, sales, and customer interactions. This system can range from simple spreadsheets to sophisticated software solutions. A CRM helps manage communication, track project progress, and maintain a record of customer preferences and past purchases. This facilitates personalized communication and strengthens customer relationships. Features such as contact management, lead tracking, sales pipeline management, and reporting capabilities are valuable for improving sales efficiency and customer satisfaction. For instance, a CRM could automatically send email reminders about upcoming project milestones or follow-up messages after a consultation.
Building Relationships with Key Clients
Building strong relationships with contractors, interior designers, and other potential clients is crucial for sustained growth. Networking events, industry conferences, and online platforms provide opportunities to connect with these key players. Offering excellent customer service, providing timely project updates, and maintaining open communication are essential for fostering trust and loyalty. Collaborating on projects and offering referral programs can further strengthen these relationships. For example, offering exclusive discounts or early access to new product lines to key clients can demonstrate appreciation and encourage continued collaboration.
Financial Management: How To Start A Cabinet Business
A robust financial plan is crucial for the success of any cabinet business. It provides a roadmap for managing resources, securing funding, and ensuring long-term profitability. This section Artikels key financial aspects to consider when starting your cabinet business, focusing on developing a comprehensive financial model, securing funding, managing cash flow, and tracking expenses.
Developing a Three-Year Financial Projection
A comprehensive financial model projects revenue, expenses, and profitability over a defined period. For a cabinet business, this typically involves forecasting sales based on market demand and pricing strategies, estimating material costs, labor expenses, overhead, and marketing costs. A three-year projection allows for realistic assessment of growth potential and identification of potential financial challenges. This projection should include monthly or quarterly breakdowns for detailed analysis. For example, a projection might show a steady increase in revenue over the three years, with a corresponding increase in profitability as economies of scale are achieved. The model should also incorporate realistic scenarios, such as a potential slowdown in the housing market, to test the business’s resilience.
Securing Funding
Securing sufficient funding is essential for starting and growing a cabinet business. Several options exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Bootstrapping, using personal savings or loans from family and friends, offers control but limits initial investment. Small business loans from banks or credit unions provide access to larger capital but require collateral and adherence to repayment schedules. Seeking investments from angel investors or venture capitalists can offer substantial funding, but typically involves relinquishing some equity in the business. The choice of funding method depends on the business’s needs, risk tolerance, and available resources. A well-structured business plan is crucial for attracting investors.
Cash Flow Management Strategies
Effective cash flow management is vital for the financial stability of a cabinet business. This involves carefully monitoring incoming and outgoing cash, projecting cash needs, and developing strategies to ensure sufficient liquidity. Strategies include implementing efficient invoicing and payment collection processes, negotiating favorable payment terms with suppliers, and managing inventory levels to minimize storage costs. Maintaining a healthy cash reserve is crucial to cover unexpected expenses and seasonal fluctuations in demand. For example, a cabinet business might experience higher demand during the spring and summer months, requiring careful planning to manage cash flow during slower periods. Regularly reviewing cash flow projections and adjusting strategies as needed is essential.
Expense Tracking and Financial Reporting
Accurate expense tracking and regular financial reporting are essential for making informed business decisions and monitoring financial performance. This involves establishing a system for recording all business expenses, categorizing them appropriately, and generating regular financial statements such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Using accounting software can streamline this process, providing automated reporting and analysis capabilities. Regularly reviewing these reports allows business owners to identify areas of inefficiency, track profitability, and make data-driven decisions to improve financial performance. For example, tracking material costs over time can reveal opportunities for cost savings through negotiation with suppliers or exploring alternative materials.
Customer Service & Delivery

Exceptional customer service and reliable delivery are crucial for building a successful cabinet business. A positive customer experience fosters loyalty, generates positive word-of-mouth referrals, and ultimately drives profitability. This section Artikels strategies for managing customer interactions, ensuring timely and efficient delivery, and leveraging customer feedback for continuous improvement.
Customer Service Protocol
A well-defined protocol streamlines the handling of customer inquiries, complaints, and returns. This involves establishing clear communication channels, assigning responsibility for handling issues, and tracking resolution times. For example, a system might include a dedicated phone line, email address, and online contact form, each with assigned personnel and response time targets (e.g., phone calls answered within 3 rings, emails responded to within 24 hours). A documented procedure for escalating complex issues to a supervisor should also be in place. For returns, a clear policy outlining acceptable reasons for return, the process for initiating a return, and the timeframe for refunds or replacements should be established and communicated to customers upfront. Tracking systems should monitor customer satisfaction metrics, such as resolution times and customer feedback scores, allowing for regular review and improvement of the protocol.
Delivery and Installation Plan
Efficient delivery and installation are vital for customer satisfaction. This requires meticulous planning, including scheduling, transportation, and on-site assembly. A scheduling system should consider factors like project size, geographical location, and customer availability. The use of route optimization software can help minimize travel time and fuel costs. The transportation aspect should include the use of appropriate vehicles to ensure the safe and damage-free delivery of cabinets. Pre-installation site surveys can help identify potential challenges and ensure smooth installation. A detailed checklist for on-site assembly, including necessary tools and materials, should be used to maintain consistency and quality. Clear communication with customers regarding delivery and installation timelines is essential to manage expectations and avoid delays. For example, providing customers with a specific delivery window and a confirmation call before arrival minimizes uncertainty.
Customer Feedback System
Gathering and utilizing customer feedback is key to continuous improvement. Implementing a system for collecting feedback through various channels, such as post-installation surveys, online reviews, and direct communication, is essential. These surveys should include questions assessing satisfaction with various aspects of the service, including communication, delivery, installation, and product quality. Analyzing this feedback can identify areas for improvement in products, processes, and customer service. For example, consistently negative feedback regarding a specific aspect of the installation process could indicate a need for additional training for installation teams or a revision of the installation procedure. Regular review and analysis of this feedback should inform strategic decisions aimed at enhancing customer experience.
Strategies for Building Customer Loyalty
Building customer loyalty involves exceeding expectations and fostering long-term relationships. This can be achieved through proactive communication, personalized service, and loyalty programs. Proactive communication might include regular updates on project progress and follow-up calls after installation. Personalized service involves tailoring communication and services to individual customer needs. Loyalty programs, such as discounts on future purchases or exclusive offers, can incentivize repeat business. Providing exceptional customer service throughout the entire customer journey builds trust and strengthens relationships. For example, a company might offer a warranty exceeding industry standards, or provide ongoing maintenance support to build long-term customer loyalty and positive word-of-mouth referrals.






