What is business code for Uber driver? It’s a question many aspiring and current drivers grapple with. Understanding the nuances of Uber’s operational framework is crucial for maximizing earnings and navigating the complexities of this gig economy platform. This guide delves into the key aspects of being an Uber driver, from understanding payment structures and app functionality to legal considerations and tax implications.
This comprehensive overview aims to equip you with the knowledge necessary to succeed as an Uber driver. We’ll explore everything from optimizing your earnings through effective strategies to understanding your rights and responsibilities as an independent contractor. We’ll also examine the competitive landscape, the impact of external factors, and resources available to help you thrive in this dynamic industry.
Uber Driver’s Earnings & Payments
Understanding Uber driver earnings is crucial for anyone considering this gig economy role. Earnings are not fixed salaries but fluctuate based on several interconnected factors, impacting the overall financial viability of driving for Uber. This section details the payment methods, influencing factors, Uber’s fee structure, and provides a comparative analysis of earning potential across different cities.
Payment Methods for Uber Drivers
Uber drivers can typically receive payments through direct deposit to their bank account, or via a debit card linked to their Uber driver account. The frequency of payments varies depending on the driver’s preferences and regional settings; some drivers receive payouts daily, while others opt for weekly or bi-weekly settlements. The choice of payment method usually involves setting up the preferred option within the Uber driver app. Instant payouts, offered in some regions, allow drivers to access their earnings more quickly, often incurring a small fee.
Factors Influencing Uber Driver Earnings
Several factors significantly impact a driver’s hourly earnings. Surge pricing, a dynamic pricing model implemented during periods of high demand (e.g., rush hour, inclement weather, major events), can substantially increase fares and, consequently, driver income. Ride distance is another key determinant; longer trips generally translate to higher earnings, compensating for increased fuel consumption and time spent driving. Conversely, wait times, the period between accepting a ride request and picking up the passenger, reduce a driver’s effective earning rate. Other factors include the type of ride (UberX, UberXL, Uber Black), the time of day, and even the driver’s acceptance rate of ride requests. A higher acceptance rate can lead to more consistent work and potentially higher overall earnings, but it also increases the likelihood of less profitable short trips.
Uber’s Fee Structure for Drivers
Uber deducts a commission from each fare earned by its drivers. This commission percentage varies depending on several factors, including the city, the type of ride service offered, and promotional offers in place. The commission is calculated as a percentage of the total fare, which includes base fare, distance, time, and any applicable surge pricing. Drivers should review the specific commission structure in their city, as it can impact their overall take-home pay. Additionally, drivers are responsible for covering their own vehicle expenses, including fuel, maintenance, insurance, and vehicle depreciation. These expenses can significantly reduce the net earnings. Understanding the total cost of operation is critical for accurate profit calculation.
Earnings Potential Comparison Across Cities
The following table provides a comparison of potential earnings for Uber drivers in select cities. These figures are averages and may vary based on factors discussed previously. Actual earnings can significantly differ based on individual driving habits, time commitment, and market conditions. Data is based on publicly available information and driver reports.
| City | Average Fare | Average Earnings Per Hour | Driver Commission (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| New York City | $25 | $20-$30 | 25-30% |
| Los Angeles | $20 | $18-$25 | 20-25% |
| Chicago | $18 | $15-$22 | 22-28% |
| San Francisco | $28 | $22-$35 | 25-30% |
Uber Driver App Functionality
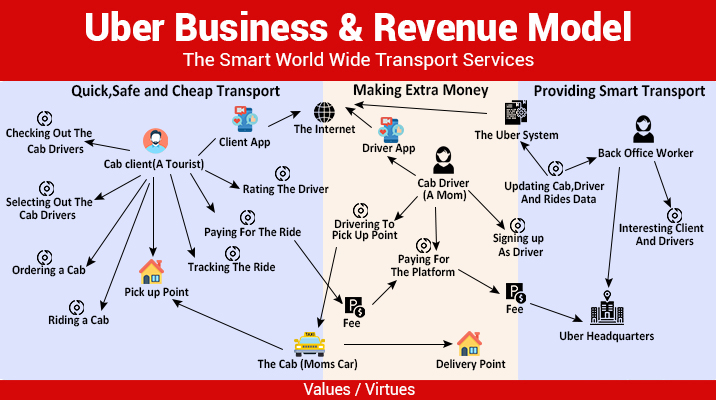
The Uber driver app is the central hub for managing all aspects of driving with the platform. Its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features are designed to streamline the ride-hailing process for drivers, from accepting requests to receiving payments. Understanding its functionality is crucial for maximizing earnings and providing efficient service.
The Uber driver app provides a range of features designed to optimize the driver experience. These features go beyond simply connecting drivers with riders; they include tools for navigation, communication, payment processing, and trip management. The app’s overall design prioritizes ease of use and efficient information delivery, aiming to minimize distractions and maximize driver safety.
Navigation System Accuracy
The app’s integrated navigation system uses GPS technology to guide drivers to pickup locations and destinations. While generally accurate, the system’s performance can be affected by factors such as GPS signal strength, real-time traffic conditions, and the accuracy of the address provided by the passenger. In areas with poor GPS reception or significant traffic congestion, the navigation might suggest alternative routes or experience minor delays in updating the route. The app typically provides multiple route options, allowing drivers to choose the most efficient path based on their knowledge of local conditions. Drivers can also manually adjust the route if necessary.
Ride Request Acceptance and Rejection
Drivers receive ride requests through the app, displayed as notifications on their device. Each request includes key information such as the passenger’s pickup location, destination, estimated fare, and estimated travel time. Drivers can accept or reject ride requests based on their availability, location, and personal preferences. Rejecting a request does not typically result in any penalty, though frequently rejecting requests might impact the driver’s rating or visibility within the app’s algorithm. The app provides clear options for accepting or declining each request, with minimal steps involved in the decision-making process.
Completing a Ride: A Step-by-Step Guide
A new Uber driver can complete a ride using the app by following these steps:
- Log in and go online: Launch the Uber Driver app and log in using your credentials. Then, tap the “Go Online” button to make yourself available for ride requests.
- Accept a ride request: When a request is received, review the details (pickup location, destination, fare). Tap “Accept” to confirm the ride.
- Navigate to the pickup location: The app will display directions to the passenger’s pickup location using its integrated navigation system. Follow the provided route.
- Confirm passenger pickup: Once you arrive at the pickup location, confirm the passenger’s identity and tap the “Start Trip” button in the app.
- Drive to the destination: Follow the app’s navigation to the passenger’s destination.
- End the trip: Upon arrival at the destination, tap the “End Trip” button in the app. This will finalize the ride and initiate the payment process.
- Receive payment: The payment is automatically processed through the app, and the driver receives the fare according to the agreed-upon pricing.
Driver Requirements & Regulations
Becoming an Uber driver involves meeting specific requirements and adhering to various regulations. These stipulations ensure passenger safety and compliance with local and national laws. Failure to meet these criteria can result in account deactivation. Understanding these requirements is crucial for prospective drivers.
Necessary Documents and Qualifications
To become an Uber driver, you must provide several essential documents. These typically include a valid driver’s license, proof of insurance, and vehicle registration. Specific requirements vary by location, so it’s crucial to check Uber’s website for your region. In addition to these, some areas may require additional documentation, such as a commercial driver’s license (CDL) depending on the vehicle type and local regulations. Age restrictions also apply; drivers must generally be at least 21 years old. Furthermore, a clean driving record is often a prerequisite, with the acceptable number of infractions varying depending on location and Uber’s policies. Finally, a background check is mandatory.
Background Checks and Safety Requirements
Uber conducts thorough background checks on all prospective drivers. These checks typically include criminal history checks, motor vehicle record (MVR) checks, and sometimes even social media screenings, depending on the jurisdiction. The aim is to identify individuals with a history of violent crimes, driving offenses, or other behaviors that might pose a risk to passengers. In addition to background checks, Uber often requires drivers to maintain a clean driving record and to undergo periodic safety checks. These measures contribute to the overall safety of the Uber platform for both drivers and passengers. Failure to meet these safety standards can lead to account suspension or termination.
Insurance Coverage for Uber Driving
Adequate insurance coverage is essential for Uber drivers. The specific requirements vary depending on whether the driver is online (waiting for a ride request) or offline, and also depending on the region. Uber often provides some level of insurance coverage, but drivers are usually required to carry their own personal auto insurance as well. This personal insurance should meet or exceed the minimum requirements set by their state or region. It’s vital for drivers to understand the intricacies of their insurance policy and its applicability to their Uber driving activities to avoid any potential liabilities in case of accidents. Gaps in coverage can leave drivers financially vulnerable.
Local Regulations and Permits
Local regulations concerning ride-sharing services vary significantly. Some cities and municipalities require specific permits or licenses for ride-sharing drivers. These permits may involve inspections of the vehicle, specific training requirements, or payment of fees. Additionally, drivers need to be aware of local traffic laws and regulations, which may include specific rules about parking, passenger capacity, and operating hours. Failure to comply with local regulations can result in fines, suspension of driving privileges, or even legal action. It is the driver’s responsibility to research and understand all applicable local laws and regulations in their operating area.
Driver Support & Resources: What Is Business Code For Uber Driver
Navigating the complexities of driving for Uber requires access to reliable support and resources. Understanding the available avenues for assistance, reporting mechanisms, and opportunities for professional development is crucial for driver success and overall satisfaction. This section details the various support channels, reporting procedures, and training resources offered by Uber.
Accessing Uber Driver Support
Uber provides multiple channels for drivers to access support. The most common method is through the driver app itself, which usually features a dedicated help section with FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and direct contact options. Drivers can also reach out via phone, contacting a dedicated support line. Finally, Uber maintains an online help center with comprehensive articles and resources covering a wide range of topics. Each channel offers varying levels of immediate response, with the app’s in-app support often providing the quickest resolution for simple issues.
Reporting Issues and Incidents
Reporting issues or incidents is a straightforward process. Within the Uber driver app, there’s typically a designated section for reporting problems, ranging from technical glitches within the app to safety concerns during a trip. This section usually provides guided prompts to clearly document the issue, including relevant details like date, time, location, and a description of the event. For serious incidents involving passenger safety or legal matters, Uber typically provides specific reporting pathways, often with direct contact information for relevant authorities. Following the app’s reporting guidelines ensures efficient investigation and resolution.
Driver Training and Professional Development
Uber offers various resources to help drivers improve their skills and knowledge. These resources may include online tutorials, webinars, and workshops covering topics such as efficient navigation, customer service best practices, and understanding local regulations. Some of these resources may be accessed directly through the driver app, while others may require registration through the Uber website. While the specific offerings may vary by region, the goal is to equip drivers with the tools and knowledge needed to thrive on the platform. For example, a driver might access a webinar on improving fuel efficiency or a tutorial on handling difficult passenger situations.
Common Driver Problems and Solutions
Effective problem-solving is key to a successful driving experience. Below is a list of common issues encountered by Uber drivers and their potential solutions:
- Problem: App malfunction or freezing. Solution: Restart the app, check for updates, or contact Uber support.
- Problem: Difficulty finding a passenger’s location. Solution: Use the app’s navigation system, communicate with the passenger, and consider using alternative navigation tools if necessary.
- Problem: Payment issues. Solution: Review the trip details within the app, check your payment settings, and contact Uber support if necessary. Ensure your bank details are correctly entered.
- Problem: Passenger complaints or disputes. Solution: Review the passenger’s feedback, follow Uber’s guidelines for handling disputes, and contact support if needed. Maintaining professionalism throughout the interaction is crucial.
- Problem: Vehicle maintenance issues. Solution: Regularly maintain your vehicle according to manufacturer recommendations. Consider having a trusted mechanic for routine checks and repairs. Proactive maintenance prevents unexpected breakdowns.
Tax Implications for Uber Drivers

Driving for Uber presents unique tax challenges, as income is generated independently, unlike traditional employment. Understanding how to correctly report this income and utilize available deductions is crucial for minimizing tax liability. This section details the tax implications for Uber drivers, offering guidance on reporting, deductions, and financial planning.
Reporting Uber Income
Uber provides independent contractors (drivers) with a yearly tax summary (typically a 1099-K form) detailing their gross earnings. This form reports the total amount of money received through the Uber platform, not net earnings after expenses. It’s crucial to remember that this is not your taxable income; it’s the starting point for calculating your tax liability. You’ll need to deduct eligible business expenses to arrive at your net income. Accurate record-keeping is essential, including tracking mileage, tolls, vehicle maintenance, and other relevant costs. Failure to accurately report your income can result in significant penalties.
Deductions and Tax Credits for Uber Drivers
Several deductions and potential tax credits can significantly reduce your tax burden as an Uber driver. These are categorized into direct and indirect expenses.
Direct Expenses
Direct expenses are directly related to your Uber driving business. These include:
- Vehicle Expenses: This is often the largest deduction. You can deduct a portion of your vehicle expenses based on the percentage of business use. This includes depreciation, gas, oil changes, repairs, insurance, and lease payments (if applicable).
- Mileage: Alternatively, you can use the standard mileage rate set by the IRS, which simplifies the calculation. For 2023, the business mileage rate was 58.5 cents per mile. This is often easier than itemizing individual vehicle expenses, but you can’t use both methods simultaneously.
- Tolls and Parking: These are directly attributable to business use and are fully deductible.
Indirect Expenses
Indirect expenses support your business operations but aren’t directly tied to each trip. These include:
- Home Office Deduction: If you have a dedicated workspace at home used exclusively for Uber-related activities, you may be able to deduct a portion of your home expenses, including utilities, rent, and mortgage interest.
- Phone and Internet: A portion of your phone and internet bills may be deductible if used for business purposes. Accurate record-keeping is crucial to substantiate this deduction.
- Professional Services: Expenses for accounting or tax preparation services are also deductible.
Tax Credits
While deductions reduce your taxable income, tax credits directly reduce the amount of tax you owe. The availability of tax credits depends on your individual circumstances and may include the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) or other relevant credits for low-to-moderate-income taxpayers.
Managing Finances and Tax Planning for Uber Driving Income
Effective financial management is crucial for Uber drivers. This includes:
- Separate Business Bank Account: Opening a separate bank account for your Uber income simplifies accounting and tax preparation.
- Consistent Record-Keeping: Maintain meticulous records of all income and expenses throughout the year. Digital tools and apps can significantly assist in this process.
- Regular Tax Payments: Consider making estimated tax payments quarterly to avoid a large tax bill at the end of the year and potential penalties.
- Consult a Tax Professional: Seeking professional tax advice can ensure you maximize deductions and minimize your tax liability.
Sample Tax Form Scenario
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario: John is an Uber driver. His 1099-K shows gross earnings of $30,000. He used the standard mileage deduction, driving 15,000 business miles at $0.585 per mile, totaling $8,775. He also had $500 in tolls and $1,000 in vehicle maintenance expenses. His total deductible expenses are $10,275 ($8,775 + $500 + $1,000). His net taxable income is $19,725 ($30,000 – $10,275). This simplified example doesn’t include all possible deductions or credits. The actual tax liability will depend on John’s tax bracket and other factors. This is a simplified illustration and doesn’t substitute for professional tax advice.
Competition and Market Dynamics
The ride-sharing industry is fiercely competitive, with Uber facing challenges from established players and emerging competitors. Understanding the market dynamics, including competitor policies, fluctuating fuel costs, seasonal demand variations, and the impact of driver ratings, is crucial for drivers to optimize their earnings and navigate the complexities of this dynamic landscape.
Comparison of Driver Policies Across Ride-Sharing Services
Uber’s driver policies, including pay structures, benefits, and requirements, vary compared to competitors like Lyft, Didi, and Ola. Lyft, for example, often offers similar pay structures but may differ in their bonus programs and driver incentives. Didi, primarily operating in China, has its own unique set of regulations and payment systems. Ola, prominent in India, presents a different competitive landscape with its own specific driver requirements and payment models. These variations influence a driver’s overall earning potential and the level of support they receive. Direct comparisons require examining specific details on each platform’s website, as policies are subject to change and vary by region.
Impact of Fluctuating Gas Prices on Driver Earnings
Fluctuating gas prices significantly impact driver earnings. When gas prices rise, net income per ride decreases, requiring drivers to work longer hours to maintain the same level of income. Conversely, falling gas prices boost profitability. For example, a 10% increase in gas prices could translate to a noticeable reduction in a driver’s take-home pay, especially for drivers who rely heavily on their vehicle for income. Effective strategies to mitigate this include optimizing driving routes to minimize fuel consumption and adjusting work hours based on fuel price fluctuations.
Effects of Seasonal Demand on Driver Income, What is business code for uber driver
Seasonal demand heavily influences driver income. Periods of high demand, such as holidays, weekends, and peak tourist seasons, typically result in higher fares and increased ride requests, leading to higher earnings. Conversely, periods of low demand may result in reduced ride requests and lower overall income. For example, during major city events, drivers can expect significantly higher fares and more frequent requests, whereas during off-peak seasons, earnings might decrease substantially. Drivers often adapt their work schedules to capitalize on periods of high demand.
Influence of Driver Ratings on Ride Requests and Income
Driver ratings play a significant role in determining ride requests and consequently, income. High ratings increase the likelihood of receiving more ride requests, as riders tend to prioritize drivers with positive feedback. Conversely, low ratings can lead to fewer ride requests, reducing overall income. Maintaining a high rating requires consistent professionalism, adherence to safety regulations, and providing a positive customer experience. A driver’s rating acts as a performance indicator, directly affecting their earning potential within the platform’s algorithm.
Legal and Contractual Aspects
Understanding the legal and contractual framework governing the relationship between Uber and its drivers is crucial for both parties. This section details the key terms and conditions, rights, responsibilities, dispute resolution processes, and common legal issues faced by Uber drivers. This information is for general understanding and should not be considered legal advice. Always consult with a legal professional for specific guidance.
Uber Driver Agreement Terms and Conditions
The Uber driver agreement, which varies slightly by region, Artikels the terms under which drivers provide services through the Uber platform. Key aspects typically include the independent contractor classification, the driver’s obligation to comply with Uber’s policies and guidelines, the use of the Uber app, payment terms, and termination clauses. These agreements often specify that drivers are not employees of Uber but rather independent contractors responsible for their own taxes, insurance, and vehicle maintenance. The agreement also details the responsibilities of both parties concerning data privacy, intellectual property rights, and the use of the Uber brand. A thorough review of the specific agreement applicable to the driver’s location is essential.
Rights and Responsibilities of Uber Drivers
As independent contractors, Uber drivers have certain rights, including the right to set their own hours, choose which trips to accept, and manage their own business expenses. However, they also have responsibilities, such as maintaining a clean driving record, adhering to Uber’s safety guidelines, and following all applicable traffic laws and regulations. Drivers are also responsible for ensuring their vehicles meet Uber’s requirements, including proper insurance and vehicle inspections. Failure to comply with these responsibilities can result in deactivation from the platform.
Dispute Resolution Process for Uber Drivers
The Uber driver agreement typically Artikels a dispute resolution process. This process might involve initial attempts at informal resolution through Uber’s support channels. If informal resolution fails, the agreement may specify procedures for arbitration or mediation, avoiding costly and time-consuming litigation. The specific details of the dispute resolution process will vary based on the driver’s location and the nature of the dispute. Understanding this process is important for drivers to effectively address any disagreements with Uber.
Common Legal Issues Faced by Uber Drivers
Uber drivers may encounter several legal issues, including disputes over payment, deactivation from the platform, and claims related to accidents or injuries. Disputes over payment can arise from discrepancies in fares, deductions, or delays in payment. Deactivation can result from violations of Uber’s terms of service or safety guidelines, potentially leading to legal challenges if the driver believes the deactivation was unjustified. Accidents involving passengers or third parties can result in liability claims, requiring drivers to understand their insurance coverage and legal responsibilities. Furthermore, the independent contractor classification itself has been a subject of ongoing legal debate and litigation in various jurisdictions. The classification can impact issues such as workers’ compensation, unemployment benefits, and tax liabilities.






