What is a business partner number? It’s more than just a simple identifier; it’s the backbone of efficient business operations, streamlining communication and collaboration across diverse supply chains. Understanding its various interpretations, formats, and uses is crucial for optimizing data accuracy and ensuring seamless integration across your business systems. This guide explores the multifaceted nature of business partner numbers, delving into their significance in modern business processes and highlighting the critical security and privacy considerations surrounding their management.
From defining the nuances of a business partner number and differentiating it from customer or vendor IDs to exploring its role in ERP and CRM systems, we’ll cover how these numbers facilitate efficient data management. We’ll examine different data structures and formats, emphasizing the importance of data validation and security protocols to safeguard sensitive information. Real-world examples and case studies will illuminate the practical applications and potential pitfalls of managing business partner numbers effectively.
Defining “Business Partner Number”
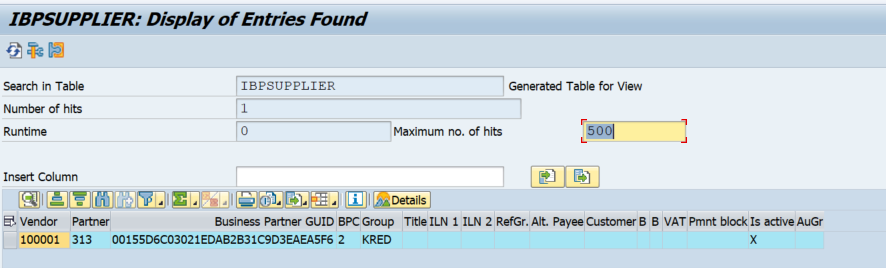
The term “business partner number” lacks a universally standardized definition, varying significantly depending on the context and the specific business system in use. It essentially serves as a unique identifier for an entity involved in business transactions with a particular organization. This entity could be a supplier, customer, distributor, or any other external party integral to the company’s operations. Understanding the nuances of this term is crucial for efficient data management and streamlined business processes.
The interpretation of a “business partner number” hinges on the specific business processes and software systems employed by an organization. Different companies may use this term to refer to different types of identifiers, leading to inconsistencies in terminology and data integration challenges. The core function remains the same: to uniquely identify a business partner within a given system.
Types of Business Partner Numbers Across Industries
The specific format and meaning of a business partner number differ widely across industries and organizations. For example, a manufacturing company might use a business partner number to track its suppliers, assigning unique identifiers based on supplier codes or internal numbering systems. A retail company, on the other hand, might use it to identify its customers, potentially leveraging customer account numbers or loyalty program identifiers. Financial institutions might use a business partner number to identify corporate clients, incorporating elements like tax identification numbers or legal entity identifiers. This diversity highlights the context-dependent nature of the term.
Distinguishing Business Partner Numbers from Customer and Vendor IDs
While a business partner number often overlaps with customer or vendor IDs, subtle distinctions exist. A customer ID typically identifies an individual or entity purchasing goods or services. A vendor ID usually identifies a supplier providing goods or services. A business partner number encompasses a broader range of relationships, including customers, vendors, and other external parties such as distributors, agents, or joint venture partners. In some systems, the terms might be used interchangeably, while others maintain a clear distinction based on the type of relationship. The key difference lies in the scope of the identifier; a business partner number can represent a more comprehensive business relationship than a customer or vendor ID alone.
Scenarios Where Business Partner Numbers Are Crucial
Business partner numbers play a vital role in various business operations. They are essential for accurate record-keeping, facilitating efficient tracking of transactions, managing relationships, and ensuring regulatory compliance. For example, in supply chain management, a unique business partner number for each supplier allows for precise tracking of inventory, orders, and payments. In customer relationship management (CRM), a business partner number helps to personalize interactions, segment customers effectively, and tailor marketing campaigns. Further, in financial reporting and auditing, accurate business partner numbers are essential for reconciling transactions and ensuring compliance with financial regulations. The absence of a robust business partner numbering system can lead to data inconsistencies, errors in financial reporting, and difficulties in managing complex business relationships.
Purpose and Usage of Business Partner Numbers

Business partner numbers (BPNs) are crucial for streamlining operations within and between organizations. They act as unique identifiers for all entities involved in business transactions, significantly improving data management and facilitating seamless communication across the supply chain. The consistent application of BPNs contributes to increased efficiency, reduced errors, and enhanced overall business performance.
Business partner numbers play a vital role in enhancing supply chain management by providing a standardized method for identifying and tracking all participants. This includes suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and even customers. The use of a unique identifier for each partner eliminates ambiguity and confusion that can arise from using different names, addresses, or other identifying information. This standardization allows for better inventory management, improved order tracking, and more accurate forecasting. Efficient tracking of goods and services throughout the supply chain becomes significantly easier, leading to reduced lead times and improved on-time delivery rates.
Facilitating Efficient Communication and Collaboration
The adoption of a standardized BPN system dramatically improves communication and collaboration across the entire business network. By using a consistent identifier, businesses can easily integrate data from different systems and departments, reducing the risk of data silos and inconsistencies. This allows for faster and more accurate information sharing, enabling better decision-making and improved responsiveness to market changes. For example, a retailer can quickly identify a supplier experiencing delays by referencing their BPN in their inventory management system, allowing for proactive mitigation strategies. Real-time data sharing becomes significantly more efficient, fostering closer collaboration and stronger relationships between business partners.
Key Benefits of Standardized Business Partner Numbers
Standardized BPNs offer several key advantages. They improve data quality by eliminating inconsistencies and ambiguities associated with multiple identifiers. This leads to increased data accuracy, reducing errors in reporting and analysis. Moreover, standardized BPNs facilitate automation of business processes, streamlining workflows and reducing manual intervention. The automation capabilities extend to tasks like order processing, invoice generation, and payment reconciliation. This ultimately results in significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency. Finally, the use of BPNs enhances compliance with industry regulations and standards, minimizing the risk of penalties and ensuring data integrity.
Hypothetical System Demonstrating Improved Data Accuracy
Imagine a hypothetical system where a global apparel retailer uses BPNs to track its supply chain. Each supplier, manufacturer, and distributor is assigned a unique BPN. When an order is placed, the system automatically records the BPN of the supplier, allowing for real-time tracking of the order’s progress. If a delay occurs, the system automatically alerts the retailer, using the supplier’s BPN to identify the source of the problem. This system eliminates the confusion caused by using different names or addresses for the same supplier across different departments. Furthermore, the system can automatically reconcile invoices with the corresponding order information, using the BPNs to ensure accuracy and prevent discrepancies. This level of integration and automation significantly reduces errors and improves the overall accuracy of data related to the supply chain. The resulting data is more reliable for forecasting, inventory management, and strategic decision-making. This hypothetical scenario demonstrates how a standardized BPN system can lead to substantial improvements in data accuracy and operational efficiency across a complex global supply chain.
Data Structures and Formats
Business partner numbers, fundamental identifiers within enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and other business applications, require careful consideration of their underlying data structures and formats to ensure data integrity, efficient processing, and seamless integration with other systems. The choice of format and structure directly impacts data storage, validation, and retrieval efficiency.
Different systems employ varying approaches to structuring and storing these crucial identifiers. Understanding these differences is vital for data exchange and interoperability.
Business Partner Number Formats
Business partner numbers can take several formats, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Common formats include purely numeric sequences, alphanumeric strings incorporating letters and numbers, and even formats incorporating check digits for error detection.
| Number Type | Length | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier ID | 10 | Numeric | 1234567890 |
| Customer ID | 8 | Alphanumeric (3 letters followed by 5 numbers) | ABC12345 |
| Internal Partner Code | 12 | Alphanumeric (YYYYMMDDXX) – Year, Month, Day, Check digits | 20240315AB |
| Global Partner ID | 16 | Alphanumeric (UUID-like format) | a1b2c3d4-e5f6-7890-1234-567890abcdef |
Data Structures for Storing Business Partner Numbers
The choice of data structure for storing business partner numbers significantly impacts database performance and data management. Common data structures include:
* Integer: Suitable for purely numeric business partner numbers. Offers efficient storage and retrieval, particularly for smaller numbers. However, it’s not suitable for alphanumeric identifiers.
* VARCHAR/TEXT: A flexible choice that accommodates both numeric and alphanumeric formats. However, it may lead to higher storage requirements compared to integer types, and searching/sorting might be less efficient.
* UUID (Universally Unique Identifier): Provides globally unique identifiers, often used for distributed systems and ensuring no collisions even with massive datasets. This format, however, tends to occupy more storage space.
Data Validation Rules for Business Partner Numbers
Implementing robust data validation rules is critical to ensuring the accuracy and reliability of business partner numbers. These rules prevent the entry of invalid or duplicate data. Examples include:
* Length validation: Checks if the number meets the predefined length. For example, a 10-digit numeric ID must contain exactly 10 digits.
* Format validation: Verifies that the number conforms to the specified format (e.g., alphanumeric, numeric, specific pattern). Regular expressions are often used for complex formats.
* Uniqueness validation: Ensures that each business partner has a unique identifier within the system. This prevents duplicate entries and data inconsistencies.
* Check digit validation: Incorporating check digits in the business partner number allows for detecting simple errors (e.g., transcription errors). Algorithms like the Luhn algorithm can be used to generate and validate check digits.
* Range validation: Ensures that the number falls within a predefined range. For example, an ID might be restricted to a specific range of numbers.
For instance, a system might reject a customer ID “ABC123456” because it exceeds the defined length of 8 characters. Similarly, a check digit validation rule would flag an entry with an incorrect check digit, indicating a potential data entry error.
Integration with Business Systems
Business partner numbers serve as a crucial link between various business systems, ensuring data consistency and efficient information flow across different applications. Their seamless integration is paramount for streamlined operations and accurate reporting. Effective integration requires careful planning and consideration of data structures and system capabilities.
Business partner numbers are fundamental to the smooth operation of many enterprise systems. Their integration ensures that data remains consistent and accessible across multiple platforms, facilitating better decision-making and operational efficiency.
Integration with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
ERP systems, such as SAP or Oracle, rely heavily on accurate and consistent business partner data. The business partner number acts as a unique identifier, linking all relevant information about a customer, vendor, or employee across various modules within the ERP system. For instance, financial transactions, purchase orders, and sales invoices are all tied to the business partner number, allowing for efficient tracking and reporting of financial activities. This integration simplifies reconciliation processes and reduces the risk of data discrepancies. Data related to payment terms, shipping addresses, and contact information are all associated with the business partner number, ensuring a complete and unified view of the partner within the ERP system.
Usage of Business Partner Numbers in Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
In CRM systems like Salesforce or Microsoft Dynamics 365, the business partner number functions as a central identifier for customer interactions and data. It links customer details, communication history, sales opportunities, and support tickets, providing a 360-degree view of the customer. Marketing campaigns can be targeted based on business partner number segmentation, enabling personalized communication and improving customer engagement. Sales teams can leverage the business partner number to access complete customer profiles, facilitating more effective sales interactions and improved customer service. The number ensures consistency across different CRM modules, facilitating accurate reporting and analysis of customer behavior and sales performance.
Integrating Business Partner Numbers with a New Software Application
Integrating business partner numbers into a new software application typically involves several steps. First, a clear understanding of the existing data structure and the new application’s requirements is crucial. Next, a mapping process needs to be defined, establishing the correspondence between the business partner number in the existing system and its representation in the new application. Data migration is then performed, transferring the relevant business partner data, including the unique identifier, into the new system. Thorough testing is essential to ensure data integrity and the accurate functioning of the integration. Finally, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are crucial to maintain data consistency and address any integration issues that may arise. A robust data validation process should be incorporated to prevent inconsistencies or duplicates.
Maintaining Data Consistency Across Different Systems
Maintaining data consistency across different systems using business partner numbers requires a structured approach. Data governance policies should be established, defining clear responsibilities for data management and ensuring data quality. Data validation rules should be implemented to prevent invalid or duplicate business partner numbers from entering any system. Regular data reconciliation processes should be carried out to identify and resolve any inconsistencies. A centralized data repository or master data management (MDM) system can improve data consistency by providing a single source of truth for business partner information. This approach minimizes the risk of data discrepancies and ensures that all systems work with a unified view of the business partner.
Security and Privacy Considerations: What Is A Business Partner Number
Protecting business partner numbers is paramount to maintaining data integrity and upholding legal compliance. The sensitive nature of this data necessitates robust security measures throughout its lifecycle, from storage and transmission to access and disposal. Failure to implement adequate security protocols can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions.
The security risks associated with business partner numbers are multifaceted. Unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction of this data can compromise business operations, expose sensitive information about partners, and potentially lead to fraudulent activities. Furthermore, the increasing reliance on digital systems and interconnected networks expands the attack surface, making robust security even more critical.
Data Encryption and Access Control, What is a business partner number
Data encryption is a cornerstone of securing business partner numbers. Employing strong encryption algorithms, both at rest and in transit, renders the data unintelligible to unauthorized individuals even if intercepted. This includes using encryption protocols like TLS/SSL for data transmitted over networks and robust encryption methods like AES-256 for data stored in databases. Access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC), limit access to business partner numbers based on an individual’s job responsibilities and need-to-know basis. This ensures that only authorized personnel can view, modify, or delete this sensitive data. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be implemented for all users accessing systems containing business partner numbers, adding an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
Compliance Requirements
Handling business partner numbers must adhere to various regulations depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the data. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in California, for example, impose strict requirements on the collection, processing, and storage of personal data, including business partner numbers if they contain personally identifiable information. These regulations mandate data minimization, purpose limitation, and data security measures to protect individuals’ privacy rights. Organizations must also comply with industry-specific regulations and best practices, such as those Artikeld by payment card industry (PCI) standards if the numbers are linked to financial transactions. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in substantial fines and legal penalties.
Security Protocol for Business Partner Numbers
A comprehensive security protocol should encompass several key elements. This includes a robust data encryption strategy as previously discussed, implementing strict access control policies using RBAC and MFA, regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities, and a well-defined incident response plan to handle security breaches effectively. Data loss prevention (DLP) tools can monitor and prevent the unauthorized transfer of business partner numbers. Regular employee training on security best practices and data privacy regulations is also crucial. Furthermore, the protocol should address data retention policies, outlining how long business partner numbers are stored and the procedures for secure data disposal when no longer needed. Regular reviews and updates to the security protocol are essential to adapt to evolving threats and technological advancements. A strong security protocol will incorporate a layered approach, combining multiple security controls to minimize the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
Illustrative Examples
Understanding the practical implications of business partner number management requires examining real-world scenarios and processes. The following examples illustrate the importance of accuracy, efficient workflows, and robust systems in managing these crucial identifiers.
Scenario: Incorrect Business Partner Number Leading to Business Problems
A global manufacturing company, “GlobalTech,” experienced significant delays and financial losses due to an incorrect business partner number. A crucial shipment of raw materials intended for their primary supplier, “ComponentSource,” was misdirected because the business partner number associated with ComponentSource in GlobalTech’s system was outdated. The incorrect number belonged to a defunct subsidiary, resulting in the shipment being sent to an inactive warehouse. This error caused a three-week production halt, costing GlobalTech an estimated $500,000 in lost revenue and additional expenses for expedited reshipment and contract renegotiation with ComponentSource. The incident highlighted the critical need for regular data cleansing and validation of business partner numbers within their system.
Visual Representation of Business Partner Number Flow
A visual representation of the business partner number flow through a procurement process would depict a flowchart. The process begins with a purchase requisition, where the relevant business partner number (for the supplier) is entered. This number then triggers a search within the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system to verify the supplier’s information and retrieve associated data, such as contact details and payment terms. The validated business partner number is then used to generate a purchase order, which is sent to the supplier. Upon receipt of goods, the business partner number is again used to match the invoice against the purchase order, ensuring accurate payment processing. Finally, the business partner number is recorded in the financial system for accounting and reporting purposes. The flowchart would clearly illustrate the multiple points where the business partner number is crucial for smooth operation.
Business Partner Number Generation and Assignment
The generation and assignment of a business partner number typically follows a structured process. First, a unique identifier is created, often using a sequential numbering system or a more complex algorithm incorporating date and time stamps to guarantee uniqueness. This number is then linked to a newly created business partner record in the system, containing all relevant details such as company name, address, contact information, and tax identification numbers. After data validation and approval, the generated business partner number is assigned to the partner, often communicated through a formal notification. The system automatically updates all relevant modules with the new business partner number, ensuring consistency across the entire organization. This process is often automated to reduce manual errors and improve efficiency.
Case Study: Benefits of a Robust Business Partner Number Management System
“RetailGiant,” a large retail chain, implemented a new business partner number management system that included data validation, automated updates, and integration with their existing ERP and CRM systems. Prior to the implementation, inconsistencies in business partner numbers resulted in duplicate payments, delayed shipments, and inaccurate reporting. After implementing the new system, RetailGiant experienced a significant reduction in these issues. They reported a 75% decrease in payment errors, a 50% reduction in shipping delays, and improved accuracy in sales and inventory reporting. The improved data quality also facilitated better supplier relationship management, leading to improved negotiation and procurement processes. The return on investment from the new system was substantial, exceeding initial expectations.






