VA Max Loan Amount Worksheet: Unlocking the potential of your VA home loan begins with understanding its limits. This worksheet is your key to navigating the complexities of VA loan eligibility and calculating the maximum loan amount you can secure. We’ll break down the factors influencing your loan amount, from your veteran status and entitlement to your credit score and the property’s appraisal value. Understanding these factors empowers you to make informed decisions and achieve your homeownership dreams.
This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step walkthrough of using the VA loan amount worksheet, offering practical examples and hypothetical scenarios to illustrate the process. We’ll also compare VA loans to conventional mortgages, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each to help you determine the best financing option for your unique circumstances. By the end, you’ll be equipped to confidently navigate the VA loan process and maximize your borrowing power.
Understanding VA Loan Amount Limits: Va Max Loan Amount Worksheet
VA loan limits, unlike conventional mortgages, aren’t solely determined by your creditworthiness or income. Instead, they are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, primarily focusing on the county in which the property is located and the type of loan being sought. Understanding these limitations is crucial for accurately assessing your borrowing power and making informed decisions about your home purchase.
Several key factors significantly impact the maximum loan amount a veteran can receive through a VA-backed mortgage. The most significant is the county in which the property is located. The Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) sets conforming loan limits annually for each county, and these limits serve as a baseline for VA loans. However, VA loans can often exceed these limits, particularly in high-cost areas, through what’s known as a “high-balance” loan. This means that while the FHFA sets a baseline, the actual maximum loan amount can be significantly higher, depending on the specific county and prevailing market conditions. The type of loan itself, such as a purchase loan versus a refinance loan, will not directly affect the maximum amount; however, the property’s value will be a crucial factor in determining the final loan amount, regardless of the loan type. Finally, the year also plays a role, as these conforming loan limits are adjusted annually to reflect changes in housing prices.
County-Specific Loan Limits
The county where the property is located directly influences the maximum VA loan amount. High-cost areas tend to have significantly higher limits than those in lower-cost areas. For instance, a veteran seeking a VA loan in a county with a high cost of living, such as certain areas of California or New York, might qualify for a substantially larger loan amount compared to a veteran in a more rural county with a lower cost of living, such as in parts of the Midwest. This disparity is directly linked to the FHFA’s conforming loan limits, which vary significantly across counties. A veteran should therefore always check the specific county limits before beginning their home search.
VA Loan Limits Across States
The following table provides a simplified comparison of VA loan limits across several states. It’s important to remember that these are examples and may not represent all counties within each state. Actual limits can vary significantly even within the same state due to differences in county-level housing costs. This data should be used for illustrative purposes only and should not be considered exhaustive or a substitute for consulting official sources for the most up-to-date information.
| State | County | Maximum Loan Amount | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | Los Angeles | $900,000 | 2024 (Example) |
| Texas | Travis | $550,000 | 2024 (Example) |
| New York | New York | $850,000 | 2024 (Example) |
| Florida | Miami-Dade | $650,000 | 2024 (Example) |
| Illinois | Cook | $500,000 | 2024 (Example) |
Using the VA Loan Amount Worksheet
A VA loan amount worksheet is a crucial tool for veterans and service members seeking to understand their borrowing power under the Department of Veterans Affairs home loan program. It helps determine the maximum loan amount a veteran is eligible for, factoring in their entitlement, property location, and other relevant financial considerations. Effectively using this worksheet simplifies the pre-qualification process and allows for a more informed home-buying experience.
The worksheet’s functionality lies in its ability to consolidate key information into a readily understandable format. It streamlines the calculation of the maximum VA loan guarantee, which is a significant portion of the overall loan amount. This calculation depends on several factors, making a worksheet indispensable for accurate estimation. By systematically inputting data, the worksheet provides a clear picture of the borrower’s financial capacity within the VA loan program’s parameters.
Worksheet Completion Steps
The accurate completion of a VA loan amount worksheet involves a methodical approach, ensuring all necessary information is correctly inputted. Inaccurate data will lead to an inaccurate loan amount estimation, potentially causing delays or complications in the home-buying process. Careful attention to detail is essential throughout the process.
- Gather Required Information: Begin by collecting all the necessary documents and information. This typically includes your Certificate of Eligibility (COE), which confirms your eligibility for a VA loan and specifies your entitlement amount. You’ll also need information about the property you intend to purchase, including its location and estimated value. Finally, gather details about your current financial situation, such as your credit score and debt-to-income ratio.
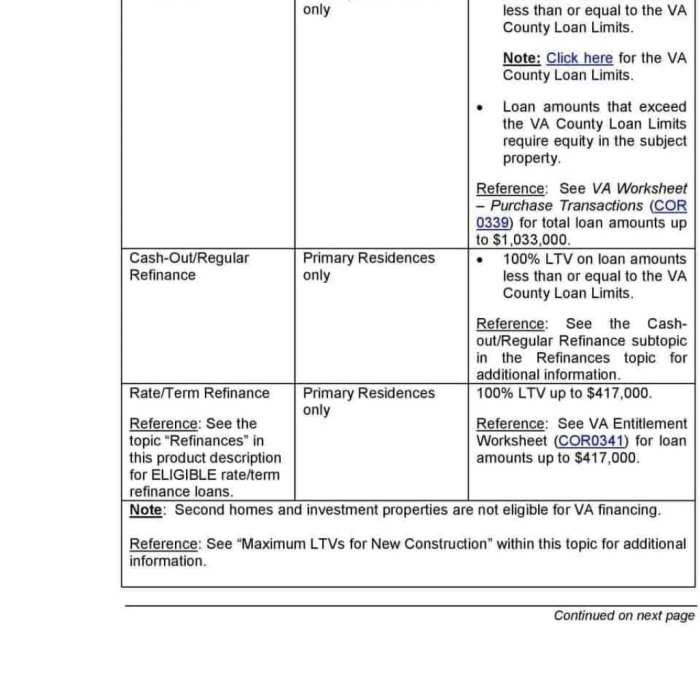
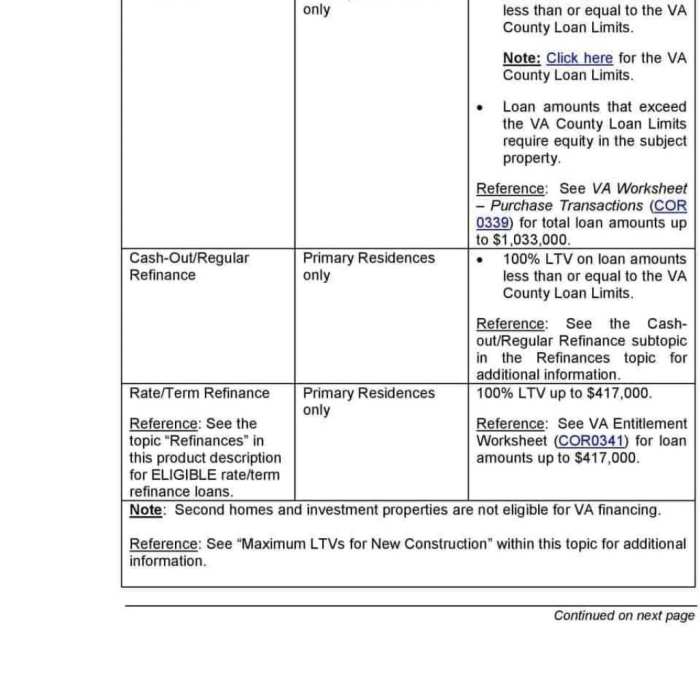
- Determine Your VA Entitlement: Your COE will state your full entitlement amount. This represents the maximum amount the VA will guarantee on your behalf. For example, a veteran with a full entitlement might have $36,000, meaning the VA guarantees up to that amount of the loan if you default. This entitlement amount is a key input for the worksheet.
- Identify County Loan Limits: VA loan limits vary by county. The worksheet will require you to input the county where the property is located. This is crucial because the VA sets maximum loan amounts based on geographic location, reflecting differences in property values across the country. For example, a county with high property values will likely have a higher loan limit than a county with lower values. You can find these limits on the VA website or through your lender.
- Calculate the Maximum Loan Amount: The worksheet will have a section where you input your entitlement and the county loan limit. The worksheet then performs the necessary calculations to determine your maximum VA loan amount. This calculation considers your entitlement and the county loan limit, ensuring the loan amount remains within the VA’s guidelines. For example, if your entitlement is $36,000 and the county loan limit is $647,200, your maximum loan amount might be calculated based on these two figures, considering any potential adjustments for a down payment.
- Review and Verify: Once the worksheet has calculated your maximum loan amount, carefully review all the inputted information to ensure accuracy. Double-check the figures for your entitlement, county loan limit, and any other relevant data. Any errors in these inputs could lead to a significant miscalculation of your borrowing capacity.
Calculating VA Loan Eligibility
Determining your eligibility for a VA loan involves understanding your veteran status and your available entitlement. The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) guarantees a portion of your loan, reducing the lender’s risk and making it easier for veterans to secure financing. This guarantee is based on your entitlement, which is determined by your military service history.
VA loan eligibility hinges on two primary factors: your veteran status and your entitlement. Veteran status is established through your service history, while entitlement represents the amount of the loan the VA will guarantee. The amount of your entitlement directly impacts the maximum loan amount you can obtain. The process involves verifying your service records and calculating your available entitlement based on your service history and any previous use of your VA home loan benefit.
Veteran Status Verification
The first step in determining VA loan eligibility is verifying your veteran status. This typically involves providing documentation to the lender, such as your Certificate of Eligibility (COE). The COE confirms your eligibility for VA home loan benefits and provides details about your entitlement. The lender will use this information to determine your eligibility and the amount of the loan they can offer. Different branches of service and periods of service may have different requirements for eligibility. For example, some service members may need a minimum amount of service time to qualify for the full VA home loan benefit.
Entitlement Calculation
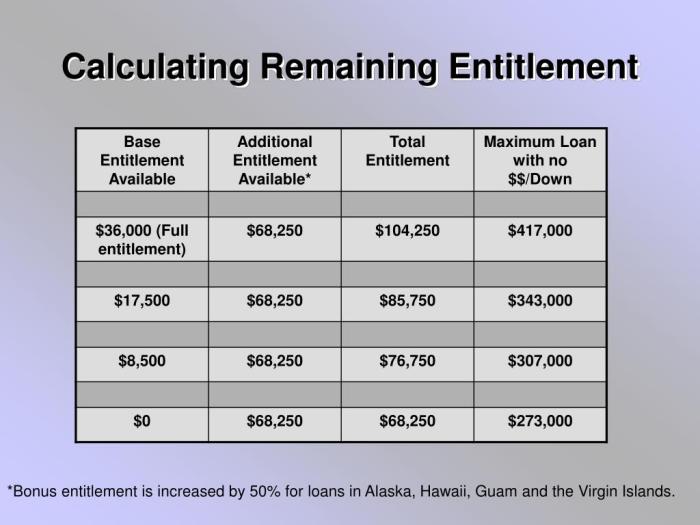
Your VA loan entitlement is the amount the VA will guarantee on your behalf to the lender. This guarantee protects the lender against losses if you default on your loan. The basic entitlement is typically $36,000, but this can vary depending on your service history and any previous use of your VA home loan benefit. For example, if you have previously used part of your entitlement for a previous VA loan, your current entitlement will be reduced accordingly. The entitlement is not a cash amount you receive; it’s the amount of loan the VA will guarantee.
Examples of Veteran Scenarios and Loan Eligibility
Let’s consider a few examples to illustrate how veteran status and entitlement affect VA loan eligibility. These are simplified examples and actual eligibility may vary based on individual circumstances and current VA regulations.
| Veteran Scenario | Service History | Previous VA Loan Use | Available Entitlement | Loan Eligibility (Example – assuming loan limits allow) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Veteran A | 10 years active duty | None | $36,000 | Up to a loan amount where the VA guarantee is $36,000 |
| Veteran B | 5 years active duty | Used $10,000 of entitlement previously | $26,000 | Up to a loan amount where the VA guarantee is $26,000 |
| Veteran C | 20 years active duty, served during wartime | None | Full entitlement (may exceed $36,000, check current VA guidelines) | Potentially higher loan amount due to increased entitlement |
It’s crucial to note that these are illustrative examples. The actual entitlement and loan eligibility depend on many factors and should be verified with the VA or a qualified mortgage lender.
Calculating Available Entitlement
Calculating your available entitlement involves determining your basic entitlement and subtracting any previously used entitlement. The formula is straightforward:
Available Entitlement = Basic Entitlement – Previously Used Entitlement
For instance, if your basic entitlement is $36,000 and you used $10,000 on a previous VA loan, your available entitlement is $26,000. This means the VA will guarantee up to $26,000 of your new loan. It is strongly recommended to contact the VA or a lender to determine your exact entitlement.
Factors Affecting Loan Amount

While your VA entitlement determines your *maximum* loan guarantee, several other factors significantly influence the actual loan amount a lender approves. These factors are assessed by lenders to determine your risk profile and ability to repay the loan. Understanding these factors is crucial for maximizing your borrowing power and securing the best possible mortgage terms.
Beyond the VA guarantee, the lender’s assessment of your financial health and the property’s value are paramount. These evaluations directly impact the final loan amount you’ll receive. A strong financial profile combined with a property appraised at or above the purchase price significantly increases your chances of securing a larger loan. Conversely, weaknesses in any of these areas can reduce the loan amount offered, or even lead to loan denial.
Credit Score Impact on Loan Amount
Your credit score is a critical factor lenders consider when assessing your loan application. A higher credit score demonstrates a history of responsible financial management, reducing the lender’s perceived risk. This typically translates to more favorable interest rates and potentially higher loan amounts. For example, borrowers with credit scores above 740 often qualify for the best rates and loan terms, potentially allowing them to borrow more than those with lower scores. Conversely, a low credit score might limit loan eligibility or result in a smaller loan amount due to the increased risk perceived by the lender. Lenders may also require a larger down payment from borrowers with lower credit scores to compensate for the added risk.
Debt-to-Income Ratio’s Influence on Loan Amount
The debt-to-income ratio (DTI) measures your monthly debt payments relative to your gross monthly income. A lower DTI indicates a greater capacity to manage additional debt, making you a less risky borrower. Lenders generally prefer borrowers with a DTI below 43%, although this can vary depending on the lender and other factors. A high DTI can restrict the loan amount offered, as lenders are cautious about approving loans that might strain your finances. For instance, a borrower with a high DTI might be approved for a smaller loan amount to keep their overall debt manageable, or they may be denied altogether.
Property Appraisal and Loan Amount
The appraised value of the property you intend to purchase is a critical determinant of the loan amount you can receive. Lenders will not typically lend more than the appraised value of the property, as this would expose them to significant risk. If the appraisal comes in lower than the purchase price, you may need to make a larger down payment, reduce the purchase price, or even walk away from the deal. A property appraised at a higher value than the purchase price, however, could allow you to borrow a larger amount or reduce the down payment needed.
| Factor | Impact on Loan Amount | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Credit Score | Higher score = Higher potential loan amount; Lower score = Lower potential loan amount or loan denial | Reflects responsible financial history; impacts interest rates and lender risk assessment. |
| Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI) | Lower DTI = Higher potential loan amount; Higher DTI = Lower potential loan amount or loan denial | Measures monthly debt payments relative to income; lower DTI indicates greater repayment capacity. |
| Property Appraisal | Appraisal ≤ Purchase Price = Loan amount limited to appraisal; Appraisal > Purchase Price = Potential for higher loan amount | Lenders generally won’t lend more than the appraised value of the property. |
VA Loan Amount Worksheet Examples
This section provides three hypothetical scenarios demonstrating how to complete a VA loan amount worksheet. Each scenario illustrates different levels of entitlement and financial situations, highlighting the variability in potential loan amounts. Understanding these examples will help you better grasp the process of determining your own VA loan eligibility.
Scenario 1: Full Entitlement, High Credit Score
Veteran: John Smith, served 10 years, full entitlement ($36,000).
County: Fairfax County, VA (High-cost area)
Credit Score: 780
Desired Home Price: $600,000
Down Payment: 0%
VA Funding Fee: 2.3% of the loan amount (based on full entitlement and no down payment)
Loan Amount Calculation:
Maximum VA loan amount is based on the Certificate of Eligibility, which is $36,000. In high-cost areas, this can be exceeded, but the amount of the loan is still determined by the property’s value and the lender’s appraisal. Assuming the property appraises at $600,000, and John qualifies for the loan based on his credit score and income, the loan amount would be $600,000. The VA funding fee would be $600,000 * 0.023 = $13,800.
Total Loan Cost: $600,000 + $13,800 = $613,800
Scenario 2: Partial Entitlement, Average Credit Score
Veteran: Jane Doe, served 4 years, partial entitlement ($18,000).
County: Rural area of Kansas (Low-cost area)
Credit Score: 700
Desired Home Price: $250,000
Down Payment: 0%
VA Funding Fee: 2.3% of the loan amount (based on partial entitlement and no down payment)
Loan Amount Calculation:
Jane’s partial entitlement limits her loan amount. While her desired home price is $250,000, her entitlement is only $18,000. Because this is a low-cost area, the loan amount will likely be approved for the full $250,000 as long as her income and credit are sufficient. The VA funding fee would be $250,000 * 0.023 = $5,750.
Total Loan Cost: $250,000 + $5,750 = $255,750
Scenario 3: Full Entitlement, Low Credit Score, Va max loan amount worksheet
Veteran: Robert Lee, served 8 years, full entitlement ($36,000).
County: Suburban area of Texas (Moderate-cost area)
Credit Score: 620
Desired Home Price: $300,000
Down Payment: 5%
VA Funding Fee: 3.6% of the loan amount (higher rate due to low credit score and full entitlement with no down payment).
Loan Amount Calculation:
Robert’s lower credit score may impact his ability to secure a loan, and the funding fee is higher. He is making a 5% down payment, reducing the loan amount. His down payment is $300,000 * 0.05 = $15,000. The loan amount will be $300,000 – $15,000 = $285,000. The VA funding fee will be $285,000 * 0.036 = $10,260.
Total Loan Cost: $285,000 + $10,260 = $295,260
Comparing VA Loans to Conventional Loans
VA loans and conventional mortgages represent distinct pathways to homeownership, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages regarding maximum loan amounts and other crucial factors. Understanding these differences is vital for prospective homebuyers to make informed decisions aligned with their financial situations and goals.
VA loans, backed by the Department of Veterans Affairs, offer several key benefits, particularly concerning loan amounts. Unlike conventional loans, which are subject to stricter lending criteria and often require larger down payments, VA loans typically allow for 100% financing, eliminating the need for a down payment. This significantly impacts the maximum loan amount a veteran can access, as the limiting factor shifts from available down payment funds to the veteran’s eligibility and the lender’s appraisal of the property. Conventional loans, on the other hand, have maximum loan amounts determined by factors such as credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and loan-to-value ratio, all of which can significantly impact the ultimate borrowing capacity.
Maximum Loan Amounts
VA loans don’t have a fixed national maximum loan amount. Instead, the maximum loan amount a veteran can receive is determined by the county loan limit set by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) for conforming loans. This county-specific limit ensures that VA loans remain competitive within the local real estate market. This contrasts with conventional loans, where conforming loan limits also exist, but exceeding these limits leads to jumbo loans, which typically have stricter lending requirements and higher interest rates. Non-conforming conventional loans can often exceed the VA loan limit in certain high-cost areas, offering greater borrowing capacity to those who qualify. For example, a veteran in a high-cost area like San Francisco might find the county’s conforming loan limit (and thus their VA loan maximum) significantly lower than the maximum loan amount available through a jumbo conventional mortgage, assuming they meet the stringent credit and income requirements.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The absence of a down payment requirement is a significant advantage of VA loans, allowing veterans to purchase homes with less upfront capital. However, VA loans typically involve funding fees, which can add to the overall cost of borrowing. Conventional loans often require a down payment, potentially limiting the maximum loan amount a borrower can obtain. However, a larger down payment can translate to a lower interest rate and potentially lower monthly payments. The specific advantages and disadvantages will vary depending on individual circumstances, including credit score, income, and the local real estate market.
Situations Favoring VA Loans
A VA loan might be more advantageous than a conventional loan in several situations. For example, a veteran with a lower credit score or limited savings might find it easier to qualify for a VA loan due to the absence of a down payment requirement. Similarly, a veteran looking to purchase a home in a competitive market might benefit from the ability to make a full-price offer without needing to factor in a down payment. Furthermore, veterans with less disposable income might find the lower monthly payments (resulting from potentially lower interest rates or the elimination of Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI)) particularly attractive. A first-time homebuyer veteran with limited savings would likely find the VA loan’s 100% financing option significantly more appealing than the down payment requirement of a conventional loan.
Resources for VA Loan Information
Navigating the world of VA loans can be complex, especially when determining your loan eligibility and potential loan amount. Fortunately, numerous reliable resources exist to guide veterans through this process. Accessing accurate and up-to-date information is crucial for making informed decisions about your home financing.
The following list highlights key resources offering comprehensive information on VA loan amounts and eligibility criteria. Each resource provides a different perspective and level of detail, allowing you to build a complete understanding of your options.
VA.gov Website
The official website of the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is the primary source for accurate and comprehensive information regarding VA home loans. This website provides detailed explanations of eligibility requirements, loan limits, and the application process. You can find interactive tools, calculators, and frequently asked questions (FAQs) designed to help you understand your VA loan benefits. Specific sections on loan limits and eligibility are clearly Artikeld, allowing veterans to quickly locate relevant information.
VA Loan Lenders
Directly contacting VA-approved lenders is another excellent way to obtain personalized information about VA loan amounts. These lenders can provide pre-qualification information based on your individual financial circumstances and credit history. They can also explain the nuances of the VA loan process, answer specific questions, and provide tailored guidance on the loan amounts you might qualify for in your area. Different lenders may have varying interpretations of guidelines or specific programs, so it’s beneficial to compare offerings.
Veteran Service Organizations (VSOs)
Organizations like the Veterans of Foreign Wars (VFW), the American Legion, and the Disabled American Veterans (DAV) offer invaluable support and resources to veterans, including guidance on VA home loans. Many VSOs have dedicated staff who are knowledgeable about VA loan programs and can assist with the application process. They often provide counseling services and can help veterans navigate potential challenges they may encounter during the loan application process. This personalized assistance is particularly helpful for veterans who may require additional support in understanding complex financial matters.
Housing Counseling Agencies
HUD-approved housing counseling agencies provide free or low-cost counseling services to help veterans understand their home-buying options, including VA loans. These agencies can offer guidance on budgeting, credit repair, and the overall home-buying process. They can help veterans determine their affordability and assist in navigating the complexities of obtaining a VA loan. Their services are often focused on providing broader financial literacy and support, helping veterans make sound financial decisions.
Illustrative Example: Property Value and Loan Amount
This example demonstrates how a veteran can determine their potential VA loan amount based on property value and their Certificate of Eligibility (COE). We’ll walk through a hypothetical scenario, highlighting the calculation process.
Let’s assume a veteran, John, has a full VA loan entitlement of $364,000. He’s found a house he loves priced at $400,000. He intends to make a down payment. The calculation of his potential VA loan amount will depend on his down payment and his entitlement.
VA Loan Amount Calculation
John’s full VA entitlement is $364,000. This represents the maximum amount the VA guarantees on his behalf to the lender. However, the actual loan amount will be less than the full entitlement if he makes a down payment. If John makes a down payment of $36,000 (10% of the property value), his loan amount is calculated as follows:
Property Value – Down Payment = Loan Amount
$400,000 – $36,000 = $364,000
In this case, John’s loan amount would be $364,000, which is equal to his full entitlement. This means the VA will guarantee the full loan amount to the lender. If the property value was higher, and John still made a $36,000 down payment, his loan amount would be capped at his entitlement. If the property value was lower, his loan amount would be the property value minus the down payment, provided it’s less than his entitlement.
Visual Representation of Loan Amount Calculation
We can represent this scenario visually through a textual description:
Imagine a rectangle representing the property value ($400,000). A smaller rectangle within it represents the down payment ($36,000). The remaining larger portion of the rectangle represents the loan amount ($364,000). This larger portion is further divided into two sections: one representing the portion covered by John’s entitlement ($364,000) and the other (non-existent in this case) representing any amount exceeding the entitlement that John would have to cover himself. Since John’s loan amount exactly matches his entitlement, the second section is absent. If the property value was higher than $400,000 with the same down payment, the entitlement section would remain the same size, while the property value and loan amount rectangles would extend beyond it. The portion extending beyond the entitlement would represent the amount John would need to pay without VA guarantee.
Final Summary
Securing a VA home loan can be a significant step towards achieving your homeownership goals. By utilizing the VA Max Loan Amount Worksheet and understanding the factors that influence your loan amount, you can confidently navigate the process and make informed decisions. Remember to carefully review your financial situation, explore all available resources, and consider consulting with a qualified mortgage professional for personalized guidance. With careful planning and a thorough understanding of the VA loan program, you can unlock the potential of your veteran benefits and find the perfect home.
Q&A
What happens if my property appraisal comes in lower than expected?
If the appraisal is lower than the purchase price, you may need to renegotiate the purchase price with the seller, increase your down payment, or explore alternative financing options.
Can I use the VA loan amount worksheet for a refinance?
While the worksheet primarily focuses on purchase loans, the principles of calculating entitlement and loan amounts can be applied to refinance situations. You’ll need to adjust the calculations to reflect your existing mortgage and the refinance amount.
Where can I find a downloadable VA loan amount worksheet?
Many lenders provide their own versions of the worksheet. You can also find templates and calculators online through reputable financial websites specializing in VA loans. Always verify the source’s credibility before using any online tool.
What if my credit score is below average?
A lower credit score may limit the loan amount you qualify for or increase your interest rate. Improving your credit score before applying for a loan can significantly improve your chances of securing a favorable loan.