What is the process of guiding business strategy using facts? This question lies at the heart of effective business leadership. It’s no longer enough to rely on gut feeling or intuition; successful strategies are built on a foundation of verifiable data, rigorous analysis, and a commitment to continuous improvement. This exploration delves into the key steps involved in transforming raw data into actionable insights, driving informed decision-making, and ultimately, achieving sustainable business growth. We’ll examine how to identify relevant KPIs, collect and analyze data from various sources, and translate those insights into concrete, measurable goals.
The journey from data collection to strategic implementation is a dynamic one, requiring adaptability and a willingness to adjust course based on new evidence. We’ll cover methods for monitoring progress, evaluating results, and incorporating feedback to refine the strategic direction. By the end, you’ll possess a practical framework for building a fact-based strategy that empowers your business to thrive in an ever-changing market.
Defining a Fact-Based Business Strategy
A fact-based business strategy prioritizes data-driven insights over intuition and assumptions. This approach ensures that strategic decisions are grounded in reality, minimizing risk and maximizing the likelihood of success. By systematically collecting, analyzing, and interpreting relevant data, businesses can develop strategies that are both effective and adaptable to changing market conditions. This methodology promotes a culture of informed decision-making, fostering efficiency and accountability throughout the organization.
A fact-based business strategy relies on several core principles. First, it necessitates a commitment to data collection across all relevant areas of the business. Second, rigorous analysis of this data is crucial to identify trends, patterns, and potential opportunities or threats. Third, the strategy must be flexible and adaptable, allowing for course correction based on ongoing data analysis. Finally, effective communication of the strategy and its underlying data is essential to ensure buy-in and alignment across the organization.
Data Sources for Accurate Strategic Decision-Making
Reliable data forms the bedrock of any effective fact-based strategy. Various sources provide valuable insights, each offering a unique perspective on the business landscape. Ignoring any of these sources risks creating a skewed and incomplete understanding of the market and the business’s position within it.
The importance of diverse data sources cannot be overstated. Relying solely on a single source can lead to inaccurate conclusions and flawed strategic decisions. A robust fact-based strategy integrates information from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive view.
- Internal Data: This encompasses sales figures, marketing campaign performance, customer relationship management (CRM) data, operational metrics, and financial statements. Analyzing internal data reveals trends in customer behavior, product performance, and operational efficiency.
- Market Research Data: This includes reports from market research firms, industry publications, and competitor analyses. This data provides insights into market size, growth potential, competitive landscape, and consumer preferences.
- Customer Data: Information gathered directly from customers through surveys, feedback forms, and social media monitoring offers invaluable insights into customer satisfaction, needs, and preferences. This data is crucial for product development, marketing, and customer service improvements.
- Economic and Industry Data: Government statistics, industry reports, and economic forecasts provide a macroeconomic context for strategic planning. Understanding broader economic trends and industry dynamics is essential for anticipating market shifts and adjusting the strategy accordingly.
Data Validation and Reliability
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data is paramount to the success of a fact-based strategy. Invalid or unreliable data can lead to flawed conclusions and ineffective strategies. A robust data validation process is therefore crucial.
Several best practices contribute to data reliability. First, data sources should be rigorously vetted for credibility and accuracy. Second, data cleaning and preprocessing techniques should be employed to identify and correct errors, inconsistencies, and outliers. Third, statistical methods can be used to assess the validity and reliability of the data. Finally, multiple data sources should be cross-referenced to verify the consistency and accuracy of the information. For example, comparing sales figures from internal systems with independent market research data can help identify discrepancies and potential errors. This rigorous approach minimizes the risk of making decisions based on flawed information.
Data Collection and Analysis for Strategic Guidance
Effective fact-based business strategy relies heavily on the meticulous collection and analysis of relevant data. This process transforms raw information into actionable insights, enabling informed decision-making and a more competitive market position. Understanding where to find this data, how to collect it, and how to interpret the results is crucial for success.
Data collection and analysis for strategic guidance involves a systematic approach to identifying, gathering, and interpreting information to inform business decisions. This process ensures that strategic choices are rooted in evidence rather than assumptions, minimizing risks and maximizing the chances of achieving business objectives.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The selection of KPIs is paramount. KPIs should directly reflect the overarching business objectives. For instance, if the objective is to increase market share, relevant KPIs might include website traffic, conversion rates, and customer acquisition cost. Conversely, if the primary goal is to improve operational efficiency, suitable KPIs could be production output, defect rates, and inventory turnover. A well-defined set of KPIs provides a clear framework for measuring progress and identifying areas needing improvement. Choosing the wrong KPIs can lead to misguided efforts and resource misallocation.
Data Collection Methodology
A robust methodology for data collection ensures the accuracy and reliability of the insights derived. This involves identifying diverse data sources, determining appropriate collection methods, and establishing a system for organizing and storing the collected information. Data sources can range from internal systems (CRM, ERP, sales reports) to external sources (market research reports, competitor analysis, customer surveys). Collection methods may include automated data extraction, manual data entry, surveys, interviews, and observational studies. A well-structured data collection process ensures data integrity and minimizes bias.
Data Organization and Presentation for Strategic Analysis, What is the process of guiding business strategy using facts
Once data is collected, organizing it in a clear and concise manner is essential for effective analysis. This often involves creating a structured database or spreadsheet, categorizing data by relevant variables, and summarizing key findings. Visualizations such as charts and graphs can further enhance understanding and facilitate communication of insights to stakeholders. A well-organized dataset allows for efficient analysis, identification of trends, and informed decision-making.
| Data Source | Data Type | Collection Method | Data Reliability Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales CRM | Sales revenue, conversion rates, customer demographics | Automated data extraction | High (directly from transactional system) |
| Customer Surveys | Customer satisfaction, product feedback, brand perception | Online surveys, email questionnaires | Medium (subject to response bias) |
| Market Research Reports | Market size, growth rate, competitor analysis | Purchase of industry reports | High (from reputable market research firms) |
| Website Analytics | Website traffic, bounce rate, time on site | Google Analytics | High (reliable tracking tools) |
Identifying Trends and Opportunities
Uncovering future market success hinges on accurately identifying emerging trends and opportunities. This requires a rigorous, fact-based approach, moving beyond intuition and relying instead on robust data analysis to inform strategic decisions. By systematically analyzing data, businesses can proactively adapt to changing market dynamics and capitalize on lucrative opportunities before competitors.
Data analysis techniques reveal patterns and insights that would otherwise remain hidden, enabling businesses to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and achieve sustainable growth. The following sections detail techniques for leveraging data to identify trends and opportunities, comparing different analytical approaches and offering a step-by-step guide to interpreting data visualizations.
Trend Identification Techniques
Identifying emerging trends requires a multifaceted approach. Several techniques, when used in combination, offer a comprehensive view of market shifts. These include analyzing market research reports, monitoring social media sentiment, tracking competitor activities, and conducting surveys to gauge customer preferences. For instance, analyzing Google Trends data can reveal shifts in consumer search behavior, signaling emerging interests and potential market opportunities. Similarly, monitoring social media conversations can uncover unmet customer needs or emerging product categories.
Comparative Analysis of Analytical Approaches
Different analytical approaches offer unique perspectives on data. Descriptive analytics provides a summary of past performance, identifying key metrics and trends. For example, calculating the year-over-year growth of sales revenue provides a clear picture of past performance. Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast future outcomes, such as predicting customer churn based on past behavior. Prescriptive analytics, on the other hand, goes a step further, recommending optimal actions based on predictions. For example, it might suggest targeted marketing campaigns to reduce churn risk. Choosing the right approach depends on the specific business question and the available data. Often, a combination of these approaches provides the most comprehensive insights.
Interpreting Data Visualizations for Strategic Decision-Making
Data visualizations are crucial for effective communication and strategic decision-making. A step-by-step approach to interpretation ensures accurate understanding and avoids misinterpretations.
- Understand the context: Before analyzing any visualization, understand the data source, the time period covered, and the variables represented. For example, a line graph showing sales revenue over time needs to be understood in the context of overall market trends and economic conditions.
- Identify key trends: Look for patterns, upward or downward trends, and significant fluctuations. For example, a sharp increase in sales might indicate a successful marketing campaign or the launch of a new product. A downward trend might signal the need for corrective action.
- Compare data points: Compare different data points to identify relationships and correlations. For example, comparing sales revenue to marketing spend can reveal the return on investment of marketing activities.
- Consider outliers: Investigate unusual data points or outliers to understand the reasons behind them. These outliers might represent opportunities or problems that require further investigation.
- Draw conclusions and make recommendations: Based on the analysis, draw clear conclusions and make data-driven recommendations for strategic decision-making. For example, if a specific marketing channel shows a high return on investment, allocate more resources to that channel.
Developing Actionable Strategies Based on Facts
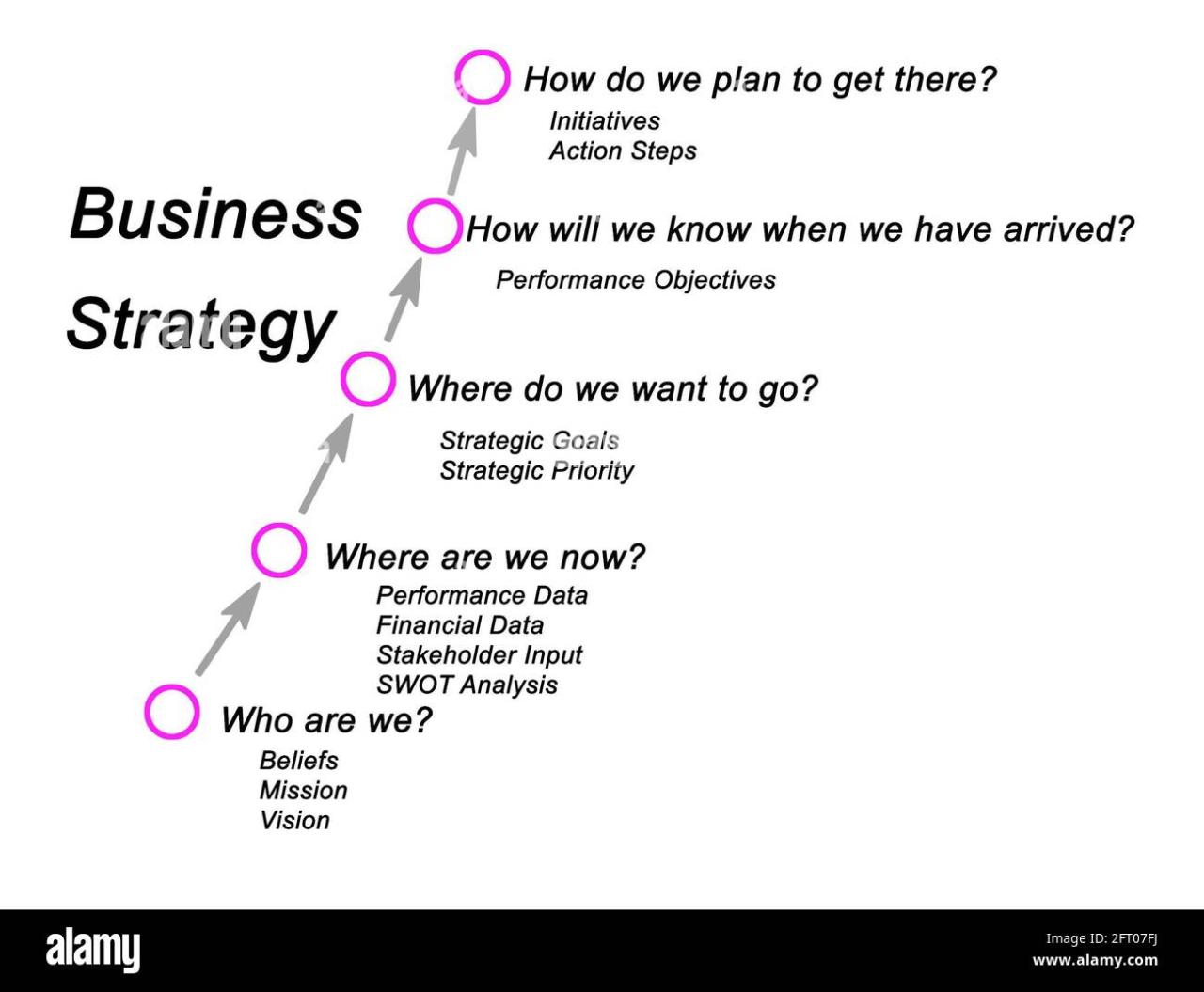
Data-driven insights are invaluable, but they only become truly useful when translated into concrete actions. This section details how to transform factual analysis into actionable strategies that drive business growth. The key lies in developing SMART goals and prioritizing initiatives based on their potential impact and feasibility.
Converting data insights into actionable strategies requires a systematic approach. This involves clearly defining SMART goals, developing strategies that directly address identified opportunities and challenges, and prioritizing these strategies based on their potential impact and feasibility. This process ensures that resources are allocated effectively to initiatives with the highest probability of success.
Defining SMART Goals Based on Data Insights
Translating data-driven insights into actionable strategies begins with setting SMART goals. SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. For example, if data analysis reveals a decline in customer engagement on a specific platform, a SMART goal could be: “Increase customer engagement on Platform X by 15% within the next quarter by implementing a new content strategy focused on user-generated content.” This goal is specific, measurable (15% increase), achievable (given sufficient resources and a well-defined strategy), relevant (addresses the decline in engagement), and time-bound (next quarter). Each goal should directly stem from a specific data-driven insight, ensuring alignment between analysis and action.
Developing Strategies to Address Opportunities and Challenges
Once SMART goals are defined, the next step involves developing strategies to achieve them. These strategies should be directly linked to the data-driven insights that informed the goals. For instance, if market research indicates a growing demand for a specific product feature, a strategy could involve accelerating the development and launch of that feature. Conversely, if data shows a high customer churn rate due to poor customer service, the strategy could focus on improving customer service processes through training programs and implementing a new customer relationship management (CRM) system. Each strategy should include specific tactics and action steps, outlining how the goal will be achieved.
Prioritizing Strategic Initiatives Based on Impact and Feasibility
Prioritization is crucial when multiple strategic initiatives compete for resources. A framework for prioritizing initiatives could involve a simple matrix plotting potential impact against feasibility. High-impact, high-feasibility initiatives should be prioritized first. For example, a marketing campaign targeting a highly receptive customer segment (high impact, high feasibility) would rank higher than developing a new product line with uncertain market demand (high impact, low feasibility). Data analysis provides the evidence needed to assess both impact and feasibility. For instance, conversion rates from previous campaigns can inform impact estimations, while resource availability and technological constraints inform feasibility assessments. This prioritization ensures that resources are allocated effectively to the initiatives most likely to deliver significant returns.
Monitoring and Evaluating Progress

Effective monitoring and evaluation are crucial for ensuring a fact-based business strategy remains on track and delivers the desired outcomes. Without consistent tracking and analysis of key performance indicators (KPIs), identifying necessary adjustments becomes difficult, potentially leading to missed opportunities or wasted resources. A robust system for collecting feedback and adapting the strategy is essential for navigating the dynamic business landscape.
Regular monitoring and evaluation allows businesses to identify early warning signs of potential problems, allowing for proactive intervention rather than reactive damage control. This iterative process of data analysis and strategic adjustment is central to the success of any fact-based approach. The continuous feedback loop ensures that the strategy remains relevant and effective in achieving its objectives.
KPI Tracking and Measurement
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) provides quantifiable data to assess the effectiveness of the implemented strategy. Selecting the right KPIs depends on the specific strategic goals, but generally includes metrics related to revenue, market share, customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and employee productivity. Regular reporting on these KPIs, perhaps on a weekly or monthly basis, provides a clear picture of progress and identifies areas needing attention. For example, a company aiming to increase market share might track website traffic, lead generation, and conversion rates. A drop in conversion rates might signal a problem with the sales process, prompting a review and adjustment of sales strategies. Data visualization tools like dashboards can make it easier to understand complex data and identify trends.
Feedback Collection and Incorporation
Establishing a system for collecting and incorporating feedback is essential for ongoing strategic adjustments. This involves multiple channels, including customer surveys, employee feedback mechanisms, market research, and competitor analysis. Regularly analyzing this feedback reveals areas where the strategy needs refinement or where unexpected opportunities might exist. For example, customer surveys can pinpoint areas of dissatisfaction, while competitor analysis can highlight emerging threats or innovative approaches. This feedback should be systematically analyzed and integrated into the ongoing strategic planning process. This might involve adjusting marketing campaigns, improving customer service protocols, or refining product development strategies.
Identifying Deviations and Adapting the Approach
Identifying deviations from the planned strategy requires a continuous comparison of actual results against the established targets and KPIs. This process involves:
- Regular Data Analysis: Conduct frequent reviews of KPI data to detect any significant variations from projected performance. This might involve using statistical process control (SPC) techniques to identify trends and anomalies.
- Variance Analysis: Investigate the root causes of any significant deviations. This requires a deep dive into the data to understand the factors contributing to the discrepancy between planned and actual results.
- Scenario Planning: Develop alternative scenarios based on the identified deviations. This involves considering various potential outcomes and adjusting the strategy accordingly. For instance, if market demand unexpectedly drops, the company might need to adjust its pricing strategy or explore new market segments.
- Strategic Adjustments: Implement necessary changes to the strategy based on the analysis of deviations and scenario planning. This might involve resource allocation shifts, adjustments to marketing campaigns, or changes to operational processes.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitor the impact of the adjustments and make further refinements as needed. This ensures the strategy remains responsive to changes in the business environment.
Illustrating the Process with a Hypothetical Scenario: What Is The Process Of Guiding Business Strategy Using Facts
This section details a hypothetical scenario to illustrate the practical application of a fact-based business strategy. We’ll follow the steps Artikeld previously, highlighting the data used, the challenges faced, and the resulting strategic decisions. The example focuses on a mid-sized coffee roaster aiming for expansion.
Let’s consider “Brewtiful Beans,” a regional coffee roaster experiencing plateauing sales despite increasing local competition. Their current strategy relies heavily on word-of-mouth and a limited online presence. They suspect a shift in consumer preferences and increased competition are impacting their growth. To address this, they decide to adopt a fact-based approach to strategic planning.
Data Collection and Analysis for Brewtiful Beans
Brewtiful Beans begins by collecting data from several sources. This includes internal sales figures (volume, revenue, customer demographics from loyalty program data), external market research reports on coffee consumption trends and competitor analysis (obtained through market research firms and publicly available information), and social media sentiment analysis regarding their brand and competitors. They also conduct customer surveys to understand preferences regarding coffee types, brewing methods, and purchasing habits. This multifaceted approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of the market and their position within it.
Identifying Trends and Opportunities for Brewtiful Beans
Analysis of the collected data reveals several key trends. Firstly, there’s a growing demand for ethically sourced, single-origin coffees, a segment Brewtiful Beans currently under-serves. Secondly, online sales are significantly increasing, while their own e-commerce platform is underperforming compared to competitors. Finally, the data suggests a strong preference among younger demographics for subscription-based coffee delivery services. These trends represent both challenges (increased competition, lagging online presence) and opportunities (expanding into ethically sourced coffee, developing a subscription service).
Developing Actionable Strategies Based on Facts for Brewtiful Beans
Based on the data analysis, Brewtiful Beans develops a three-pronged strategy. First, they will source high-quality, ethically sourced single-origin beans to cater to the growing demand. Second, they will invest in improving their online presence and e-commerce platform, focusing on user experience and online marketing. Third, they will launch a subscription service offering curated coffee selections delivered directly to customers’ homes. The investment in each area is directly proportional to the potential return indicated by the data.
The key strategic decisions are: 1) Sourcing high-quality, ethically sourced single-origin beans; 2) Significantly improving the online presence and e-commerce platform; and 3) Launching a subscription-based coffee delivery service.
Monitoring and Evaluating Progress for Brewtiful Beans
Brewtiful Beans will monitor the success of these strategies by tracking key performance indicators (KPIs). These include website traffic and conversion rates for the e-commerce platform, subscriber growth for the subscription service, and sales figures for the new single-origin coffees. Regular data analysis will allow them to adjust their strategy as needed, ensuring it remains aligned with evolving market trends and consumer preferences. They will use A/B testing on the website to optimize conversion rates and customer segmentation to personalize marketing efforts. This iterative approach will ensure continuous improvement and maximize the impact of their fact-based strategy.






