What is the business code for Instacart? Unraveling this question reveals a complex interplay of technology, logistics, and strategic partnerships. Instacart’s success hinges on its ability to connect customers with groceries through a network of shoppers and retail partners, a process facilitated by sophisticated technology and data-driven decision-making. This deep dive explores the intricate mechanisms that power this popular grocery delivery service, examining its business model, technological infrastructure, and competitive landscape.
From its initial conception as a convenient grocery delivery service, Instacart has evolved into a significant player in the e-commerce landscape. Its operational framework encompasses a multifaceted approach, encompassing partnerships with major grocery chains, a robust technological platform, and a vast network of independent shoppers. Understanding Instacart’s business model requires analyzing its revenue streams, cost structures, and overall strategic positioning within the fiercely competitive grocery delivery market. This involves exploring the complexities of its relationships with various stakeholders, from customers and shoppers to retail partners and investors.
Instacart’s Business Model

Instacart operates as a third-party grocery delivery and pick-up service, connecting customers with local grocery retailers. Its success hinges on a multi-sided platform model, leveraging technology to streamline the process of ordering, fulfilling, and delivering groceries. This model generates revenue through various channels, including commissions from retailers, delivery fees charged to customers, and optional membership subscriptions.
Instacart’s Core Business Operations and Revenue Streams
Instacart’s core operations involve facilitating grocery orders from participating retailers. Customers place orders through the Instacart app or website, specifying their desired items and delivery time. Independent contractors, known as Instacart shoppers, then shop for the groceries at the designated store, check out, and deliver the order to the customer. Instacart generates revenue primarily through three streams: commissions paid by partner retailers for each order fulfilled, delivery fees charged directly to the customer, and subscription fees from Instacart Express members who enjoy unlimited free delivery on orders above a certain value. These revenue streams are interdependent, with each contributing significantly to Instacart’s overall profitability.
Types of Services Offered
Instacart provides several services catering to diverse customer and business needs. For consumers, it offers grocery delivery and pick-up options from a wide range of retailers. Customers can choose a specific delivery window or opt for pick-up at a designated store location. Instacart also offers Instacart Express, a membership program providing unlimited free delivery on orders exceeding a certain threshold. For businesses, Instacart offers a suite of solutions designed to enhance their online presence and reach new customers. These include features like customized branding, targeted marketing options, and integration with existing e-commerce platforms. Furthermore, Instacart provides analytics and reporting tools to help businesses track their performance and optimize their offerings.
Comparison with Other Grocery Delivery Services
Instacart’s business model shares similarities with other grocery delivery services like DoorDash, Uber Eats, and Walmart Grocery. However, key differentiators exist. Unlike DoorDash and Uber Eats, which primarily focus on restaurant delivery, Instacart specializes exclusively in grocery delivery and pick-up. Compared to Walmart Grocery, Instacart boasts a wider network of retail partners, providing customers with more choice and convenience. A key competitive advantage for Instacart is its vast network of independent shoppers, offering greater flexibility and scalability compared to services relying solely on employed delivery drivers. The Instacart Express membership program also differentiates it, providing a recurring revenue stream and fostering customer loyalty.
Instacart Order Process Flowchart
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with the customer placing an order on the Instacart app. This would lead to order processing by Instacart’s system, which then assigns the order to a shopper. The shopper shops for the groceries at the designated store, checks out, and then prepares the order for delivery. Finally, the shopper delivers the order to the customer, completing the process. Each stage would be represented by a distinct box in the flowchart, with arrows indicating the flow of the process.]
Key Players and Their Interactions
The Instacart ecosystem comprises several key players whose interactions are crucial to its success.
| Player | Role | Interaction with other players | Value Proposition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customers | Place orders, receive groceries | Interact with Instacart app/website, shoppers, and retailers indirectly | Convenience, selection, time savings |
| Shoppers | Shop for and deliver groceries | Interact with Instacart app, retailers, and customers | Income generation, flexible work schedule |
| Retailers | Provide groceries, fulfill orders | Interact with Instacart platform, shoppers, and customers indirectly | Increased sales, expanded reach, access to new customer base |
| Instacart | Platform operator, technology provider | Connects all players, manages orders, processes payments | Revenue generation through commissions, fees, and subscriptions |
Instacart’s Technology and Infrastructure: What Is The Business Code For Instacart
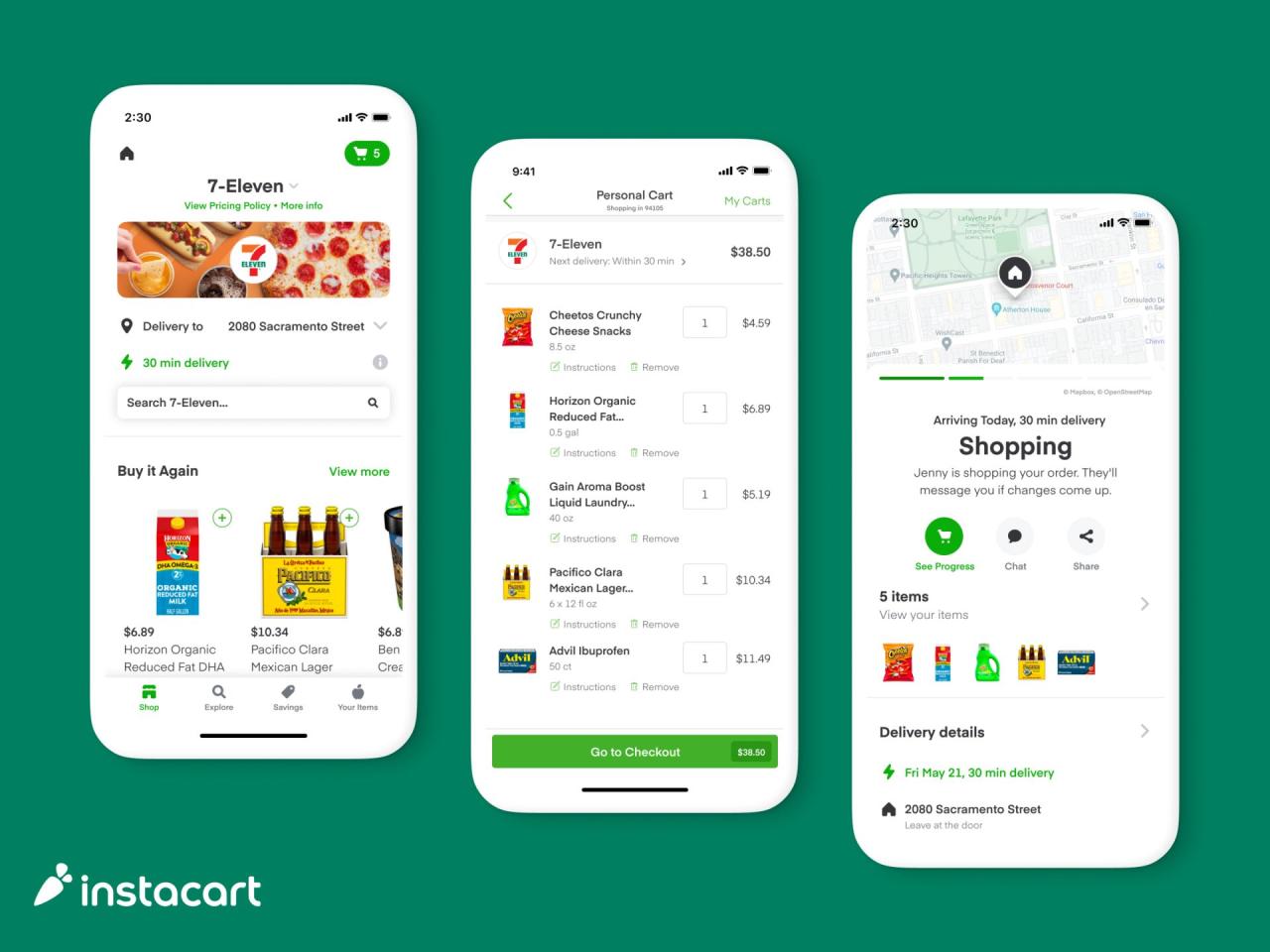
Instacart’s success hinges on a sophisticated technological infrastructure supporting its entire operation, from user interface to complex logistics and data analysis. This intricate system enables the seamless connection between customers, shoppers, and partner stores, ultimately delivering a convenient and efficient grocery delivery experience. Understanding the underlying technology is key to appreciating Instacart’s competitive advantage.
Instacart’s technology is built around a multi-faceted platform encompassing mobile applications, a robust website, a sophisticated order management system, and a complex logistics network. This system manages millions of orders daily, requiring a highly scalable and reliable infrastructure to handle peak demand and ensure timely delivery.
User Experience and Order Management
The Instacart app and website are designed for intuitive user navigation. Customers can easily browse products, add items to their carts, schedule deliveries, and track their orders in real-time. The order management system automatically routes orders to nearby shoppers, manages substitutions, and handles payments. Features like chat functionality and real-time order updates enhance transparency and customer satisfaction. The platform’s responsiveness and ease of use are crucial for maintaining high customer engagement and retention.
Logistics and Delivery Network
Instacart’s logistics network is a critical component of its operations. It relies heavily on a large network of independent contractors known as “shoppers.” These shoppers are recruited through the Instacart app and undergo a background check process. The company employs sophisticated routing algorithms to optimize delivery routes, considering factors such as shopper location, order volume, and traffic conditions. Real-time tracking and communication tools allow for efficient order fulfillment and timely delivery. The effectiveness of this network is constantly being refined through data analysis and algorithmic improvements.
Data Analytics Capabilities and Business Decision-Making
Instacart collects and analyzes vast amounts of data, including customer preferences, shopping patterns, delivery times, and shopper performance. This data is used to optimize various aspects of the business, such as inventory management, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns. Machine learning algorithms are employed to predict demand, personalize recommendations, and improve the efficiency of the delivery network. For example, predictive analytics might identify peak demand periods and allow for proactive shopper recruitment or allocation of resources. Data-driven insights are crucial for strategic decision-making across all departments.
Technological Innovations and Industry Impact
Instacart has consistently introduced technological innovations that have reshaped the grocery delivery industry. Examples include the implementation of advanced routing algorithms that minimize delivery times and fuel consumption, the use of machine learning for personalized recommendations and proactive customer service, and the development of features such as contactless delivery, enhancing safety and convenience during the pandemic. These innovations have not only improved efficiency but also set a new standard for the industry, driving competition and innovation among other players.
Key Technological Components of Instacart’s Platform
The following components are crucial to Instacart’s functioning:
- Mobile Application (iOS and Android): Provides a user-friendly interface for customers to browse, order, and track groceries.
- Website: Offers a desktop alternative for customers who prefer browsing on a larger screen.
- Order Management System: Handles order processing, routing, and real-time tracking.
- Shopper App: Enables shoppers to accept orders, navigate to stores, and manage deliveries.
- Routing Algorithms: Optimize delivery routes for efficiency and speed.
- Payment Gateway: Facilitates secure online transactions.
- Data Analytics Platform: Collects, analyzes, and interprets vast amounts of data to inform business decisions.
- Inventory Management System: Tracks product availability and manages stock levels at partner stores.
- Customer Support System: Provides channels for customers to address concerns and receive assistance.
Instacart’s Partnerships and Relationships

Instacart’s success hinges on its intricate network of partnerships and relationships, encompassing major grocery retailers, smaller chains, and a vast army of independent shoppers. Understanding these collaborations is crucial to grasping the company’s overall business model and its ability to scale operations. The nature of these relationships, both their benefits and drawbacks, significantly impacts Instacart’s profitability, brand reputation, and long-term sustainability.
Key Retail Partners and Collaborations
Instacart partners with a diverse range of grocery retailers, from national giants like Kroger and Costco to regional chains and even smaller, independent stores. These partnerships are typically structured as revenue-sharing agreements, where Instacart receives a commission on each order fulfilled. The level of integration varies depending on the retailer; some retailers fully integrate their inventory and pricing data with Instacart’s platform, allowing for seamless order placement and fulfillment, while others maintain a more independent system. For example, Kroger’s deep integration provides a highly streamlined experience for customers, while a smaller, local grocer might rely more on manual order management through Instacart’s system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Partnerships with Different Retailer Types
The advantages and disadvantages of Instacart’s partnerships differ significantly depending on the size and type of retailer. Large national chains benefit from expanded reach and increased online sales, while smaller retailers gain access to a sophisticated technology platform and a broader customer base. However, larger retailers might experience reduced control over the customer experience and pricing, while smaller retailers may face challenges in managing the logistical complexities of Instacart’s fulfillment process. The cost of integration and the commission rates negotiated also vary significantly, influencing the overall profitability of the partnership for both parties.
Instacart’s Relationship with Independent Shoppers
Instacart’s independent shopper network is a cornerstone of its operations. These shoppers are classified as independent contractors, not employees, meaning they are responsible for their own taxes, insurance, and other employment-related costs. Instacart provides them with an app to manage orders, track their earnings, and communicate with customers. Compensation is typically based on a combination of base pay, tips, and bonuses, with variations depending on factors such as order size, distance, and delivery time. Working conditions are largely determined by the individual shopper’s availability and workload, offering flexibility but also lacking the benefits and protections afforded to traditional employees. This model has been a source of both praise for its flexibility and criticism for its lack of worker protections and inconsistent earnings.
Methods for Managing Relationships with Retailers and Shoppers
Instacart employs various methods to manage its complex network of relationships. With retailers, this involves dedicated account managers, regular performance reviews, and ongoing communication to address operational challenges and explore new opportunities. For shoppers, Instacart uses its app to provide real-time feedback, ratings, and support. The company also relies on a system of incentives and penalties to encourage high-quality service and efficient order fulfillment. This includes performance-based bonuses for shoppers and potential penalties for late deliveries or poor customer ratings. Active communication channels, both formal and informal, are crucial to maintaining a positive and productive relationship with both retailers and shoppers.
Benefits and Challenges of Instacart’s Partnerships
| Partner Type | Benefits | Challenges | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large National Chains (e.g., Kroger) | Increased online sales, expanded reach, access to Instacart’s technology | Reduced control over customer experience, commission fees, potential logistical complexities | Kroger, Safeway |
| Regional and Local Grocers | Access to broader customer base, increased online visibility, technology platform | Integration costs, commission fees, potential competition with larger chains | Local family-owned stores, smaller regional chains |
| Independent Shoppers | Flexibility, potential for high earnings, ability to set own schedule | Inconsistent income, lack of benefits, responsibility for taxes and insurance | Individual Instacart shoppers |
Instacart’s Competitive Landscape and Future Outlook
Instacart operates in a fiercely competitive online grocery delivery market, facing established players and emerging startups alike. Its success hinges on navigating this landscape effectively, leveraging its strengths while mitigating its weaknesses to secure future growth. Understanding its competitive position and potential future scenarios is crucial for assessing its long-term viability.
Instacart’s Competitive Advantages and Disadvantages
Competitive Landscape Analysis
Instacart’s primary competitors include established players like Walmart+, Amazon Fresh, and Kroger, along with regional and specialized delivery services. Walmart+, leveraging its extensive store network and existing customer base, poses a significant threat, particularly in terms of price competitiveness. Amazon Fresh benefits from its robust logistics infrastructure and Prime membership ecosystem. Smaller, localized competitors often offer hyper-local service and potentially faster delivery times within specific geographic areas. Instacart’s competitive advantage lies in its extensive network of partner retailers, providing customers with a broader selection of grocery options compared to competitors with their own private-label offerings. However, its reliance on third-party retailers also presents a weakness, as it lacks direct control over pricing, inventory, and customer experience within those stores. The gig economy model, while providing flexibility, can lead to inconsistent service quality and challenges in managing a large, dispersed workforce.
Strategies for Maintaining a Competitive Edge
Instacart employs several strategies to maintain its competitive edge. These include expanding its partnerships with additional retailers, enhancing its technology platform to improve delivery speed and efficiency, and investing in personalized marketing and customer loyalty programs. For example, its introduction of Instacart Express, a paid membership program, mirrors Amazon Prime, offering customers benefits such as free delivery and reduced service fees. Furthermore, strategic acquisitions of smaller companies can broaden its service offerings and enhance its technological capabilities. A focus on improving its own-brand products and expanding its non-grocery offerings, such as alcohol delivery, could further differentiate Instacart from its competitors.
Future Growth Areas and Challenges
Potential future growth areas for Instacart include expanding into new geographic markets, both domestically and internationally, and further developing its technology to offer more advanced features, such as AI-powered grocery recommendations and automated inventory management. The expansion into areas like meal kit delivery and prepared food services could also attract new customer segments. However, challenges remain, including maintaining profitability in a price-competitive market, managing its large independent contractor workforce effectively, and adapting to evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements. Competition from established retailers with integrated online and offline operations will continue to intensify.
Potential Future Scenarios for Instacart, What is the business code for instacart
The following scenarios illustrate potential future paths for Instacart:
- Scenario 1: Continued Growth and Market Leadership: Instacart successfully leverages its network effects, technological advancements, and strategic partnerships to maintain its position as a leading online grocery delivery platform. This scenario involves continued expansion into new markets and service offerings, resulting in substantial revenue growth and profitability.
- Scenario 2: Consolidation and Acquisition: Facing intense competition, Instacart is acquired by a larger player in the e-commerce or grocery industry, such as Amazon or Walmart, leveraging its existing infrastructure and customer base to enhance their own online grocery offerings.
- Scenario 3: Niche Market Focus: Instacart focuses on specific market segments or geographic areas, potentially specializing in high-value grocery delivery or catering to unique customer needs. This allows it to compete effectively against larger players by concentrating on a defined target audience.
- Scenario 4: Disruption and Decline: Instacart fails to adapt to evolving market dynamics and technological advancements, leading to declining market share and ultimately business failure. This scenario would involve a failure to innovate and compete effectively on price and service quality.
Instacart’s Internal Operations and Management
Instacart’s internal operations are a complex interplay of technology, logistics, and human resources, all working in concert to deliver groceries to customers efficiently and reliably. Understanding these internal processes is key to appreciating the company’s overall success and its challenges. This section will delve into the organizational structure, order fulfillment, customer service, quality control, and supply chain management that underpin Instacart’s business model.
Organizational Structure and Management Hierarchy
Instacart’s organizational structure is not publicly available in complete detail. However, it’s generally understood to be a hierarchical structure, with a CEO at the top, followed by various vice presidents and directors overseeing different departments such as technology, operations, marketing, and finance. Below these senior executives are teams of managers and employees responsible for specific functions. The company likely employs a matrix structure to some degree, allowing for cross-functional collaboration on projects and initiatives. The exact reporting structure and departmental divisions remain largely confidential, reflecting standard business practices for a publicly traded company.
Order Fulfillment Processes
Order fulfillment at Instacart involves several key steps. First, a customer places an order through the Instacart app. The order is then routed to a nearby shopper who accepts the task. The shopper then goes to the designated grocery store, shops for the items, and checks out. Finally, the shopper delivers the groceries to the customer’s specified location. Throughout this process, Instacart’s technology plays a critical role in order routing, communication between shoppers and customers, and real-time tracking of order status. The efficiency of this process is crucial for meeting customer expectations regarding delivery times and order accuracy.
Customer Service and Dispute Resolution
Instacart provides customer service through various channels, including phone, email, and in-app support. The company aims to resolve customer issues promptly and efficiently. Disputes may arise from issues such as incorrect items, damaged goods, or late deliveries. Instacart typically addresses these issues through refunds, replacements, or credits. The process often involves communication between the customer, the shopper, and Instacart’s customer service representatives to gather information and reach a fair resolution. Customer reviews and feedback mechanisms are also crucial in identifying areas for improvement in customer service.
Quality Control and Customer Satisfaction Measures
Instacart employs several measures to ensure quality control and customer satisfaction. These include shopper ratings and reviews, order accuracy checks, and proactive communication with customers. Shoppers are rated by customers based on their performance, and consistently low ratings can lead to account suspension or termination. Instacart also uses technology to monitor order fulfillment and delivery times, allowing for early identification and resolution of potential issues. Customer feedback is actively solicited and analyzed to identify trends and areas needing improvement. Proactive measures such as offering substitutions when items are out of stock are also implemented to enhance customer satisfaction.
Supply Chain and Inventory Management
Instacart’s supply chain management relies heavily on its partnerships with various grocery retailers. The company does not own or manage its own inventory; instead, it leverages the existing inventory and infrastructure of its retail partners. This eliminates the need for Instacart to invest heavily in warehousing and inventory management. However, it also means that Instacart is dependent on the availability and accuracy of inventory data provided by its partners. Maintaining strong relationships with these partners is therefore critical for ensuring a reliable and consistent supply of groceries. Instacart’s technology plays a crucial role in real-time inventory tracking and order optimization, minimizing out-of-stock situations and enhancing efficiency.
Instacart’s internal operations are characterized by a sophisticated blend of technology, robust logistical processes, and a strong emphasis on customer satisfaction. The company’s ability to manage its complex supply chain, ensure timely order fulfillment, and resolve customer issues efficiently is crucial to its ongoing success. Maintaining a balance between efficiency and customer experience remains a key challenge for the company.






