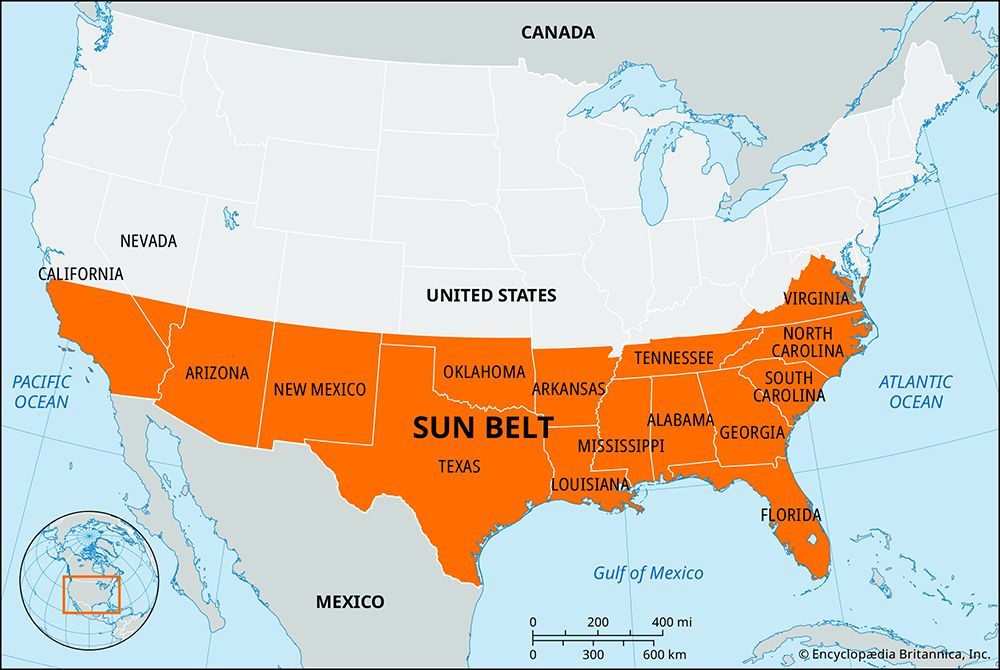
Defining “Sunbelt Loans”
The term “Sunbelt loans” isn’t a formally defined financial category like, say, a mortgage or auto loan. Instead, it’s a colloquial term referencing loans originated within the Sun Belt region of the United States. This region, characterized by its warm climate and generally strong economic growth, encompasses a significant portion of the country and, consequently, a substantial lending market. Understanding the nuances of this regional lending landscape requires a closer look at its geographical scope, the types of loans offered, and the institutions involved.
The geographical scope of Sunbelt loans is fluid, but generally includes states in the southern and southwestern United States. This typically encompasses states like Florida, Georgia, Texas, Arizona, California, Nevada, and New Mexico, among others. The precise boundaries can be debated, but the core characteristic is the warm, sunny climate and the often-associated rapid population and economic growth. This growth fuels a significant demand for various financial products, making it a lucrative area for lenders.
Types of Sunbelt Loans
Sunbelt loans encompass a wide range of financial products, mirroring the diverse financial needs of the region’s residents and businesses. These can include mortgages for residential and commercial properties, auto loans, personal loans, small business loans, and lines of credit. The specific types of loans available will vary depending on the lender and the borrower’s creditworthiness and financial situation. For example, Florida might see a high volume of mortgages due to its tourism industry and population influx, while Texas might see a higher demand for business loans due to its robust energy sector.
Financial Institutions Associated with Sunbelt Lending
A multitude of financial institutions operate within the Sun Belt, offering various loan products. These include national banks like Bank of America and Wells Fargo, regional banks with a strong Sun Belt presence (e.g., Regions Bank, SunTrust (now Truist)), credit unions serving local communities, and numerous online lenders. The competitive landscape fosters innovation and often leads to a wider array of loan options and potentially more competitive interest rates for borrowers. The specific institutions involved will vary significantly based on the particular state and locality within the Sun Belt.
Sunbelt Loan Interest Rates by State
Interest rates for Sunbelt loans vary significantly based on several factors, including the type of loan, the borrower’s credit score, the prevailing market interest rates, and the specific lender. The following table provides a *hypothetical* example, illustrating the potential range of interest rates for a standard 30-year fixed-rate mortgage across four Sun Belt states. It’s crucial to remember that these are illustrative figures and actual rates will fluctuate considerably. Always consult multiple lenders to secure the best possible rate.
| State | Average Interest Rate (Hypothetical) | Range (Hypothetical) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Florida | 6.5% | 5.5% – 7.5% | Higher demand in certain areas |
| Texas | 6.2% | 5.0% – 7.0% | Influenced by energy sector performance |
| California | 7.0% | 6.0% – 8.0% | Higher cost of living impacts rates |
| Arizona | 6.8% | 5.8% – 7.8% | Seasonal variations can affect rates |
Economic Factors Influencing Sunbelt Loans
The Sunbelt’s economic dynamism significantly impacts the lending landscape. Factors like population shifts, real estate market fluctuations, and regional economic stability all play crucial roles in shaping loan demand, availability, and terms. Understanding these interconnected elements is key to navigating the complexities of the Sunbelt loan market.
Population Growth and Loan Demand
The Sunbelt’s robust population growth fuels a surge in demand for various loan products. Increased migration to these states necessitates more housing, leading to a higher demand for mortgages. Simultaneously, the influx of new residents creates opportunities for businesses, resulting in increased demand for commercial loans and lines of credit to fund expansion and startups. This heightened demand directly impacts lending institutions, prompting them to adjust their lending strategies and potentially increase interest rates to manage risk. For example, the rapid growth of cities like Austin, Texas, and Phoenix, Arizona, has seen a corresponding explosion in mortgage applications and commercial loan requests.
Real Estate Markets and Loan Availability
The health of the Sunbelt’s real estate markets directly correlates with loan availability and terms. Booming real estate markets, characterized by rising property values and high demand, typically lead to increased loan availability as lenders see attractive investment opportunities. Conversely, a downturn in the real estate market can make lenders more cautious, tightening lending standards and potentially increasing interest rates to mitigate risk. For instance, during periods of rapid appreciation, lenders might offer more favorable terms, including lower interest rates and higher loan-to-value ratios. Conversely, during market corrections, stricter underwriting criteria and higher interest rates become the norm.
Economic Stability Across Sunbelt Regions and Lending Practices
Economic stability varies considerably across different Sunbelt regions. States with diverse economies and robust job markets, like Florida and Texas, generally experience more favorable lending conditions compared to areas heavily reliant on specific industries that might be susceptible to economic downturns. Lenders assess regional economic indicators, such as unemployment rates, income levels, and industry diversification, to gauge the risk associated with lending in a particular area. This risk assessment directly impacts the terms and availability of loans, with more economically stable regions typically benefiting from more favorable lending practices. For example, a lender might offer more competitive rates in a region with consistently low unemployment and strong economic growth compared to a region experiencing economic instability.
Hypothetical Recession Scenario and Sunbelt Loan Applications
Let’s imagine a hypothetical scenario: a nationwide recession hits the United States. In the Sunbelt, we’d likely see a significant decrease in loan applications, particularly for mortgages and commercial loans. The decline in consumer confidence and increased job insecurity would reduce demand for new homes and business expansions. Lenders, anticipating higher default rates, would likely tighten their lending criteria, increasing interest rates and reducing the amount of money available for loans. This scenario could disproportionately affect regions of the Sunbelt that are heavily reliant on a single industry, like tourism or construction, making them more vulnerable to economic downturns. This could lead to a noticeable slowdown in real estate activity and a decrease in overall economic growth in those specific areas. The overall impact would depend on the severity and duration of the recession and the resilience of the various Sunbelt economies.
Types of Borrowers Utilizing Sunbelt Loans
Sunbelt loans, catering to the unique financial needs of the rapidly growing Sunbelt region, attract a diverse range of borrowers. Understanding these borrower profiles is crucial for lenders to tailor their offerings and effectively manage risk. This analysis will dissect the demographics, financial situations, and loan purposes of typical Sunbelt loan applicants, offering insights into the market’s dynamics.
Sunbelt loans – The Sunbelt’s economic boom attracts individuals and businesses from various backgrounds, leading to a wide spectrum of loan applications. Factors like population growth, job creation, and real estate appreciation all influence the types of borrowers seeking financing. We’ll examine these factors through the lens of credit scores, income levels, and the reasons behind loan applications.
Demographic Groups Seeking Sunbelt Loans
The Sunbelt region’s population is incredibly diverse, resulting in a varied borrower base. We see a significant number of younger individuals, drawn by job opportunities and a more affordable cost of living (compared to coastal areas) who often require loans for home purchases or starting businesses. Simultaneously, established families are also seeking loans, frequently for home improvements, refinancing, or debt consolidation. Retirement communities in the Sunbelt also contribute to a demographic of older borrowers, possibly seeking reverse mortgages or loans to cover healthcare expenses. This blend of age groups, combined with a growing Hispanic population, creates a dynamic and multifaceted lending environment.
Loan Purposes and Borrower Needs, Sunbelt loans
Sunbelt loans serve a wide array of purposes. Home purchases are a significant driver, fueled by the region’s population growth and relative affordability of housing compared to other parts of the country. This includes both first-time homebuyers and those upgrading or relocating. Business ventures are another significant category. The entrepreneurial spirit is strong in many Sunbelt cities, leading to a high demand for loans to fund startups, expansions, or acquisitions. Beyond these two main categories, borrowers also utilize Sunbelt loans for debt consolidation, home improvements, and financing educational expenses.
Borrower Profiles Based on Credit Scores and Income Levels
The creditworthiness and income levels of Sunbelt loan applicants vary significantly. We can broadly categorize borrowers into three groups:
- Prime Borrowers: These individuals boast excellent credit scores (750+) and substantial income, often securing loans with favorable interest rates for large-scale purchases like high-value homes or significant business investments. Example: A high-earning tech professional relocating from Silicon Valley to Austin, Texas, seeking a mortgage for a luxury home.
- Subprime Borrowers: This group possesses lower credit scores (below 620) and potentially lower income levels. They may face higher interest rates and stricter lending requirements. Example: A small business owner in Florida with a moderate credit history seeking a loan to expand their operations, demonstrating a strong business plan to mitigate risk.
- Near-Prime Borrowers: This segment falls between prime and subprime, with credit scores ranging from 620-749. They represent a substantial portion of the market, often seeking loans for home purchases, refinancing, or debt consolidation. Example: A young couple in Arizona with good income but building their credit history, seeking a mortgage for their first home.
Examples of Loan Applications Demonstrating Diverse Borrower Needs
Let’s illustrate with specific examples:
- Maria Rodriguez: A first-generation immigrant in Phoenix, Arizona, with a strong work ethic and growing business. She seeks a small business loan to expand her successful catering company, demonstrating strong financial projections and a clear business plan. Her credit score is 680.
- John Smith: A recently retired couple in Naples, Florida, seeking a reverse mortgage to supplement their retirement income and cover healthcare costs. They have a high net worth but are seeking a loan that leverages their home equity.
- Sarah Jones: A young professional in Atlanta, Georgia, with an excellent credit score and stable income, seeking a mortgage for a new condominium. She’s looking for a competitive interest rate and flexible loan terms.
Regulatory Landscape of Sunbelt Lending
The Sunbelt, encompassing a vast swathe of the southern and southwestern United States, presents a complex and often fragmented regulatory landscape for lending practices. Understanding this landscape is crucial for both lenders and borrowers, as inconsistencies across states significantly impact interest rates, loan terms, and consumer protections. This section will delve into the intricacies of state-specific regulations, the role of federal oversight, and the potential impact of future regulatory shifts on the Sunbelt loan market.
State-Specific Regulations Governing Lending Practices
State-level regulations play a dominant role in shaping the Sunbelt lending environment. Each state within the region has its own unique set of laws governing interest rates, fees, licensing requirements for lenders, and consumer protections. For instance, some states may have usury laws that cap the maximum allowable interest rate on loans, while others may have more lenient regulations. These variations create a patchwork of rules, leading to significant differences in the cost and availability of loans across the Sunbelt. Consider the contrasting regulatory approaches of states like Texas, known for its relatively deregulated lending environment, compared to California, which enforces stricter consumer protection measures. These differences directly influence the types of loans offered, the terms available to borrowers, and the overall competitiveness of the lending market within each state.
Comparison of Consumer Protection Laws Across States
Consumer protection laws related to Sunbelt loans vary significantly across different states. Some states have robust laws requiring lenders to disclose all fees and interest rates clearly, provide borrowers with ample opportunity to understand the loan terms before signing, and establish clear processes for handling loan defaults. Other states may have weaker consumer protection laws, leaving borrowers more vulnerable to predatory lending practices. For example, some states have stricter requirements for payday lenders, while others have less stringent oversight, potentially leading to higher default rates and financial hardship for borrowers. This disparity underscores the need for borrowers to carefully research the specific regulations in their state before entering into any loan agreement.
Role of Federal Agencies in Overseeing Sunbelt Lending Activities
While state laws form the primary regulatory framework, federal agencies also play a crucial role in overseeing Sunbelt lending activities. The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), for example, has jurisdiction over many types of consumer financial products and services, including loans. The CFPB works to ensure that lenders comply with federal laws designed to protect consumers from unfair, deceptive, or abusive practices. Other federal agencies, such as the Federal Reserve and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), also have oversight responsibilities depending on the type of lender and the type of loan involved. The interplay between federal and state regulations creates a complex web of rules that lenders must navigate.
Impact of Changes in Regulatory Frameworks on the Sunbelt Loan Market
Changes in regulatory frameworks, whether at the state or federal level, can significantly impact the Sunbelt loan market. For example, increased consumer protection regulations could lead to higher compliance costs for lenders, potentially resulting in higher interest rates or a reduction in the availability of certain types of loans. Conversely, deregulation could lead to increased competition and lower interest rates, but might also increase the risk of predatory lending practices. Recent changes in federal regulations, such as those related to payday lending, have already had a noticeable impact on the market in some Sunbelt states, demonstrating the dynamic nature of this regulatory environment and its profound effect on access to credit and the overall financial health of Sunbelt communities.
Future Trends in Sunbelt Lending
The Sunbelt region, known for its robust economic growth and population influx, is poised for significant changes in its lending landscape. Understanding these future trends is crucial for both lenders and borrowers navigating this dynamic market. Factors like interest rate fluctuations, technological advancements, and the emergence of innovative lending models will shape the future of Sunbelt loans.
Interest Rate Shifts and Loan Accessibility
Fluctuations in interest rates will directly impact the accessibility of Sunbelt loans. Rising interest rates, for example, could lead to higher borrowing costs, potentially reducing the number of individuals and businesses able to secure loans. Conversely, a period of lower interest rates could stimulate loan demand, making financing more readily available. This dynamic interplay necessitates a proactive approach from lenders, requiring them to adapt their lending strategies to accommodate changing market conditions. We’ve seen this effect historically; during periods of economic uncertainty, like the 2008 financial crisis, stricter lending standards and higher interest rates made loans harder to obtain, particularly in rapidly growing regions like those in the Sunbelt. Conversely, periods of low interest rates, like those seen in the years following the 2008 crisis, fueled increased borrowing and investment.
Technological Advancements in Sunbelt Lending
Technological advancements are rapidly transforming the Sunbelt lending industry. The rise of fintech companies and the increasing adoption of AI and machine learning are streamlining loan application processes, improving credit scoring accuracy, and enabling faster loan approvals. Blockchain technology holds the potential to enhance transparency and security in loan transactions, reducing fraud and improving efficiency. For example, automated underwriting systems can analyze vast datasets to assess risk more efficiently than traditional methods, potentially leading to quicker approvals and more accessible credit for qualified borrowers. Furthermore, the use of online platforms and mobile applications is expanding access to loans, especially for borrowers in underserved communities.
Innovative Lending Models in the Sunbelt
The Sunbelt region is fertile ground for the development of innovative lending models. We can expect to see a rise in alternative lending options, such as peer-to-peer lending platforms and crowdfunding initiatives, providing more choices for borrowers. Furthermore, the increasing focus on sustainable development may lead to the growth of green loans, specifically designed to finance environmentally friendly projects. For instance, a solar panel installation company in Arizona might utilize a green loan to fund its expansion, aligning with the region’s emphasis on renewable energy. Similarly, a small business in Florida focused on sustainable tourism could leverage alternative financing options to grow its operations.
Projected Growth in Sunbelt Loan Volume
| Year | Projected Loan Volume (Billions of USD) | Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 150 | – |
| 2025 | 165 | 10% |
| 2026 | 185 | 12% |
| 2027 | 210 | 13.5% |
| 2028 | 240 | 14.3% |
This table projects a steady increase in Sunbelt loan volume over the next five years, driven by population growth, economic expansion, and the increasing adoption of innovative lending models. The growth rate is expected to remain relatively consistent, reflecting the sustained dynamism of the Sunbelt economy. These figures are based on current economic forecasts and historical lending trends in the region, taking into account factors like population growth, job creation, and investment in infrastructure. While unforeseen economic downturns could impact these projections, the underlying growth drivers suggest continued expansion in the Sunbelt lending market.
Sunbelt Loans vs. Other Regional Loan Markets
The Sunbelt region, encompassing the southern and southwestern United States, presents a distinct loan market compared to other regions like the Northeast and Midwest. Understanding these differences is crucial for both lenders and borrowers, as varying economic conditions, risk profiles, and regulatory environments significantly impact loan terms and approval rates.
Loan terms, risk assessments, and approval rates fluctuate across the US, reflecting regional economic disparities and regulatory nuances. This analysis will illuminate the key distinctions between Sunbelt loan markets and those in other regions, providing insights into the advantages and disadvantages of borrowing in each.
Comparative Loan Terms Across Regions
Interest rates, loan amounts, and repayment periods often vary significantly depending on the region. For instance, Sunbelt states, fueled by population growth and a robust construction industry, might see more competitive rates for mortgages and commercial real estate loans compared to the Northeast, where property values are generally higher and competition may be less intense. Conversely, personal loans in areas with higher unemployment rates, such as some parts of the Midwest, may carry higher interest rates to offset increased risk. The availability of different loan products also varies. For example, agricultural loans might be more prevalent in the Midwest, while loans supporting tourism-related businesses might be more common in the Sunbelt.
Regional Differences in Risk Assessment
Lenders employ diverse risk assessment models tailored to specific regional characteristics. In the Sunbelt, rapid population growth and fluctuating housing markets introduce unique risks, prompting lenders to scrutinize credit scores and debt-to-income ratios more rigorously. Conversely, in more established markets like the Northeast, lenders might place greater emphasis on the stability of employment and the longevity of a borrower’s residence. Furthermore, natural disaster risk, higher in some Sunbelt areas, can influence loan terms and insurance requirements, increasing the overall cost of borrowing. The Midwest, with its cyclical agricultural economy, might see risk assessments focused on crop yields and commodity prices.
Factors Influencing Loan Approval Rates
Several factors contribute to the variations in loan approval rates across different regions. Economic indicators such as unemployment rates, average income levels, and housing market volatility play a significant role. Regions with strong economic growth and low unemployment generally exhibit higher loan approval rates. Regulatory environments also play a part; stricter lending regulations in certain states may lead to lower approval rates. Furthermore, the concentration of lenders and the competitiveness of the market influence approval rates. A highly competitive market, such as that in some Sunbelt cities, could potentially result in higher approval rates due to increased competition among lenders. Conversely, less competitive markets might have stricter lending standards.
Illustrative Examples of Regional Loan Advantages and Disadvantages
Consider a small business owner seeking a loan to expand their operations. In a rapidly growing Sunbelt city, they might find attractive loan offers with competitive interest rates, reflecting the region’s economic dynamism. However, the intense competition and high demand for loans could also lead to more stringent requirements and a more competitive application process. In contrast, a similar business owner in a smaller Midwest town might encounter fewer loan options, potentially facing higher interest rates to compensate for perceived higher risk, but the less competitive market might result in a simpler application process. For a homeowner seeking a mortgage, securing financing in a stable Northeast market might be less challenging due to established property values and a lower risk profile, though interest rates might not be as competitive as those in some Sunbelt areas experiencing rapid growth. However, the higher property values in the Northeast might require a larger down payment.