Where can we find TCS process for business continuity management? This crucial question underscores the importance of understanding Tata Consultancy Services’ (TCS) robust approach to ensuring business resilience. This exploration delves into TCS’s comprehensive Business Continuity Management (BCM) framework, examining its methodologies, strategies, and technological underpinnings. We’ll uncover how TCS identifies and mitigates risks, plans for disruptions, and leverages technology to maintain operational continuity across various industries. Understanding TCS’s BCM is vital for businesses seeking best practices in risk management and disaster recovery.
From risk assessment and planning to implementation, testing, and ongoing maintenance, we will dissect the intricacies of TCS’s BCM process. We’ll examine the key technologies employed, including cloud computing and data analytics, and explore how TCS integrates security measures into its overall strategy. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of where to find this critical information and how TCS ensures business continuity in a constantly evolving threat landscape.
TCS Business Continuity Management Overview
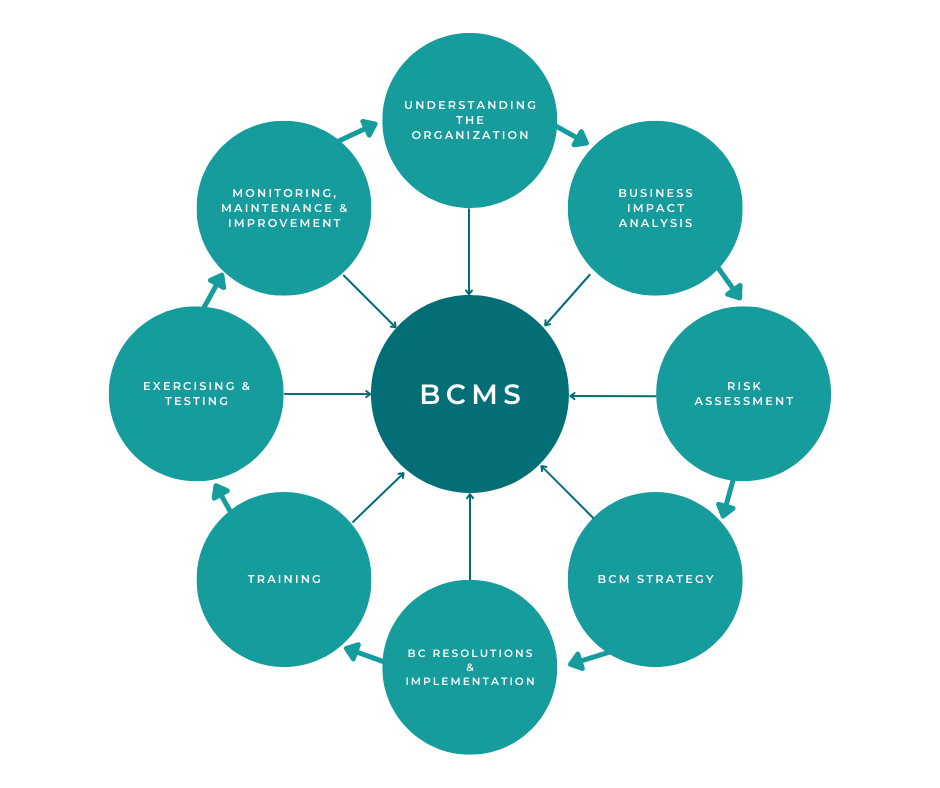
TCS’s approach to Business Continuity Management (BCM) is a comprehensive, proactive strategy designed to ensure the continued operation of critical business functions during disruptive events. It goes beyond simple disaster recovery, encompassing risk assessment, mitigation planning, and robust recovery procedures to minimize business interruption and maintain operational resilience. The framework is underpinned by a commitment to minimizing the impact of disruptions on clients, employees, and stakeholders.
TCS’s BCM framework is guided by several key principles. These include a strong emphasis on risk identification and assessment, using advanced analytics and industry best practices to understand potential threats. Proactive mitigation strategies are developed and implemented to reduce the likelihood and impact of these risks. Comprehensive recovery plans, including detailed procedures and tested failover mechanisms, are central to the framework. Regular testing and training exercises ensure that plans are current, effective, and understood by all relevant personnel. Finally, continuous improvement is integral, with post-incident reviews used to refine processes and enhance resilience.
TCS’s BCM solutions are widely applied across diverse industries. Examples include financial services, where robust BCM is crucial for maintaining regulatory compliance and preventing financial losses; healthcare, where the continuity of patient care is paramount; and manufacturing, where disruptions can lead to significant production downtime and supply chain issues. The framework’s adaptability allows for customization to meet the specific needs and regulatory requirements of each industry sector.
TCS BCM Services Compared to a Competitor
The following table compares TCS’s BCM services with those of a major competitor (for illustrative purposes, we will use a hypothetical competitor, “Competitor X”). Note that specific service offerings and descriptions may vary based on the latest updates from both providers. This comparison is for illustrative purposes only and should not be taken as definitive.
| Service Name | TCS Description | Competitor X Description | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Assessment & Analysis | Utilizes advanced analytics and industry benchmarks to identify and assess potential threats, prioritizing risks based on likelihood and impact. Includes qualitative and quantitative risk analysis methodologies. | Offers risk assessment services but may rely less heavily on advanced analytics and may not prioritize risks in the same way. | TCS emphasizes a more data-driven and sophisticated approach to risk assessment. |
| Business Impact Analysis (BIA) | Conducts thorough BIA to determine the impact of potential disruptions on critical business functions, identifying recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs). | Provides BIA services, but the depth and methodology may differ. | Differences may exist in the level of detail and the specific methodologies used. |
| Disaster Recovery Planning | Develops comprehensive disaster recovery plans that incorporate various recovery strategies, including failover mechanisms, data backup and restoration procedures, and alternative site arrangements. | Offers similar services, but the level of customization and the range of recovery strategies may vary. | The extent of customization and the inclusion of advanced technologies may differ. |
| Business Continuity Training & Exercises | Provides comprehensive training programs and conducts regular drills and simulations to ensure staff preparedness and plan effectiveness. | Offers training and exercises but the frequency and scope might vary. | TCS might emphasize more frequent and realistic simulations. |
Identifying and Assessing Business Risks within TCS’s BCM
TCS’s Business Continuity Management (BCM) framework relies on a robust risk identification and assessment methodology to proactively mitigate potential disruptions. This process ensures business resilience by identifying vulnerabilities and developing strategies to minimize their impact on critical operations. The methodology integrates qualitative and quantitative data analysis to provide a comprehensive understanding of risk exposure.
TCS employs a structured approach to identify and assess business risks, encompassing various methodologies and tools tailored to the specific context and nature of the threat. This includes regular risk assessments, scenario planning, and vulnerability analyses. The goal is to develop a prioritized list of risks, enabling the allocation of resources and the implementation of effective mitigation strategies.
Risk Identification and Assessment Methodology, Where can we find tcs process for business continuity management
TCS’s risk identification and assessment methodology is a cyclical process, regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the business environment and technological landscape. It incorporates both top-down and bottom-up approaches, gathering insights from various stakeholders across the organization. This ensures a comprehensive view of potential risks, encompassing both known vulnerabilities and emerging threats. The process leverages established frameworks and best practices, such as ISO 22301, to ensure alignment with international standards.
Types of Risks Addressed in TCS BCM Plans
TCS BCM plans address a wide range of risks that could potentially disrupt business operations. These risks are categorized based on their source and potential impact. Examples include:
* Natural Disasters: Earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and other natural events that can damage infrastructure and disrupt operations. Contingency plans include backup facilities, data replication, and disaster recovery procedures.
* Cyberattacks: Malware infections, denial-of-service attacks, and data breaches that can compromise sensitive information and disrupt IT systems. Mitigation strategies include robust cybersecurity measures, incident response plans, and data backup and recovery procedures.
* Pandemics: Outbreaks of infectious diseases that can impact employee health, limit workforce availability, and disrupt supply chains. TCS’s response includes remote work capabilities, business continuity plans for critical functions, and health and safety protocols.
* Supply Chain Disruptions: Interruptions in the flow of goods and services, which can impact production, delivery, and customer service. Mitigation strategies include diverse sourcing, inventory management, and supplier relationship management.
* Political and Economic Instability: Geopolitical events, economic downturns, and regulatory changes that can impact market conditions and business operations. Risk mitigation strategies involve scenario planning, diversification, and robust financial management.
Steps Involved in a TCS Risk Assessment
A comprehensive risk assessment is crucial for effective BCM planning. The steps involved in a typical TCS risk assessment include:
The process begins with defining the scope of the assessment, identifying critical business functions, and establishing assessment criteria. This ensures that the assessment is focused and relevant to the organization’s specific needs.
- Risk Identification: Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities that could impact business operations. This involves brainstorming sessions, surveys, and vulnerability assessments.
- Risk Analysis: Evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of each identified risk. This often involves qualitative and quantitative analysis, as discussed below.
- Risk Prioritization: Ranking risks based on their likelihood and potential impact, using a risk matrix or similar tool. This helps to focus resources on the most critical risks.
- Risk Response Planning: Developing strategies to mitigate, transfer, accept, or avoid each identified risk. This includes developing detailed contingency plans and recovery procedures.
- Risk Monitoring and Review: Regularly monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies and updating the risk assessment as needed. This ensures that the BCM plan remains relevant and effective.
Qualitative and Quantitative Data in Risk Analysis
TCS utilizes both qualitative and quantitative data in its risk analysis to gain a comprehensive understanding of potential threats.
Qualitative data provides context and insight into the nature of risks. This might include expert opinions, historical data on similar events, and stakeholder feedback. For example, expert interviews can help assess the likelihood of a cyberattack based on industry trends and emerging threats.
Quantitative data provides numerical measures of risk, enabling a more objective assessment. This can include financial data, historical incident reports, and statistical modeling. For example, analyzing historical data on system failures can help estimate the likelihood and potential financial impact of IT outages.
By combining qualitative and quantitative data, TCS develops a more nuanced and accurate assessment of risk, allowing for more effective mitigation strategies.
TCS BCM Planning and Implementation Strategies
TCS’s Business Continuity Management (BCM) planning and implementation are crucial for ensuring operational resilience and minimizing disruption during unforeseen events. A robust BCM plan incorporates risk assessment, strategy development, and regular testing and improvement cycles, ensuring TCS can maintain critical business functions even in challenging circumstances. This section details the key aspects of TCS’s BCM planning and implementation strategies.
Stages in Developing a TCS BCM Plan
Developing a comprehensive TCS BCM plan involves several sequential stages. These stages ensure a thorough and effective plan that addresses potential threats and vulnerabilities across the organization. The process typically begins with a detailed assessment of business risks and impact, followed by the development of recovery strategies and the implementation of these strategies. Regular testing and updates are crucial to maintaining the plan’s effectiveness. The plan’s development is an iterative process, incorporating lessons learned from testing and real-world incidents. Each stage involves detailed documentation and stakeholder engagement to ensure alignment and understanding across the organization.
TCS Recovery Strategies
TCS employs a multi-faceted approach to recovery, leveraging various strategies to ensure business continuity. These strategies are designed to minimize downtime and data loss in the event of a disruption. Backup and recovery mechanisms are fundamental, providing a means to restore data and systems to their pre-disruption state. Failover mechanisms, such as redundant systems and geographically dispersed data centers, allow for seamless transition to backup resources in case of primary system failure. Relocation strategies, involving the temporary movement of operations to alternative facilities, are implemented for large-scale disruptions affecting primary locations. The choice of strategy depends on the nature and scale of the incident, as well as the criticality of the affected business functions. For example, a minor server failure might be handled through simple backup and recovery, while a major natural disaster might necessitate a full-scale relocation.
Business Impact Analysis (BIA) Techniques at TCS
TCS utilizes several BIA techniques to identify and assess the impact of potential disruptions on its business operations. These techniques provide a structured approach to understanding the criticality of various business functions and the potential consequences of their interruption. Quantitative techniques, such as financial modeling, are used to estimate the financial losses associated with downtime. Qualitative techniques, such as stakeholder interviews and surveys, are employed to gather insights into the impact on various stakeholders. A combination of these techniques provides a comprehensive understanding of the potential impact of disruptions, allowing for the prioritization of recovery efforts. For example, TCS might use financial modeling to assess the cost of downtime for a critical e-commerce platform, while stakeholder interviews could help assess the impact of a system outage on customer satisfaction.
TCS Disaster Recovery Plan Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates the steps involved in TCS’s disaster recovery plan. Note that this is a simplified representation and the actual plan involves greater detail and complexity.
“`
[Start] –> [Incident Detection & Notification] –> [Incident Assessment & Confirmation] –> [Activation of DR Plan] –> [Resource Allocation & Mobilization] –> [System Restoration & Data Recovery] –> [Business Operations Resumption] –> [Post-Incident Review & Lessons Learned] –> [Plan Update & Improvement] –> [End]
“`
Each stage involves specific actions and responsibilities, meticulously documented within the comprehensive TCS Disaster Recovery Plan. The plan’s effectiveness is regularly tested through drills and simulations, ensuring its readiness to handle various scenarios. Continuous improvement is a core principle, with lessons learned from each test and incident incorporated into subsequent updates.
TCS BCM Testing and Maintenance Procedures: Where Can We Find Tcs Process For Business Continuity Management

Regular testing and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of TCS’s Business Continuity Management (BCM) plans. These processes validate the plans’ accuracy, identify weaknesses, and ensure they remain aligned with evolving business needs and potential threats. A robust testing and maintenance regime is essential for TCS to maintain its operational resilience and minimize disruption during unforeseen events.
TCS employs a multi-layered approach to testing and maintaining its BCM plans, incorporating various methods to assess preparedness and identify areas for improvement. This approach includes regular reviews, simulations, and exercises, all designed to enhance the effectiveness and adaptability of the BCM framework. The frequency and scope of these activities are determined by the criticality of the business function and the potential impact of disruption.
Types of BCM Tests Conducted by TCS
TCS utilizes a range of testing methodologies to validate its BCM plans, each offering a different level of complexity and realism. These tests are designed to assess the effectiveness of various response strategies and identify potential gaps in preparedness. The choice of testing method depends on the specific business function being tested and the resources available.
Tabletop exercises are frequently employed for initial assessments and smaller-scale scenarios. These exercises involve a facilitated discussion among key personnel, walking through potential disaster scenarios and evaluating the effectiveness of response plans. Full-scale simulations, on the other hand, involve a more comprehensive and realistic test, often including the participation of a wider range of staff and the utilization of actual systems and resources. These simulations provide a more thorough evaluation of the plan’s effectiveness under pressure. Other methods, such as partial simulations or functional drills, may also be employed depending on the specific needs.
Frequency and Scope of BCM Testing
The frequency and scope of BCM testing at TCS vary depending on the criticality of the business function and the potential impact of disruption. Critical business functions, those with a high potential for significant financial or reputational damage, are typically tested more frequently and with a greater scope. For example, data center recovery plans might be tested annually with a full-scale simulation, while less critical functions might undergo tabletop exercises every two years. The scope of testing also considers the potential impact of various threats, such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or pandemics. Regular reviews of the BCM plans are conducted at least annually, often more frequently, to ensure they remain current and effective.
TCS BCM Plan Maintenance and Updates
Maintaining and updating BCM plans is an ongoing process at TCS. This involves regularly reviewing the plans to ensure they remain accurate and effective, incorporating lessons learned from past incidents and adapting to changes in the business environment and technology. This continuous improvement process ensures that the plans remain relevant and effective in mitigating future disruptions. Regular updates are driven by factors such as changes in legislation, technology upgrades, and lessons learned from past tests and real-world incidents. A dedicated team is responsible for managing and maintaining the BCM plans, ensuring their accuracy and relevance. This team works closely with various business units to incorporate feedback and updates from across the organization.
BCM Test Summary Table
| Test Type | Frequency | Personnel Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Tabletop Exercise | Annually or Bi-annually (depending on criticality) | BCM Team, Business Unit Representatives, IT Staff (as relevant) |
| Full-Scale Simulation | Every 2-3 years (depending on criticality) | BCM Team, Business Unit Representatives, IT Staff, Security Team, potentially external vendors |
| Partial Simulation/Functional Drill | As needed, based on risk assessments and updates | Relevant Business Unit and IT personnel |
Communication and Collaboration in TCS BCM
Effective communication and collaboration are paramount to TCS’s Business Continuity Management (BCM) strategy, ensuring a swift and coordinated response during disruptions. A robust communication framework, encompassing various channels and clearly defined roles, is crucial for minimizing downtime and maintaining business operations. This section details the communication protocols, team responsibilities, technological leverage, and communication flow within TCS’s BCM framework.
Communication Protocols During Business Disruptions
TCS employs a multi-layered communication strategy leveraging various channels to ensure timely and accurate information dissemination during a business disruption. These protocols are designed to reach all stakeholders – employees, clients, vendors, and internal teams – with appropriate information at each stage of the incident. Examples include utilizing dedicated emergency hotlines, email alerts, SMS notifications, and internal communication platforms such as collaboration tools and enterprise social networks. Specific communication protocols are tailored to the nature and severity of the disruption, prioritizing critical information dissemination. For instance, during a major natural disaster impacting multiple locations, a tiered approach might be employed, prioritizing communication with employees in affected areas about safety and evacuation procedures before disseminating broader updates about business operations.
Roles and Responsibilities of Teams in TCS BCM Response
TCS’s BCM response involves a coordinated effort from several specialized teams, each with clearly defined roles and responsibilities. The BCM team itself acts as the central coordinating body, responsible for activating the BCM plan, monitoring the situation, and overseeing communication efforts. The IT team plays a crucial role in restoring IT infrastructure and ensuring data security. The HR team focuses on employee safety and well-being, providing support and guidance during the crisis. The legal and compliance team addresses any legal or regulatory ramifications. Finally, the communication team manages internal and external communications, ensuring timely and accurate information flow to all stakeholders. Each team’s responsibilities are clearly Artikeld in the BCM plan, ensuring a seamless and efficient response.
Technological Leverage for Communication and Collaboration
TCS leverages technology extensively to facilitate communication and collaboration during incidents. This includes utilizing dedicated communication platforms for secure and efficient information exchange among response teams. Collaboration tools enable real-time updates, document sharing, and video conferencing, facilitating coordinated decision-making across geographical locations. Automated alert systems ensure timely notifications to relevant personnel, minimizing response time. Data analytics and visualization tools provide real-time insights into the impact of the disruption, enabling data-driven decision-making. For instance, dashboards might display the status of critical systems, employee safety reports, and the overall impact on business operations. The use of these technologies ensures that communication is efficient, secure, and readily accessible to all relevant personnel.
Communication Flow During a Crisis
The following diagram illustrates the communication flow within TCS during a crisis:
[Diagram Description: Imagine a central node labeled “BCM Command Center.” Arrows radiate outwards to nodes representing: “IT Team,” “HR Team,” “Legal & Compliance Team,” “Communication Team,” “Affected Employees,” and “Clients/Vendors.” Arrows also connect these nodes to each other to illustrate the information exchange. For example, an arrow goes from “BCM Command Center” to “IT Team” indicating instructions and updates. An arrow from “IT Team” to “BCM Command Center” shows status reports. Similarly, arrows flow between the “Communication Team” and all other nodes, representing the flow of information to and from various stakeholders. The diagram showcases a centralized, coordinated approach to crisis communication within TCS.]
Technological Solutions in TCS BCM
TCS leverages a robust suite of technological solutions to bolster its Business Continuity Management (BCM) initiatives, ensuring business resilience and minimizing disruption during crises. These technologies are integrated across various BCM functions, from risk assessment to recovery execution, enabling proactive and efficient response strategies. The integration of these tools is critical to TCS’s ability to maintain operational continuity even in the face of significant challenges.
Cloud computing forms a cornerstone of TCS’s BCM capabilities. By migrating critical applications and data to cloud platforms, TCS enhances data accessibility, scalability, and disaster recovery capabilities. This allows for seamless failover to alternative locations, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity in the event of a localized disruption, such as a natural disaster or cyberattack affecting a physical data center. The inherent redundancy and scalability of cloud environments allow for rapid resource allocation and scaling to meet fluctuating demands during a crisis. For example, during a sudden surge in customer requests following a major incident, TCS can quickly provision additional computing resources in the cloud to handle the increased workload without compromising performance.
Cloud Computing’s Role in TCS BCM
The adoption of cloud computing significantly enhances TCS’s BCM capabilities in several key areas. Firstly, it provides enhanced data accessibility, allowing authorized personnel to access critical information from anywhere with an internet connection. This is particularly crucial during a crisis when on-site access may be limited or impossible. Secondly, cloud-based solutions offer superior scalability, enabling TCS to rapidly adjust its IT infrastructure to meet the changing demands of a crisis. Finally, cloud platforms typically incorporate robust disaster recovery features, including automatic failover to redundant systems, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity. This is achieved through geographically dispersed data centers and automated recovery processes.
Data Analytics in TCS BCM Operations
TCS employs advanced data analytics techniques to proactively identify and mitigate potential risks. By analyzing vast amounts of data from various sources, including operational logs, security alerts, and external threat intelligence feeds, TCS can pinpoint vulnerabilities and develop targeted mitigation strategies. For instance, predictive analytics can identify patterns indicative of potential outages or security breaches, enabling proactive intervention and preventing significant disruptions. Real-time monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) allows for immediate detection of anomalies and rapid response to emerging threats. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of incidents and enhances overall business resilience.
Security Measures Integrated into TCS BCM Strategy
Security is intrinsically interwoven into TCS’s BCM strategy. A multi-layered security approach, incorporating robust access controls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems, protects critical data and infrastructure. Regular security audits and penetration testing identify and address vulnerabilities, minimizing the risk of cyberattacks. Incident response plans are rigorously tested and refined to ensure rapid and effective response to security breaches. This comprehensive approach ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical information, supporting the overall objective of business continuity. For example, multi-factor authentication and regular security awareness training for employees minimize the risk of unauthorized access, while encryption protects sensitive data both in transit and at rest.






