What business code is Instacart? Understanding Instacart’s success requires delving into its multifaceted business model, a complex interplay of technology, partnerships, and a vast network of shoppers. From its core revenue streams derived from delivery fees and commission to its sophisticated logistics network and data-driven operations, Instacart’s code for success is a blend of innovation and strategic alliances with grocery giants. This exploration unveils the intricacies of its operations, revealing the key elements that have propelled its growth in the competitive online grocery delivery market.
This analysis dissects Instacart’s operations, examining its technology infrastructure, relationships with grocery stores, shopper network management, and customer acquisition strategies. We’ll explore the challenges and triumphs that have shaped Instacart into the dominant force it is today, providing a comprehensive overview of its business model and its position within the ever-evolving landscape of grocery delivery.
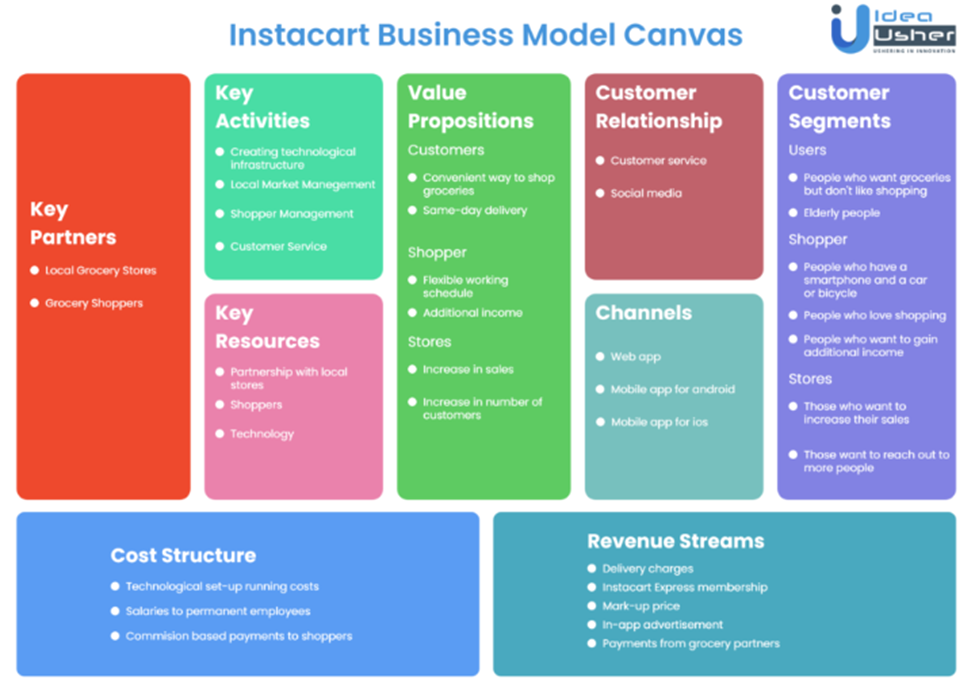
Instacart’s Business Model

Instacart operates as a third-party grocery delivery and pick-up service, connecting consumers with local grocery stores and providing a convenient online platform for ordering and receiving groceries. Its success hinges on effectively managing a complex ecosystem of customers, shoppers, and retail partners.
Core Revenue Streams, What business code is instacart
Instacart generates revenue primarily through two channels: delivery fees charged to customers and commissions earned from retail partners. Delivery fees vary based on order size, location, and delivery speed, while commissions are a percentage of the grocery sales Instacart facilitates. Additionally, Instacart offers paid membership programs, like Instacart Express, which provide subscribers with benefits such as free delivery on orders above a certain value. These memberships contribute a significant, recurring revenue stream.
Pricing Structure for Customers and Shoppers
For customers, Instacart’s pricing is multifaceted. Customers pay for the groceries themselves at the prices set by the retail partner. On top of this, they pay a delivery fee, which can vary depending on factors like order size, delivery speed, and distance to the store. Membership programs like Instacart Express offer discounted or waived delivery fees, thereby influencing customer purchasing behavior. Shoppers, on the other hand, are independent contractors who earn income based on the number of orders they fulfill, tips received from customers, and a small per-item commission. This incentivizes shoppers to complete orders efficiently and provide excellent customer service.
Comparison to Other Grocery Delivery Services
Instacart’s business model shares similarities with other grocery delivery services like DoorDash, Uber Eats, and Walmart Grocery, all of which rely on a network of independent contractors to fulfill orders. However, Instacart differentiates itself through its partnerships with a wider range of grocery stores, including both national chains and smaller, local retailers. This broader reach provides customers with more options and potentially enhances customer loyalty. Other services may focus more heavily on restaurant delivery, while Instacart’s primary focus remains grocery delivery and pick-up.
Operating Costs Breakdown
Instacart’s operating costs are substantial and include several key components. The largest portion likely comprises payments to its independent shoppers, including their earnings and associated benefits (if any). Significant expenses also involve technology infrastructure (website, app, logistics software), marketing and advertising, customer service, and the costs associated with managing its network of retail partners. Furthermore, warehouse and fulfillment center costs, particularly in urban areas with high real estate prices, contribute to overall operating expenses. Finally, insurance and legal costs are also a substantial factor.
Simplified Visual Representation of Instacart’s Revenue Flow
| Revenue Source | Description | Percentage of Total Revenue (Estimate) | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delivery Fees | Charges to customers for delivery services. | 30% | Order size, distance, delivery speed, membership status |
| Retailer Commissions | Percentage of grocery sales facilitated through Instacart. | 50% | Sales volume, negotiated commission rates, retail partner relationships |
| Membership Fees (Instacart Express) | Recurring subscription fees from members. | 15% | Number of subscribers, subscription price, member retention rate |
| Other Revenue (e.g., advertising) | Additional revenue streams from advertising or other services. | 5% | Advertising contracts, effectiveness of advertising campaigns |
Instacart’s Technology and Infrastructure: What Business Code Is Instacart
Instacart’s success hinges on a sophisticated technological infrastructure supporting its entire operation, from customer-facing apps to complex logistics and data analytics. This intricate system enables the seamless connection between shoppers, customers, and partner retailers, facilitating the rapid delivery of groceries. Understanding the technology behind Instacart reveals the complexity and innovation driving its market position.
Instacart’s App and Website Functionality
Instacart’s user-facing applications (mobile app and website) provide a streamlined experience for customers. The apps feature intuitive search functions, personalized recommendations based on past purchases and browsing history, and real-time order tracking. The backend integrates with various retailer systems to provide accurate product information, pricing, and availability. Furthermore, the platform facilitates communication between customers and shoppers, allowing for substitutions and special requests. The technology employs robust security measures to protect user data and payment information, ensuring a safe and reliable shopping experience. Scalability is a critical aspect, enabling the platform to handle peak demand periods without significant performance degradation.
Instacart’s Logistics Network and Order Fulfillment
Instacart’s logistics network is a crucial component of its operation. It involves a complex interplay of algorithms and real-time data to optimize order routing, shopper assignment, and delivery scheduling. The system considers factors such as shopper location, order size, delivery time windows, and store proximity to minimize delivery times and maximize efficiency. Order fulfillment begins with the customer placing an order through the app. The order is then routed to the nearest store with the necessary items in stock. A shopper is assigned to the order, and they proceed to the store to shop and fulfill the order. The shopper then delivers the groceries to the customer, utilizing GPS tracking to ensure timely delivery. This process is supported by sophisticated routing algorithms and real-time communication channels. The system dynamically adjusts to changes in demand and unforeseen circumstances, such as traffic congestion or item unavailability.
Instacart’s Data Analytics Capabilities
Instacart leverages extensive data analytics to optimize its operations and enhance customer experience. The company collects data from various sources, including customer purchase history, shopper performance metrics, and real-time delivery information. This data is analyzed using machine learning algorithms to predict demand, optimize inventory management, improve route planning, and personalize customer recommendations. For example, by analyzing purchase patterns, Instacart can anticipate peak demand periods and proactively allocate resources to ensure timely order fulfillment. Similarly, analyzing shopper performance data helps identify top-performing shoppers and optimize their assignments. This data-driven approach is crucial for maintaining efficiency and profitability in a dynamic and competitive market.
Key Technological Challenges Faced by Instacart
Instacart faces several significant technological challenges. Maintaining the scalability of its platform to handle peak demand and rapid growth is paramount. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of real-time data, especially concerning product availability and inventory levels at partner stores, is another challenge. Managing the complexities of its vast logistics network, including optimizing delivery routes and coordinating a large network of independent shoppers, requires constant refinement of its algorithms and systems. Furthermore, the company must continuously invest in security measures to protect user data and prevent fraud. Finally, competing with other grocery delivery services and adapting to evolving consumer preferences necessitates ongoing technological innovation.
Software and Hardware Components Crucial to Instacart’s Operations
The smooth functioning of Instacart relies on a combination of software and hardware. Here’s a list of essential components:
- Mobile Application (iOS and Android): The customer-facing app, providing order placement, tracking, and communication functionalities.
- Web Application: The desktop version of the app, offering similar functionalities.
- Order Management System (OMS): The central system managing order routing, shopper assignment, and tracking.
- Inventory Management System (IMS): Integrating with partner stores to provide real-time inventory information.
- Route Optimization Software: Algorithms for efficient route planning and delivery scheduling.
- GPS Tracking System: For real-time tracking of shoppers and deliveries.
- Data Warehousing and Analytics Platform: For storing and analyzing large datasets to improve efficiency and personalize customer experience.
- Cloud Infrastructure (AWS, Google Cloud, etc.): Providing the scalable computing resources necessary to support the platform.
- Shopper Communication Platform: Facilitating communication between customers and shoppers.
- Payment Gateway Integration: Secure processing of online payments.
- Smartphones and GPS Devices: Used by shoppers for navigation and communication.
- Delivery Vehicles: Cars, scooters, bicycles, etc., used for grocery delivery.
Instacart’s Relationship with Grocery Stores
Instacart’s success hinges on its intricate relationships with a diverse network of grocery stores, ranging from large national chains to smaller regional players. These partnerships are multifaceted, encompassing technological integration, contractual agreements, and shared marketing efforts, all designed to facilitate seamless online grocery ordering and delivery. The nature of these relationships varies depending on the size and specific needs of each grocery partner.
Instacart’s Partnerships with Different Grocery Chains
Instacart partners with a wide array of grocery stores, including national chains like Kroger, Costco, and Aldi, as well as regional and local supermarkets. The specific terms of each partnership are confidential, but generally involve a combination of technology integration, marketing collaborations, and revenue-sharing agreements. These partnerships allow Instacart to offer a broad selection of products and services to its customers, while providing grocery stores with access to a new customer base and enhanced delivery capabilities.
Instacart’s Integration with Grocery Store Inventory Management Systems
Successful integration with a grocery store’s inventory management system is critical for Instacart’s operation. This integration ensures real-time visibility into product availability, pricing, and location within the store. This allows Instacart shoppers to accurately fulfill orders and avoids situations where items are unavailable or substituted without customer notification. The integration process usually involves custom software development and API connections between Instacart’s platform and the store’s internal systems. This requires significant technical expertise and coordination between both parties. The level of integration varies depending on the store’s existing technological infrastructure and its willingness to collaborate.
Contractual Agreements Between Instacart and Retail Partners
The contractual agreements between Instacart and its retail partners are complex and typically involve several key components. These include revenue-sharing models, where Instacart receives a commission on each order fulfilled, as well as stipulations regarding data sharing, branding, and marketing responsibilities. Agreements also address issues such as liability in case of order errors or damaged goods. The specific terms are negotiated individually and are likely to differ based on factors such as the store’s size, market position, and negotiating power. These contracts often involve long-term commitments and include clauses addressing termination and dispute resolution.
Benefits and Challenges of Partnerships with Different Sized Grocery Stores
Instacart’s partnerships with various sized grocery stores present unique benefits and challenges. Large national chains may offer greater economies of scale, but negotiations can be more complex and involve significant lead times. Smaller, regional stores might offer more flexibility and a personalized approach, but their technological infrastructure may be less sophisticated, requiring greater investment in integration. Large chains often have established customer loyalty programs that Instacart must integrate with, while smaller stores may lack the resources for extensive marketing collaborations.
Comparison of Instacart Partnerships
The following table compares the features of three different grocery store partnerships with Instacart, highlighting key differences and challenges. It’s important to note that the details of these partnerships are largely confidential, and this table represents a generalized overview based on publicly available information and industry analysis.
| Store Name | Partnership Type | Key Features | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kroger | Extensive, multi-year agreement | Wide product selection, strong brand recognition, significant market share, integration with Kroger’s loyalty program. | Complex negotiations, potential conflicts with Kroger’s own online grocery initiatives. |
| Aldi | Focus on cost-effectiveness and efficiency | Access to a price-conscious customer base, potential for high order volume. | Limited product selection compared to larger chains, potential challenges in managing order fulfillment due to Aldi’s unique store format. |
| Local Supermarket (Example: “Fresh Foods Market”) | Targeted partnership for local reach | Strong community ties, personalized service, opportunity to build brand awareness in a specific geographic area. | Smaller scale, potentially limited technological infrastructure, challenges in scaling operations to meet demand. |
Instacart’s Shopper Network

Instacart’s shopper network is the backbone of its grocery delivery service, connecting customers with a vast pool of independent contractors who shop for and deliver groceries. The success of Instacart hinges on the efficiency and reliability of this network, requiring careful management of recruitment, compensation, training, and support.
Becoming an Instacart Shopper
The process of becoming an Instacart shopper is relatively straightforward. Applicants typically begin by completing an online application, providing information about their driving record, background check, and availability. After a background check and potentially a brief interview, successful candidates are provided with the necessary tools and information to begin shopping. They must then download the Instacart shopper app and complete any required training modules. The entire process, from application to acceptance, generally takes a few days to a couple of weeks.
Instacart Shopper Compensation
Instacart shoppers’ compensation is multifaceted and depends on several factors. They earn a combination of base pay, tips, bonuses, and potential promotional earnings. The base pay varies depending on factors like the order’s size, distance, and demand. Tips, entirely at the customer’s discretion, often constitute a significant portion of a shopper’s earnings. Bonuses are sometimes offered for completing orders quickly and efficiently or during peak demand periods. Promotional opportunities, such as extra pay for shopping at specific stores or during certain hours, are also available. The overall earnings are therefore variable and not guaranteed, making it essential for shoppers to manage their time and workload effectively. For example, a shopper might earn $15-$25 per hour, but this can fluctuate significantly depending on the factors mentioned.
Training and Support for Instacart Shoppers
Instacart provides training and support to its shoppers through its app and online resources. The app includes tutorials on how to navigate the shopping interface, manage orders, and interact with customers. Shoppers also have access to online help centers and frequently asked questions (FAQs) to address any issues or questions that may arise. While formal structured training may be limited, the app serves as a constant source of guidance and support throughout the shopper’s workday. Furthermore, the Instacart community forum allows shoppers to share tips, best practices, and support each other.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Working as an Instacart Shopper
Working as an Instacart shopper offers several benefits, including flexibility and independence. Shoppers can set their own hours and work as much or as little as they choose. The work is also relatively easy to learn, and there is potential for significant earnings, particularly with good time management and customer service skills. However, there are also drawbacks. Earnings are not guaranteed, and shoppers are responsible for their own taxes and expenses, such as vehicle maintenance and fuel. The work can also be physically demanding, requiring significant walking and lifting. Furthermore, the gig nature of the work lacks the stability and benefits of traditional employment, such as health insurance or paid time off.
A Typical Instacart Shopper’s Workday
A typical Instacart shopper’s workday begins by logging into the app and selecting available orders. Orders are typically displayed with details like the store, delivery location, and estimated payout. Shoppers choose orders based on factors such as proximity, payout, and their own availability. After selecting an order, the shopper travels to the designated grocery store, shops for the items, and checks the order for accuracy. Once the shopping is complete, the shopper then proceeds to deliver the groceries to the customer’s address, ensuring timely and efficient delivery. Throughout the process, the shopper interacts with customers through the app, addressing any questions or concerns. Post-delivery, the shopper marks the order as complete, and the payment is processed. The entire process, from order selection to delivery, can take anywhere from one to several hours depending on the size and complexity of the order and the distance between locations.
Instacart’s Customer Base and Market Position
Instacart’s success hinges on its ability to attract and retain a substantial customer base within a fiercely competitive grocery delivery market. Understanding its target demographic, marketing strategies, and market share is crucial to analyzing its overall position. This section will delve into these key aspects of Instacart’s customer-centric operations.
Instacart’s Target Customer Demographic and Marketing Strategies
Instacart’s target audience is broad, encompassing a diverse range of demographics united by a common need for convenient grocery delivery. However, certain segments are more heavily targeted than others. High-income households, busy professionals, families with young children, and individuals with mobility limitations represent significant portions of Instacart’s customer base. These groups value the time-saving benefits and ease of access offered by the platform. Marketing strategies reflect this targeting, utilizing digital advertising across social media platforms, search engines, and targeted email campaigns. Partnerships with popular brands and loyalty programs further enhance customer acquisition. Geographic targeting also plays a role, with increased marketing efforts in areas with high population density and a strong presence of Instacart’s partner grocery stores.
Instacart’s Customer Retention Strategies
Customer retention is a critical aspect of Instacart’s business model. The company employs several strategies to encourage repeat business. These include personalized recommendations based on past purchases, exclusive discounts and promotions for loyal customers, a streamlined and user-friendly mobile application, and a robust customer service system to address any issues promptly. Loyalty programs, offering rewards points and exclusive benefits, incentivize continued usage. Regular communication through email updates and in-app notifications also helps maintain engagement and awareness of new features and offers. A focus on consistently high-quality service, from order accuracy to timely delivery, is paramount to fostering customer loyalty.
Instacart’s Market Share and Competition
Instacart holds a significant market share in the online grocery delivery sector, although precise figures fluctuate and are often disputed. Its main competitors include DoorDash, Uber Eats, Walmart+, and regional players. While Instacart’s market leadership is undeniable in some areas, competition is intense, and the market is constantly evolving. Instacart’s competitive advantage lies in its extensive network of grocery store partnerships, its large shopper network, and its focus on building a strong brand recognition and reputation for reliable service. However, ongoing competition requires continuous innovation and adaptation to maintain its market position.
The Ideal Instacart Customer Profile
The ideal Instacart customer is typically time-constrained, tech-savvy, and values convenience above all else. They are likely to be employed professionals, busy parents, or individuals with limited mobility, residing in urban or suburban areas with good internet access. Their purchasing behaviors reflect their need for speed and efficiency, opting for frequent, smaller-sized orders rather than large, infrequent trips to the grocery store. They are often willing to pay a premium for the convenience of home delivery and are receptive to personalized recommendations and targeted promotions. They are also likely to utilize Instacart’s various features, such as substitutions and order customization, to tailor their shopping experience.






