How to start a financial planning business is a question many aspiring entrepreneurs ask. This comprehensive guide navigates the complexities of establishing a successful financial planning firm, from meticulous market research and strategic business planning to navigating legal compliance and building a strong client base. We’ll delve into creating compelling service offerings, implementing effective marketing strategies, and leveraging technology to optimize operations. Ultimately, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to launch and grow a thriving financial planning business.
Starting your own financial planning business requires careful planning and execution. This involves not only understanding the financial markets and planning strategies but also mastering the legal and regulatory aspects of the industry. Building a strong brand and acquiring clients requires a multi-faceted approach, combining online and offline marketing with effective networking and client relationship management. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can significantly increase your chances of success.
Market Research and Business Planning
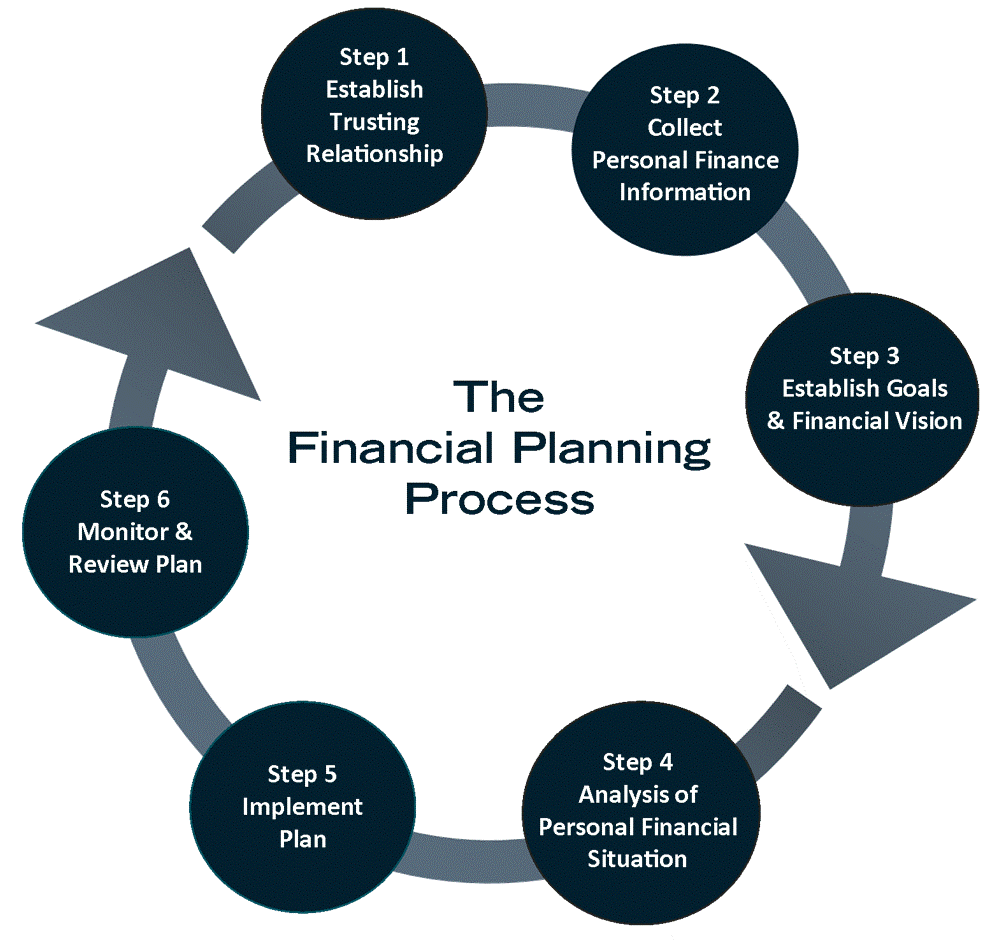
Launching a successful financial planning business requires meticulous market research and a robust business plan. Understanding your competitive landscape, defining your niche, and projecting your financial performance are crucial for long-term viability. This section details the essential steps in developing a comprehensive plan for your financial planning venture.
Competitive Analysis of Established Financial Planning Firms
To effectively compete, understanding your rivals is paramount. This analysis compares three hypothetical firms—Firm A, Firm B, and Firm C—illustrating different approaches to the market. These are illustrative examples and should be replaced with actual research on firms in your specific geographic area.
| Firm | Services Offered | Target Market | Pricing Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firm A | Comprehensive financial planning, investment management, retirement planning, tax planning. | High-net-worth individuals, families. | Fee-based, tiered pricing based on assets under management (AUM). Higher AUM attracts lower percentage fees. |
| Firm B | Retirement planning, estate planning, insurance planning. | Pre-retirees and retirees with moderate assets. | Hourly rate, with packages for bundled services. |
| Firm C | Basic financial planning, budgeting, debt management. | Young professionals and individuals with limited financial resources. | Fixed fees per service, with discounted packages. |
This comparison highlights the diverse service offerings, target markets, and pricing models available within the financial planning industry. Your business plan should clearly define how your firm will differentiate itself within this competitive landscape.
Business Plan: Target Market, Service Offerings, Marketing Strategy, and Financial Projections
A well-defined business plan is the cornerstone of a successful launch. This plan Artikels key aspects for your first three years.
Target Market
Your ideal client profile should be clearly defined. For example, you might target young professionals (25-40 years old) seeking guidance on debt management, saving for a down payment, and investing. This allows for focused marketing efforts.
Service Offerings
Based on your target market, determine the specific services you’ll provide. This could include financial planning, budgeting, investment management, retirement planning, or tax planning. Clearly define the scope of each service to avoid misunderstandings.
Marketing Strategy
A multi-faceted approach is crucial. This could include online marketing (, social media), networking events, referrals from existing clients, and collaborations with complementary businesses (e.g., real estate agents). Allocate a realistic budget for each marketing activity.
Financial Projections (Year 1)
Financial projections are critical for securing funding and tracking progress. The following is a simplified example; actual figures will depend on your specific circumstances.
| Item | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
| Revenue | 50,000 |
| Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) | 5,000 |
| Gross Profit | 45,000 |
| Operating Expenses (rent, salaries, marketing) | 30,000 |
| Net Income | 15,000 |
Projected income statements and balance sheets for years two and three should follow a similar format, adjusting for anticipated growth and changes in expenses. Remember to include realistic assumptions for client acquisition, revenue growth, and expense management.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis helps identify internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats.
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| Expertise in a specific niche (e.g., retirement planning for educators) | Lack of brand recognition |
| Strong network of professional contacts | Limited marketing budget |
| Competitive pricing | Inexperience in running a business |
| Opportunities | Threats |
| Growing demand for financial planning services | Increased competition from established firms |
| Technological advancements (e.g., robo-advisors) | Economic downturn affecting client investment |
| Partnerships with other businesses | Changes in financial regulations |
This analysis helps formulate strategies to capitalize on opportunities, mitigate threats, and address weaknesses.
Projected Income Statement and Balance Sheet (Year 1), How to start a financial planning business
The following represents a simplified example, and should be tailored to your specific business model and projections.
Projected Income Statement (Year 1)
| Revenue | $50,000 |
|---|---|
| Expenses: | |
| Salaries | $20,000 |
| Rent | $5,000 |
| Marketing | $3,000 |
| Software/Technology | $2,000 |
| Professional Fees | $1,000 |
| Other Expenses | $4,000 |
| Total Expenses | $35,000 |
| Net Income | $15,000 |
Projected Balance Sheet (Year 1)
| Assets | Liabilities | Equity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cash | $10,000 | Accounts Payable | $2,000 | Owner’s Equity | $18,000 |
| Accounts Receivable | $5,000 | ||||
| Equipment | $3,000 | ||||
| Total Assets | $18,000 | Total Liabilities | $2,000 | Total Equity | $18,000 |
Remember to consult with a financial professional to refine these projections and ensure they align with your business goals.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: How To Start A Financial Planning Business
Launching a financial planning business requires meticulous attention to legal and regulatory compliance. Failure to adhere to these rules can result in significant penalties, legal action, and irreparable damage to your reputation. Understanding and fulfilling your legal obligations is paramount to building a successful and sustainable business.
Necessary Licenses and Certifications
The specific licenses and certifications needed to operate a financial planning business vary significantly depending on your location and the services you offer. For instance, in the United States, individuals offering investment advice may need to register with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) as an investment advisor representative or hold a Series 65 or 66 license. State-level licensing requirements also exist, often requiring registration with the state’s securities regulator. In the UK, financial planners might need to be authorized by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). It is crucial to research and understand the regulatory landscape in your jurisdiction, potentially consulting with a legal professional specializing in financial services regulation to ensure full compliance. The consequences of operating without the necessary licenses can be severe, including hefty fines and legal repercussions. Furthermore, obtaining the appropriate certifications demonstrates professionalism and builds client trust.
Business Registration Procedures
Registering your financial planning business involves several key steps. First, you need to choose a business structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, etc.) which will influence your registration process and legal liabilities. Next, you’ll need to register your business name with the relevant authorities, potentially including your state or local government. This may involve securing a business license and obtaining an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS (in the US) or a similar tax identification number in your country. You may also need to register with professional organizations related to financial planning to enhance your credibility and access industry resources. The specific requirements vary by location, and seeking assistance from a business registration service or legal counsel is highly recommended to ensure a smooth and compliant registration process. Failing to register correctly can lead to penalties and hinder your ability to operate legally.
Compliance with Financial Regulations and Data Privacy Laws
Financial planning businesses must adhere to numerous regulations designed to protect clients and maintain market integrity. These include regulations concerning client confidentiality, the handling of client assets, and anti-money laundering (AML) compliance. Data privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, mandate strict protocols for handling client personal data. Failure to comply with these laws can result in substantial fines and reputational damage. Businesses must implement robust data security measures, obtain explicit consent for data collection, and ensure clients have control over their data. Staying informed about changes in these regulations is essential for continued compliance. Regular audits and internal compliance checks are crucial to mitigate risks and ensure ongoing adherence to the relevant legal frameworks.
Legal Documents Checklist
Establishing and operating a compliant financial planning business requires a comprehensive set of legal documents. This checklist is not exhaustive and may vary based on location and business structure but provides a starting point:
- Business registration documents (articles of incorporation, LLC operating agreement, etc.)
- Licenses and certifications
- Client agreements and contracts
- Privacy policy compliant with relevant data protection laws (e.g., GDPR, CCPA)
- Terms of service
- Insurance policies (professional liability, errors and omissions, etc.)
- AML/KYC compliance program documentation
- Data security policies and procedures
Maintaining organized records of all legal documents is critical for demonstrating compliance and managing potential legal issues effectively. Regular review and updates of these documents are necessary to reflect changes in regulations and best practices.
Marketing and Client Acquisition
Successfully launching a financial planning business hinges on effectively reaching your target audience and converting prospects into clients. A robust marketing and client acquisition strategy is crucial for sustainable growth and profitability. This section Artikels key components for building a strong client base.
A comprehensive marketing plan should encompass both online and offline strategies, leveraging various channels to maximize reach and impact. It’s essential to define your ideal client profile to tailor your messaging and choose the most effective channels. Furthermore, building a strong network and implementing referral programs are vital for organic growth.
Ideal Client Profile
Defining your ideal client profile (ICP) is paramount. This involves identifying the demographics, financial situations, goals, and needs of your target market. For example, your ICP might be high-net-worth individuals aged 45-65, nearing retirement, concerned about estate planning and legacy preservation. Alternatively, it could be young professionals aged 25-35, focused on debt management, saving for a down payment, and investing for long-term growth. A clearly defined ICP allows for targeted marketing efforts, ensuring your resources are used efficiently. Understanding your ICP’s pain points and aspirations enables the creation of resonant marketing materials.
Online Marketing Strategies
Online marketing offers a cost-effective and scalable way to reach a wide audience. This includes creating a professional website showcasing your expertise and services. The website should be optimized for search engines () to improve visibility in online searches. Social media marketing, utilizing platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, or Instagram, allows for direct engagement with potential clients. Content marketing, such as blog posts, articles, and videos, establishes your credibility and expertise, attracting organic traffic. Paid advertising on platforms like Google Ads and social media can accelerate growth by targeting specific demographics and interests. Email marketing is crucial for nurturing leads and building relationships with prospects.
Offline Marketing Strategies
Offline marketing complements online efforts, creating tangible connections with your community. Networking events, industry conferences, and community involvement build brand awareness and foster relationships. Print advertising in local publications or targeted newsletters can reach specific demographic segments. Participating in local business groups and chambers of commerce provides networking opportunities and builds credibility. Consider sponsoring local events or charities to enhance your brand image and connect with potential clients.
Referral Programs
Referral programs leverage the power of word-of-mouth marketing. Satisfied clients are often your best advocates. Incentivizing referrals, such as offering discounts or bonuses, encourages existing clients to recommend your services. Building strong relationships with clients is key to generating positive referrals. A well-structured referral program should clearly Artikel the process and benefits for both the referrer and the referred client.
Examples of Effective Marketing Materials
Effective marketing materials should be concise, informative, and visually appealing. Website content should clearly articulate your services, expertise, and value proposition. Social media posts should be engaging and shareable, offering valuable insights or tips related to financial planning. Email campaigns should be personalized and segmented, offering relevant content based on the recipient’s interests and needs. For example, an email to a young professional might focus on debt management strategies, while an email to a retiree might highlight income planning solutions. Brochures or presentations can be used for in-person interactions.
Potential Referral Sources and Relationship Building
Identifying and cultivating relationships with potential referral sources is critical. This includes accountants, lawyers, insurance agents, and real estate agents, who frequently interact with individuals needing financial planning services. Building relationships requires proactive engagement, such as attending industry events, offering educational resources, and providing excellent service. Regular communication, such as newsletters or invitations to exclusive events, helps maintain these valuable relationships. Formal referral partnerships with clear agreements can streamline the referral process and ensure mutual benefit.
Technology and Tools
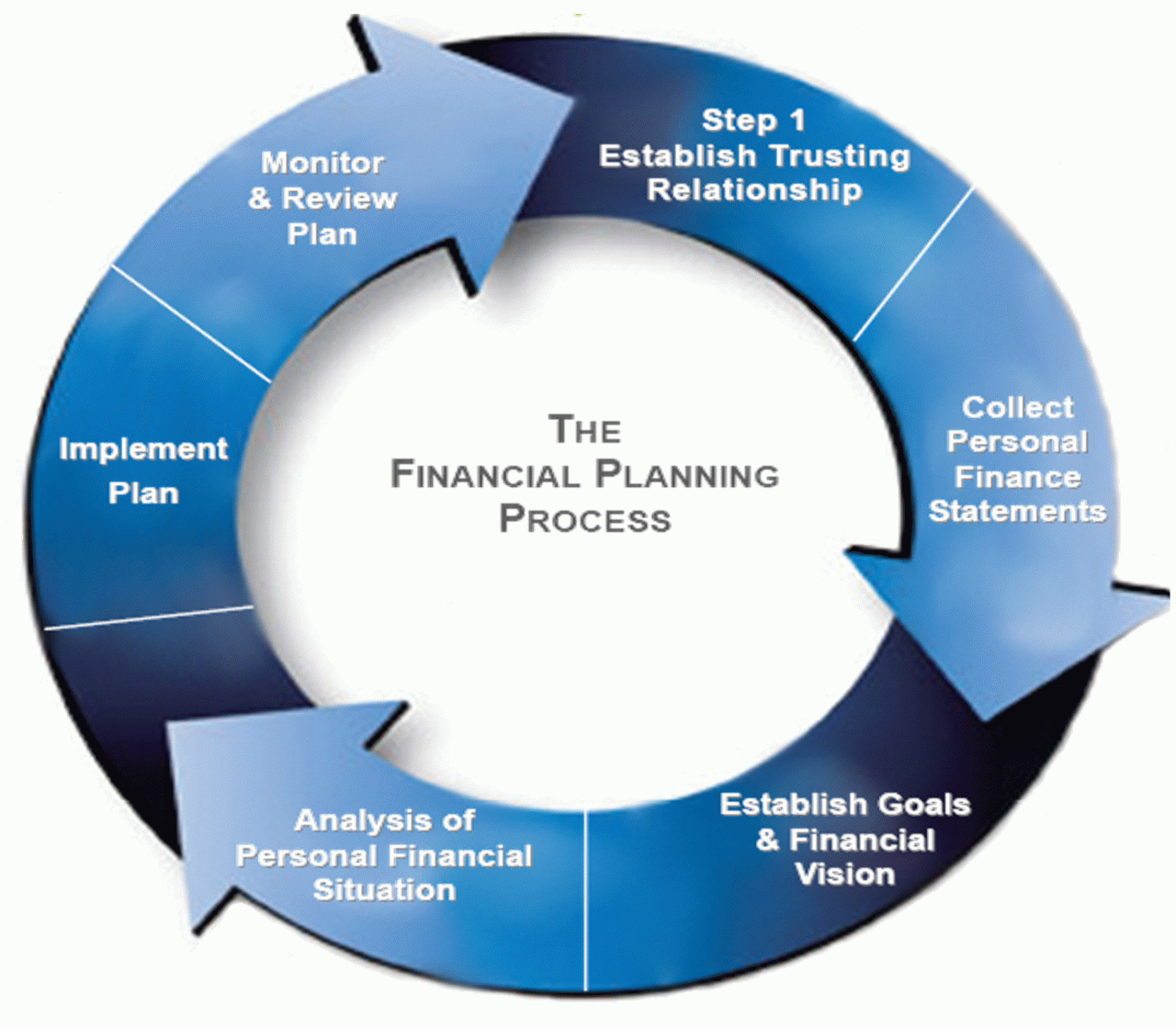
Launching a successful financial planning business requires leveraging the right technology. The tools you choose will significantly impact your efficiency, client experience, and overall profitability. This section explores the essential software, infrastructure, and security measures needed to build a robust and secure operation.
Financial Planning Software Solutions
Choosing the right financial planning software is crucial. Several platforms offer varying features and price points, catering to different business sizes and client needs. Factors to consider include ease of use, integration capabilities, reporting features, and client portal access.
- MoneyGuidePro: A comprehensive platform known for its robust financial planning capabilities, including cash flow analysis, retirement planning, and tax optimization. It’s generally considered a premium option with a higher price tag, reflecting its advanced features. Pricing varies depending on the number of users and modules selected.
- RightCapital: This cloud-based platform offers a user-friendly interface and strong reporting capabilities. It integrates with several other financial applications, simplifying data management. RightCapital typically offers tiered pricing based on the number of clients and features accessed.
- eMoney Advisor: A popular choice among financial advisors, eMoney offers a wide range of tools for financial planning, client communication, and practice management. Its comprehensive suite of features often comes with a higher price point compared to some competitors. Pricing models are typically subscription-based and vary depending on the specific features and user needs.
Essential Technology Infrastructure
A secure and efficient technology infrastructure is paramount for a financial planning business. This involves more than just software; it encompasses hardware, network security, and data backup strategies.
- Secure Servers and Cloud Storage: Utilizing reputable cloud storage providers (like Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure) ensures data redundancy and accessibility. This also allows for secure off-site backups, minimizing the risk of data loss due to hardware failure or disaster.
- Robust Cybersecurity Measures: Implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and multi-factor authentication are crucial for protecting sensitive client data. Regular security audits and employee training on cybersecurity best practices are essential.
- Reliable Internet Connectivity: Consistent and high-speed internet access is crucial for seamless operation. Consider having a backup internet connection to ensure uninterrupted service during outages.
- Client Relationship Management (CRM) System: A CRM system (such as Salesforce or HubSpot) helps manage client interactions, track communication, and streamline workflow processes. This ensures efficient client service and fosters strong client relationships.
Data Security and Best Practices
Protecting client data is not just a best practice; it’s a legal and ethical obligation. Strict adherence to data security protocols is essential to maintain client trust and avoid legal repercussions.
- Encryption: Employing end-to-end encryption for all data transmission and storage ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the correct decryption key.
- Access Control: Implement role-based access control to restrict access to sensitive data based on employee roles and responsibilities. This limits the potential impact of data breaches.
- Regular Data Backups: Regularly backing up data to a secure off-site location ensures business continuity in case of hardware failure or disaster. The frequency of backups should be determined by the volume and sensitivity of data.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adherence to regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) is mandatory, ensuring compliance with data privacy laws.
Client Onboarding and Financial Plan Management Workflow
A well-defined workflow ensures smooth client onboarding and efficient management of financial plans. This streamlined process minimizes errors and improves client satisfaction.
The diagram above illustrates a simplified workflow. The actual process will vary based on individual client needs and the complexity of their financial situation. However, the core steps remain consistent: initial consultation, data gathering and analysis, financial plan creation, implementation, ongoing monitoring, and periodic review.
Financial Management and Operations
Launching a financial planning business requires meticulous financial planning to ensure its long-term viability. This involves creating a comprehensive budget, implementing a suitable pricing strategy, managing cash flow effectively, and securing appropriate insurance coverage. Ignoring these aspects can lead to significant financial instability and jeopardize the business’s success.
Startup Costs and Ongoing Operational Expenses
A detailed budget is crucial for a successful launch. This budget should encompass all anticipated start-up costs, including licensing fees, office space (or virtual office setup costs), technology investments (software, hardware, etc.), marketing and advertising expenses, professional fees (legal, accounting), and initial operating capital. Ongoing operational expenses should also be meticulously estimated, including rent or lease payments, utilities, salaries (if applicable), professional development, marketing campaigns, insurance premiums, and software subscriptions. Consider creating a spreadsheet with monthly and annual projections for at least the first three years, incorporating realistic growth estimates and potential contingencies. For example, a start-up might allocate $10,000 for initial website development, $5,000 for marketing materials, and $2,000 monthly for office rent. These figures should be adjusted based on location, business model, and service offerings.
Pricing Models for Financial Planning Services
Several pricing models exist for financial planning services, each with advantages and disadvantages. These include hourly rates, project-based fees, retainer fees, and percentage-based fees (on assets under management). Hourly rates offer flexibility but can be unpredictable in terms of revenue. Project-based fees provide clarity for both the planner and client but require precise scope definition. Retainer fees offer predictable income but might not reflect the actual time spent on a client. Percentage-based fees are common for wealth management but can limit the planner’s ability to serve clients with smaller portfolios. The optimal pricing model depends on the target market, the complexity of services offered, and the planner’s business goals. For instance, a financial planner specializing in retirement planning might opt for project-based fees for individual retirement plans, while a wealth manager might use a percentage-based fee structure for high-net-worth clients.
Cash Flow Management and Financial Stability
Maintaining positive cash flow is vital for business survival. Strategies include accurate forecasting, invoicing promptly, offering payment plans, negotiating favorable payment terms with vendors, and tracking expenses diligently. Maintaining a healthy cash reserve is crucial to cover unexpected expenses and periods of low revenue. Effective cash flow management involves using tools like cash flow statements, budgeting software, and accounts receivable management systems. For example, offering clients the option to pay in installments can improve cash flow, while negotiating longer payment terms with suppliers can ease short-term financial pressures. A robust financial plan should include strategies for managing seasonal variations in revenue and addressing potential financial shortfalls.
Essential Insurance Policies
Protecting your business from financial risks requires comprehensive insurance coverage. Essential policies include professional liability insurance (errors and omissions insurance), general liability insurance, cyber liability insurance (to protect against data breaches), and potentially business interruption insurance. The specific needs will vary depending on the business structure and services offered. Professional liability insurance protects against claims of negligence or errors in professional advice, while general liability insurance covers accidents or injuries on business premises. Cyber liability insurance is increasingly important given the reliance on technology in financial planning. Business interruption insurance provides coverage for lost income during periods of unforeseen disruptions. The cost of these policies should be factored into the overall budget.






