How to start a yacht charter business? This question marks the beginning of a potentially lucrative yet complex entrepreneurial journey. The allure of sun-drenched waters, luxurious yachts, and discerning clientele is undeniable, but success requires meticulous planning, significant investment, and a deep understanding of the industry’s intricacies. From market research and securing the necessary licenses to acquiring a fleet and crafting a compelling marketing strategy, building a thriving yacht charter business demands careful consideration at every stage. This guide navigates you through the essential steps, offering practical advice and insights to help you chart a course towards success.
This comprehensive guide will explore the various facets of establishing a yacht charter business, covering everything from initial market analysis and financial projections to legal compliance, yacht acquisition and maintenance, marketing and sales strategies, operations management, crew recruitment and training, and finally, financial management and growth strategies. Each section will provide detailed information, actionable steps, and real-world examples to help aspiring entrepreneurs navigate the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities within this exciting industry.
Market Research and Business Planning
Successfully launching a yacht charter business requires meticulous market research and a robust business plan. Understanding your target audience, competitive landscape, and potential financial performance is crucial for long-term viability. This section details the key elements of this critical planning phase.
Target Market Characteristics
The target market for yacht charters is diverse, encompassing both individual leisure travelers and corporate clients. High-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) and affluent families represent a significant segment, seeking luxury experiences and personalized service. Corporate clients often utilize yacht charters for team-building events, client entertainment, or executive retreats. Further segmentation can be achieved by considering factors such as age, geographic location, preferred yacht types (sailing yachts, motor yachts, catamarans), and desired charter duration (day trips, weekend getaways, extended cruises). Understanding these nuances allows for targeted marketing and tailored service offerings.
Competitive Analysis
Three major competitors in the luxury yacht charter market, each with distinct service and pricing strategies, are:
| Competitor | Service Focus | Pricing Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| CharterWorld | Wide selection of yachts globally; emphasis on online booking convenience. | Variable pricing based on yacht type, location, and season; competitive rates with transparent pricing structure. |
| Boatbookings | Specializes in crewed yacht charters; focuses on personalized service and curated experiences. | Premium pricing reflecting the higher level of service; targeted towards luxury travelers. |
| Simpson Marine | Strong presence in Asia; focuses on sales and charter of new and pre-owned yachts. | Pricing varies greatly depending on the yacht; offers both bareboat and crewed options, catering to diverse budgets. |
SWOT Analysis: Hypothetical Charter Business in the Mediterranean
Let’s analyze a hypothetical yacht charter business operating in the Mediterranean, specifically the Greek Islands.
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| Prime location with high tourist demand | High initial investment costs (yacht purchase/lease, licenses, insurance) |
| Beautiful scenery and diverse islands for exploration | Seasonality; reduced demand during off-peak months |
| Potential for partnerships with local hotels and tourism businesses | Competition from established charter companies |
| Opportunities for bespoke itineraries and add-on services (water sports, private chefs) | Dependence on weather conditions; potential for cancellations |
| Opportunities | Threats |
| Expansion into new markets or charter types (e.g., eco-tourism charters) | Economic downturns affecting tourism spending |
| Developing a strong online presence and digital marketing strategy | Increased fuel costs and operational expenses |
| Leveraging social media for brand building and customer engagement | Changes in regulations and environmental concerns |
Financial Projection (First Three Years)
This projection assumes a start-up with one 40-foot sailing yacht, operating primarily during the peak season (May-October).
| Year | Startup Costs | Revenue | Profit/Loss |
|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | $300,000 (yacht purchase, licenses, insurance, marketing) | $150,000 (assuming 50% occupancy during peak season at an average daily rate of $500) | -$150,000 |
| Year 2 | $10,000 (maintenance, marketing) | $250,000 (increased occupancy and potentially higher rates) | $240,000 |
| Year 3 | $20,000 (maintenance, marketing, potential expansion) | $350,000 (further growth in occupancy and potentially adding a second yacht) | $330,000 |
Note: These figures are estimates and will vary depending on numerous factors, including yacht size, location, marketing effectiveness, and operating costs. Detailed financial modeling is crucial for a comprehensive business plan. A sensitivity analysis should also be performed to assess the impact of various factors on profitability. Real-life examples of successful yacht charter businesses show that initial losses are common, but profitability can be achieved within the second or third year through effective management and marketing strategies.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Launching a yacht charter business requires meticulous attention to legal and regulatory frameworks. Failure to comply can result in significant fines, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. This section details the crucial legal aspects of establishing and operating a yacht charter business, specifically focusing on the Caribbean region, though many principles apply more broadly. Understanding these requirements is paramount for a successful and sustainable enterprise.
Licenses and Permits in the Caribbean
The specific licenses and permits needed to operate a yacht charter business vary significantly across the Caribbean islands. Generally, you’ll need a business license from the relevant island’s government, often obtained through the local chamber of commerce or equivalent body. Beyond this, maritime licenses and permits related to vessel operation and charter activities are essential. These might include a charter operator’s license, a commercial vessel operating license, and potentially permits for specific activities like scuba diving or fishing excursions offered alongside the yacht charter. Each island’s maritime authority will have its own application process and requirements, including inspections to ensure the yacht meets safety standards. For example, the British Virgin Islands and the Cayman Islands have well-defined processes and requirements, which are publicly available on their respective government websites. Thorough research into the specific regulations of the chosen operating region is crucial. It is highly advisable to seek legal counsel specializing in maritime law in the target jurisdiction.
Insurance Requirements for Yacht Charter Businesses, How to start a yacht charter business
Comprehensive insurance is non-negotiable for yacht charter businesses. Two key areas are liability insurance and hull insurance. Liability insurance protects the business from claims arising from accidents, injuries, or damage to property caused by the chartered yacht or its operations. This coverage is crucial to mitigate potential financial losses from lawsuits. Hull insurance covers damage to the yacht itself, whether from accidents, weather events, or other unforeseen circumstances. The level of coverage needed will depend on the value of the yacht and the type of charters offered. Additional insurance policies might be necessary, such as coverage for personal injury to passengers, medical expenses, and environmental damage. The cost of insurance can vary considerably based on factors like the size and type of yacht, the charter area, and the business’s claims history. Securing insurance from a reputable provider with experience in the marine industry is vital.
Legal Responsibilities Regarding Safety and Passenger Welfare
Yacht charter business owners bear significant legal responsibility for the safety and well-being of their passengers. This includes adhering to all relevant safety regulations, ensuring the yacht is properly maintained and equipped, and providing adequately trained crew members. Safety protocols should be clearly documented and communicated to passengers. Emergency procedures, including evacuation plans, must be in place and practiced regularly. The owner is legally obligated to provide a safe environment, and failure to do so can lead to serious legal repercussions. This extends to providing appropriate safety equipment, such as life jackets, flares, and first-aid kits, and ensuring the crew is qualified in their roles, including first aid and CPR. Regular safety inspections and maintenance logs are essential for demonstrating compliance with regulations and mitigating risks. Adherence to international maritime safety standards (like SOLAS) is generally expected.
Sample Yacht Charter Contract
A well-drafted contract is crucial to protect both the charter business and the client. A sample contract should include:
Party Identification: Clearly identifying the charter company and the client.
Description of the Yacht: Details of the yacht, including its name, registration number, and specifications.
Charter Period: Precise start and end dates and times of the charter.
Charter Fee: The total cost of the charter, including any additional fees or taxes.
Payment Terms: Schedule for payments, including deposits and final payment.
Cancellation Policy: Conditions under which either party can cancel the charter and the associated penalties.
Liability Clause: Clearly defining the liability of each party in case of accidents or damage.
Insurance: Confirmation that the yacht is adequately insured.
Governing Law: Specifies the jurisdiction whose laws will govern the contract.
Dispute Resolution: Mechanism for resolving any disputes that may arise.
This sample contract is a basic framework and should be reviewed and adapted by legal counsel to meet the specific needs and legal requirements of the jurisdiction. It is vital to have a legally sound contract to minimize potential disputes and protect the business’s interests.
Yacht Acquisition and Maintenance
Launching a successful yacht charter business hinges significantly on the acquisition and meticulous upkeep of your fleet. The initial investment and ongoing operational costs are substantial, demanding careful consideration of various factors to ensure profitability. This section delves into the key aspects of yacht acquisition and the associated maintenance responsibilities.
Purchasing Versus Leasing Yachts
The decision to purchase or lease a yacht for charter operations presents a critical strategic choice. Purchasing offers long-term ownership and potential appreciation, but demands a considerable upfront capital investment and ongoing maintenance responsibilities. Leasing, conversely, reduces the initial financial burden and allows for greater flexibility in terms of yacht type and duration of operation, though it typically results in higher operational costs over the long term.
| Factor | Purchasing | Leasing |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | High | Low |
| Monthly Costs | Moderate (maintenance, insurance) | High (lease payments) |
| Long-Term Costs | Potentially lower overall | Potentially higher overall |
| Flexibility | Low (tied to specific yacht) | High (can change yachts) |
| Depreciation | Yacht depreciates over time | Lease payments don’t directly impact yacht value |
For example, a luxury motor yacht purchased for $2 million might depreciate significantly over 10 years, while leasing a similar yacht over the same period might cost considerably more in total lease payments. The optimal choice depends on the business’s financial capacity, risk tolerance, and long-term strategic goals.
Ongoing Maintenance Costs
Operating a charter yacht incurs substantial ongoing expenses. These costs can be broadly categorized into crew salaries, fuel consumption, routine maintenance, and unforeseen repairs. Accurate budgeting for these expenditures is crucial for profitability.
Crew salaries, for instance, can represent a significant portion of operating costs, varying based on the size of the yacht and the number of crew members required. Fuel costs fluctuate significantly depending on market prices and the yacht’s fuel efficiency. Routine maintenance includes regular cleaning, engine servicing, and preventative measures to avoid costly breakdowns. Unforeseen repairs, such as engine malfunctions or hull damage, can be unpredictable and expensive, necessitating a robust contingency fund. A reputable yacht management company can provide detailed cost projections based on the specific yacht and operational plan.
For instance, a 50-foot catamaran might require a crew of two, with salaries totaling $100,000 annually. Fuel costs could average $20,000 annually, while routine maintenance and minor repairs might amount to another $30,000. Larger yachts will, of course, have considerably higher costs across all categories.
Charter Yacht Maintenance Schedule
A comprehensive maintenance schedule is vital for ensuring the yacht’s operational readiness and longevity. This schedule should incorporate regular inspections and preventative maintenance to minimize the risk of breakdowns and costly repairs.
| Frequency | Maintenance Task | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | Hull and Deck Inspection | Check for any damage, debris, or leaks. |
| Weekly | Engine Room Check | Inspect engine oil levels, coolant levels, and belts. |
| Monthly | Systems Check | Inspect all onboard systems, including watermakers, generators, and air conditioning. |
| Annually | Major Servicing | Conduct a comprehensive inspection and servicing of the engine, generator, and other major systems. |
This is a basic example; a more detailed schedule will vary depending on the yacht’s size, type, and age.
Comparison of Yacht Types for Charter Operations
Different yacht types cater to various market segments and operational requirements. The choice of yacht type influences capacity, features, and operating costs.
| Yacht Type | Capacity | Features | Operating Costs (Estimated Annual) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sailboat (40ft) | 6-8 Guests | Simple, fuel-efficient, environmentally friendly | $30,000 – $50,000 |
| Motor Yacht (50ft) | 8-12 Guests | More luxurious amenities, higher speed | $70,000 – $120,000 |
| Catamaran (45ft) | 8-10 Guests | Spacious, stable platform, shallow draft | $50,000 – $80,000 |
Note that these operating cost estimates are approximate and can vary considerably based on factors such as location, maintenance requirements, and crew costs.
Marketing and Sales Strategies

Successfully launching a yacht charter business hinges on a robust marketing and sales strategy capable of reaching high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) and converting them into loyal clients. This requires a multi-faceted approach leveraging both online and offline channels, targeting specific niche markets, and building a strong brand identity.
Three Unique Marketing Strategies for High-Net-Worth Individuals
Attracting HNWIs requires sophisticated marketing that emphasizes exclusivity, personalized service, and a strong understanding of their needs and preferences. Generic advertising won’t suffice. Instead, focus on building relationships and creating bespoke experiences.
- Exclusive Partnerships with Luxury Concierge Services: Collaborate with high-end concierge services and luxury travel agencies that cater to HNWIs. These partnerships provide access to a pre-qualified audience already accustomed to luxury experiences. This allows for targeted marketing within their existing client base, minimizing wasted advertising spend. For example, partnering with a firm that manages private jets could lead to cross-promotional opportunities and shared client access.
- Experiential Marketing Events: Host exclusive yacht viewing events or private cocktail parties in upscale locations frequented by HNWIs. These events offer a chance to showcase your yachts, build personal connections, and create a memorable brand experience. Imagine an exclusive preview event at a prestigious marina, complete with gourmet catering and live music, allowing potential clients to experience the luxury firsthand.
- Personalized Digital Marketing Campaigns: Utilize targeted online advertising on platforms frequented by HNWIs, such as LinkedIn, bespoke online publications, and luxury lifestyle websites. Develop highly personalized email campaigns based on individual preferences and past travel history. This level of personalization demonstrates an understanding of the client’s needs and increases the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
Building a Professional Website and Online Booking System
A professional website is crucial for attracting and converting potential clients. It should be visually stunning, easy to navigate, and showcase the luxury and exclusivity of your yacht charter services.
The website must feature high-quality photographs and videos of the yachts, detailed descriptions of the amenities and services offered, client testimonials, and a user-friendly online booking system. The booking system should allow clients to easily check availability, select dates, and make secure payments. Consider integrating a live chat feature for immediate customer support. A well-designed website, such as one using a platform like Wix or Squarespace, with professional photography and a seamless booking process, instills confidence and encourages conversions. For example, a detailed itinerary builder allows clients to customize their charter experience.
Utilizing Social Media to Promote Yacht Charter Services
Social media platforms, particularly Instagram and Facebook, are effective channels for showcasing the luxury and lifestyle associated with yacht charters. However, avoid generic posts; instead, focus on high-quality visuals and engaging content that resonates with the target audience.
High-quality images and videos of yachts in stunning locations, coupled with client testimonials and behind-the-scenes glimpses of the charter experience, can significantly increase engagement. Running targeted ad campaigns on these platforms, focusing on demographics and interests relevant to HNWIs, will further enhance reach and brand awareness. For example, a short video showcasing a sunset cruise with a stunning view can be far more engaging than a simple text-based advertisement.
Marketing Campaign Targeting Corporate Events
A targeted marketing campaign focusing on corporate events positions yacht charters as a unique and memorable team-building or client appreciation activity.
The campaign should emphasize the benefits of chartering a yacht for corporate events, such as enhanced team bonding, increased productivity, and a unique networking opportunity. Marketing materials should showcase examples of successful corporate events held on yachts, including testimonials from satisfied clients. This could include case studies detailing successful corporate retreats or conferences held aboard chartered yachts, highlighting the return on investment for companies choosing this unique event option. Direct outreach to corporate event planners and decision-makers is crucial.
Operations and Customer Service
Successfully operating a yacht charter business requires meticulous attention to detail and a commitment to providing exceptional customer service. Efficient day-to-day operations, proactive emergency response, and strong client relationships are crucial for profitability and repeat business. This section details the key operational aspects and best practices for ensuring smooth and memorable charter experiences.
Crew Scheduling and Client Communication
Effective crew scheduling is paramount. A well-defined rota, considering individual crew member skills and certifications, ensures adequate coverage across all shifts and charter durations. This requires anticipating potential absences and having a robust system for filling in gaps. Efficient communication with clients begins pre-charter with detailed itinerary confirmations and provisioning discussions. Throughout the charter, regular updates, whether it’s confirming a change in plans or providing weather reports, are crucial for maintaining transparency and client satisfaction. Post-charter, prompt feedback requests and follow-up communications strengthen client relationships and aid in future business. For example, a well-structured communication plan might involve daily check-in calls with the captain and weekly email updates to the client detailing the itinerary and any planned changes.
Emergency Procedures and Unforeseen Circumstances
Comprehensive emergency procedures are non-negotiable. This includes detailed protocols for medical emergencies, mechanical failures, and severe weather conditions. These procedures should be clearly documented, readily accessible to all crew members, and regularly practiced through drills. A well-equipped onboard medical kit, satellite communication systems, and a comprehensive emergency contact list are essential components. Furthermore, contingency plans should be developed to address unforeseen circumstances, such as sudden equipment malfunctions or unexpected guest requests. For instance, having a pre-arranged agreement with a nearby repair service or a backup yacht in case of a major mechanical issue can significantly minimize disruption to charter operations.
Best Practices for Exceptional Customer Service
Exceptional customer service goes beyond meeting expectations; it’s about exceeding them. Proactive communication, personalized attention, and anticipating client needs are key. This includes remembering preferences from previous charters, tailoring activities to specific interests, and attending to even the smallest details. Building rapport with clients through genuine interaction and providing a welcoming and luxurious onboard experience fosters loyalty and positive word-of-mouth referrals. For example, a small gesture like remembering a client’s favorite drink or arranging a special surprise onboard can significantly enhance their experience. Regular client feedback collection and analysis helps identify areas for improvement and ensures continuous service enhancement.
Yacht Preparation Checklist for Charter
A thorough pre-charter checklist is essential for ensuring a smooth and safe charter. This checklist should be meticulously followed before each charter departure.
- Safety Checks: Comprehensive inspection of all safety equipment, including life rafts, life jackets, fire extinguishers, and navigation systems. Verification of all safety certificates and documentation.
- Technical Systems: Testing of all onboard systems, including engines, generators, watermakers, air conditioning, and communication equipment. Addressing any identified maintenance issues.
- Provisioning: Stocking the yacht with sufficient food and beverages based on the client’s preferences and the charter duration. Ensuring adequate supplies of water, ice, and other consumables.
- Cleaning and Hygiene: Thorough cleaning of the entire yacht, including cabins, bathrooms, and all common areas. Maintaining high hygiene standards throughout the yacht.
- Documentation: Verification of all necessary permits, licenses, and insurance documentation. Preparation of all relevant charter agreements and guest information.
Crew Management and Training
A successful yacht charter business hinges on a highly skilled and well-managed crew. The quality of the crew directly impacts the guest experience, influencing reviews and repeat bookings. Efficient crew management involves careful recruitment, comprehensive training, and strategies to maintain a positive and productive onboard environment.
Essential Skills and Qualifications for Yacht Crew Members
The skills and qualifications required vary significantly depending on the role. However, certain core competencies are essential across all positions. For example, all crew members should possess excellent communication skills, be adaptable to diverse situations, maintain a professional demeanor, and be physically fit to handle the demands of life at sea. Specific qualifications are more role-dependent. Captains require extensive nautical experience and relevant certifications, such as a Master’s license. Chefs need culinary expertise and experience catering to high-end clientele, often requiring formal culinary training and demonstrable experience in a high-pressure environment. Stewards require impeccable service skills and attention to detail. Engineers need mechanical aptitude and experience with various marine systems. All crew members benefit from training in safety procedures, including first aid and fire prevention.
Recruiting, Hiring, and Training Yacht Crew
The process begins with identifying the required crew based on the size and type of yacht. Recruitment strategies might include utilizing specialized maritime recruitment agencies, online job boards, and networking within the yachting industry. Thorough background checks and reference checks are crucial. Interviews should assess not only technical skills but also personality, teamwork abilities, and professionalism. Once hired, comprehensive training is essential. This might include onboard familiarization with the yacht’s systems, safety drills, and customer service training. Formal certifications in areas such as food safety and STCW (Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping) are often mandatory or highly desirable. Ongoing professional development opportunities should be provided to enhance skills and maintain high standards.
Maintaining Crew Morale and Fostering a Positive Work Environment
Maintaining a positive onboard environment is paramount for crew retention and operational efficiency. Clear communication channels, fair and consistent leadership, and a respectful work environment are essential. Opportunities for crew downtime and recreation are important for preventing burnout. Regular crew meetings can address concerns, provide feedback, and foster teamwork. Offering competitive salaries and benefits packages, including paid time off and opportunities for career advancement, is also crucial for attracting and retaining top talent. Addressing conflicts promptly and fairly is key to preventing larger issues. Regular performance evaluations provide constructive feedback and opportunities for improvement.
Roles and Responsibilities of Key Crew Members
| Role | Responsibilities | Qualifications | Key Skills |
|---|---|---|---|
| Captain | Overall safety and operation of the yacht, navigation, crew management | Master’s license, extensive nautical experience | Leadership, navigation, safety management |
| Chef | Planning and preparation of meals, menu planning, inventory management | Culinary training, experience in high-end catering | Culinary skills, menu planning, inventory management |
| First Mate/Engineer | Assisting the captain, maintenance of yacht systems, technical expertise | Relevant engineering qualifications, experience with marine systems | Mechanical aptitude, problem-solving, technical expertise |
| Steward/Hostess | Guest service, cabin maintenance, cleaning, laundry | Experience in hospitality, excellent customer service skills | Customer service, organization, attention to detail |
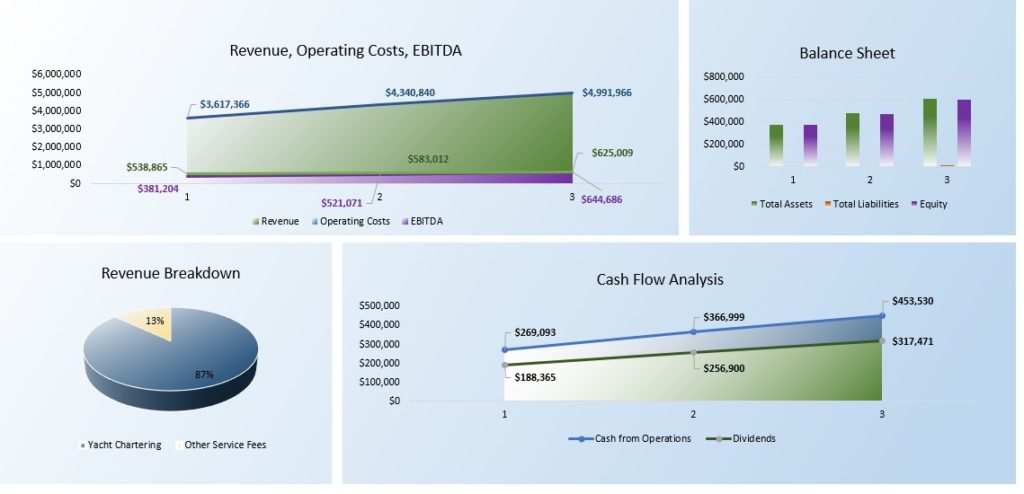
Financial Management and Growth: How To Start A Yacht Charter Business

Successfully navigating the financial landscape is crucial for the long-term viability and growth of any yacht charter business. This involves meticulous record-keeping, strategic cash flow management, and a well-defined plan for reinvesting profits to fuel expansion and enhance service offerings. Ignoring these aspects can lead to financial instability and hinder the business’s potential.
Effective financial management in a yacht charter business relies on accurate tracking of income and expenses, proactive cash flow management, and strategic planning for future growth. This section will Artikel key strategies for achieving these objectives and ensuring the financial health of your enterprise.
Income and Expense Tracking Methods
Implementing a robust accounting system is paramount. This should include detailed records of all income streams, such as charter fees, ancillary services (e.g., provisioning, water sports), and any additional revenue generated. Expenses should be categorized meticulously, encompassing fuel costs, maintenance and repairs, crew salaries, insurance premiums, marketing expenditures, and administrative overheads. Utilizing accounting software designed for small businesses, or hiring a professional accountant, will streamline this process and provide valuable financial insights. Regular reconciliation of bank statements against accounting records is crucial for identifying discrepancies and ensuring accuracy. Consider using a chart of accounts to systematically categorize all financial transactions. This will simplify reporting and analysis, providing a clear picture of the business’s financial performance.
Cash Flow Management and Profitability
Maintaining a healthy cash flow is essential for operational stability. This requires careful budgeting, forecasting, and proactive management of receivables (payments owed to the business) and payables (payments owed by the business). Developing a detailed cash flow projection, anticipating seasonal fluctuations in demand, and securing adequate lines of credit can help mitigate potential cash shortages. Pricing strategies should incorporate all operational costs and desired profit margins. Regularly reviewing financial statements, including profit and loss statements and balance sheets, is crucial for identifying areas for improvement and ensuring profitability. Consider offering flexible payment plans for clients to improve cash flow. For instance, allowing clients to pay a deposit upfront and the remaining balance closer to the charter date.
Expansion Strategies
Expansion opportunities for a successful yacht charter business are diverse. Adding more yachts to the fleet increases charter capacity and revenue potential. This should be carefully considered based on market demand and financial feasibility. Expanding service areas, targeting new demographics (e.g., corporate clients, families), or offering specialized charter experiences (e.g., fishing charters, diving excursions) can also drive growth. Strategic partnerships with hotels, resorts, or travel agencies can broaden the customer base. Acquiring a smaller, competing charter business could provide immediate access to established clients and resources. For example, a company initially operating in the Mediterranean could expand to the Caribbean, leveraging established brand recognition and client relationships to penetrate a new market.
Profit Reinvestment Plan
A well-defined plan for reinvesting profits is crucial for sustained growth. A portion of profits should be allocated to upgrading existing yachts, acquiring new vessels, enhancing marketing efforts, or investing in technology improvements (e.g., online booking systems, improved communication tools). Consider setting aside funds for unforeseen maintenance or repairs. Investing in crew training and development enhances service quality and employee satisfaction, leading to increased customer loyalty and positive word-of-mouth referrals. Diversifying investments outside the core business, such as purchasing real estate related to the yacht charter industry or investing in other complementary businesses, can provide additional streams of income and mitigate risk. For instance, investing in a marina or a yacht maintenance facility could create synergies and generate additional revenue streams.






