Which of the following companies has a market-oriented business definition – Which company has a market-oriented business definition? This question lies at the heart of understanding modern business success. A market-oriented approach prioritizes understanding and meeting customer needs, a stark contrast to product-oriented strategies that focus primarily on production. This exploration delves into the characteristics of market-oriented businesses, examining real-world examples and contrasting them with less customer-centric models. We’ll analyze how market research informs decision-making, how market orientation contributes to competitive advantage, and how companies communicate their commitment to this customer-first philosophy.
We will dissect the strategies of several publicly traded companies, analyzing their mission statements and annual reports to assess their degree of market orientation. This analysis will reveal the key factors that contribute to the success of market-oriented companies, showcasing the tangible benefits of a customer-centric approach. We’ll also examine how companies adapt to changing market conditions and evolving customer needs, highlighting the importance of flexibility and responsiveness in maintaining a strong market position.
Defining Market Orientation

A market-oriented business prioritizes understanding and meeting customer needs above all else. It’s a fundamental business philosophy that shapes every aspect of operations, from product development and marketing to sales and customer service. This approach contrasts sharply with product-oriented strategies, which focus primarily on internal capabilities and production efficiency rather than external market demands.
Market orientation involves a deep commitment to understanding the target market, analyzing its needs and preferences, and then adapting the business’s offerings and strategies accordingly. This requires continuous market research, robust customer feedback mechanisms, and a willingness to innovate and adapt based on real-time market insights.
Characteristics of a Market-Oriented Business Strategy
A truly market-oriented business exhibits several key characteristics. These go beyond simply conducting market research; they represent a deeply ingrained corporate culture. They actively cultivate a customer-centric approach throughout the organization.
- Customer Focus: The entire organization is geared towards understanding and fulfilling customer needs. This includes not just the marketing department, but also product development, sales, and customer service teams.
- Competitor Analysis: Market-oriented businesses don’t operate in a vacuum. They actively monitor competitors’ strategies, strengths, and weaknesses to identify opportunities and maintain a competitive edge.
- Cross-Functional Coordination: Information about customer needs and market trends is shared effectively across different departments, ensuring a unified and consistent approach.
- Proactive Innovation: Market-oriented businesses are constantly seeking ways to improve their products and services based on customer feedback and market analysis. This involves a willingness to embrace change and adapt to evolving customer expectations.
- Long-Term Perspective: While short-term profits are important, market-oriented businesses prioritize building strong customer relationships and fostering brand loyalty for sustained success.
Market-Oriented vs. Product-Oriented Businesses
The core difference lies in the primary focus: market orientation emphasizes customer needs, while product orientation prioritizes internal capabilities. A product-oriented business might develop a product based on its existing technology or production capacity, then try to find a market for it. A market-oriented business, conversely, would thoroughly research market needs and preferences before developing a product designed to satisfy those specific demands.
For example, a product-oriented approach might lead a company to produce a large quantity of a specific type of widget based on efficient manufacturing processes, even if market demand for that specific widget is low. A market-oriented approach would instead conduct extensive market research to identify what type of widget is actually needed and then tailor its production to meet that demand, perhaps producing a smaller quantity of a more desirable variant.
Approaches to Customer Needs in Market-Oriented and Non-Market-Oriented Companies
Market-oriented companies actively seek customer feedback through various channels—surveys, focus groups, social media monitoring, and customer service interactions—to understand unmet needs and pain points. They use this information to inform product development, marketing campaigns, and overall business strategy.
Non-market-oriented companies, on the other hand, may have limited or infrequent interaction with customers. Their approach to customer needs might be reactive rather than proactive, addressing issues only when they are explicitly brought to their attention. They might rely on assumptions about customer preferences rather than data-driven insights. This reactive approach can lead to missed opportunities and decreased customer satisfaction. A classic example is a company continuing to produce a product despite declining sales, failing to adapt to changing consumer preferences.
Identifying Market-Oriented Companies
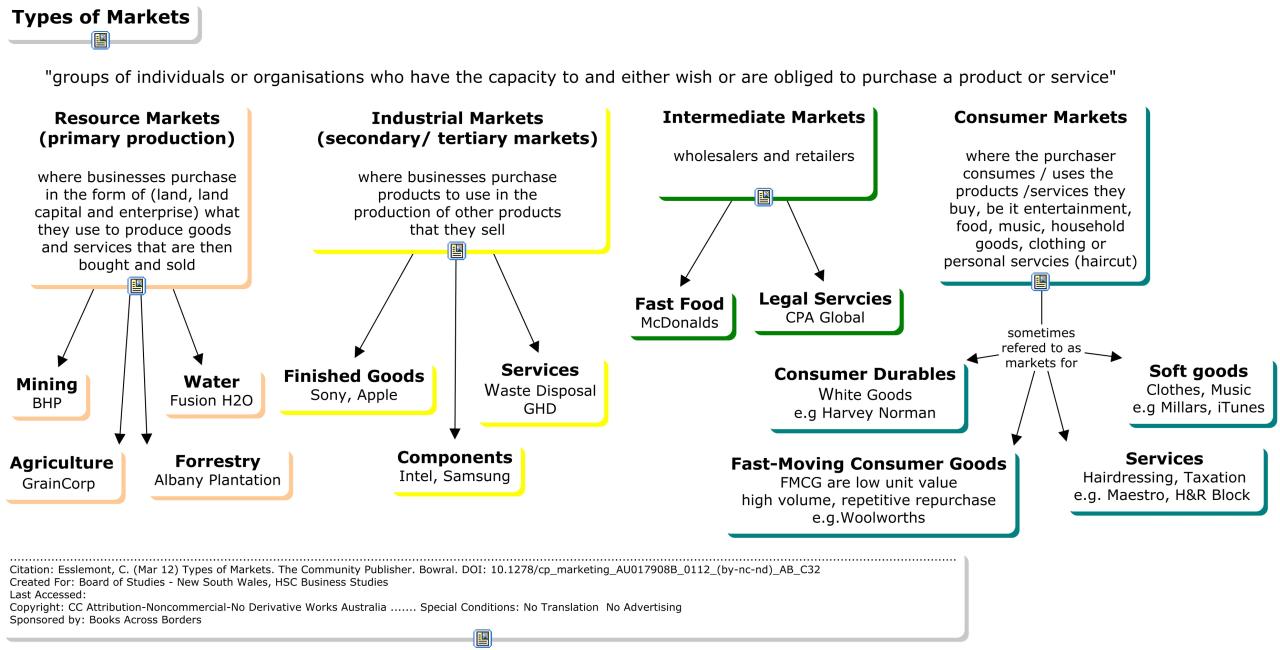
Market orientation, a crucial business philosophy, centers on understanding and meeting customer needs. Companies exhibiting a strong market orientation consistently outperform their competitors by prioritizing customer satisfaction, internal communication, and continuous adaptation to market dynamics. Identifying such companies provides valuable insights into successful business strategies.
Examples of Publicly Traded Market-Oriented Companies
The following table showcases publicly traded companies renowned for their market orientation, highlighting their approaches and the evidence supporting their strategies.
| Company Name | Industry | Description of Market Orientation | Evidence of Market Orientation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple Inc. | Consumer Electronics | Apple prioritizes a seamless user experience and cultivates a strong brand loyalty through innovative product design, robust ecosystems, and excellent customer service. They continuously gather customer feedback and adapt their products accordingly. | Regular software updates based on user feedback, extensive Apple Stores focusing on customer experience, consistent product innovation driven by market research. |
| Netflix, Inc. | Streaming Entertainment | Netflix uses data analytics extensively to understand viewing habits and personalize recommendations. This allows them to tailor content creation and marketing strategies for specific audience segments. They are highly responsive to user feedback and continuously iterate on their platform features. | Personalized recommendations, A/B testing of new features, continuous investment in original content based on data-driven insights, rapid iteration on platform improvements. |
| Amazon.com, Inc. | E-commerce | Amazon focuses on customer convenience and providing a wide selection of products at competitive prices. They utilize data analytics to personalize the shopping experience and anticipate customer needs. Their customer service is a key differentiator. | Personalized product recommendations, extensive customer reviews and ratings, fast and reliable shipping, proactive customer service initiatives. |
| Procter & Gamble | Consumer Goods | P&G utilizes extensive market research to understand consumer preferences and adapt their product offerings accordingly. They have a strong focus on brand building and marketing campaigns targeted at specific consumer segments. | Continuous product innovation based on market research, targeted advertising campaigns, strong brand portfolio catering to diverse consumer needs. |
Business Strategies of Companies with Differing Market Orientations
Three companies representing varying levels of market orientation illustrate the spectrum of approaches. A highly market-oriented company like Apple prioritizes customer feedback and continuous innovation, adapting rapidly to market trends. A moderately market-oriented company might focus on specific customer segments, but may not be as agile in responding to market shifts. A less market-oriented company may prioritize internal efficiencies over customer needs, resulting in slower adaptation and potentially lower customer satisfaction.
Key Factors Contributing to the Success of Market-Oriented Companies
Several factors contribute to the success of market-oriented companies. These include a strong understanding of customer needs, effective internal communication, a culture of innovation, and the ability to adapt quickly to changing market conditions. Furthermore, a commitment to data-driven decision-making, leveraging market research and analytics, is paramount.
Influence of Market Research on Decision-Making
Market research plays a pivotal role in the decision-making process of market-oriented companies. It provides crucial insights into customer preferences, market trends, and competitor activities. This data informs decisions related to product development, marketing strategies, pricing, and overall business strategy, ensuring alignment with customer needs and market demands. For example, a company might conduct surveys, focus groups, or analyze sales data to understand customer satisfaction and identify areas for improvement. This feedback directly informs product development, marketing campaigns, and customer service strategies.
Analyzing Company Statements and Reports: Which Of The Following Companies Has A Market-oriented Business Definition

Determining a company’s market orientation requires a thorough examination of its publicly available communications. Analyzing mission statements and annual reports provides valuable insights into a company’s strategic focus and its commitment to understanding and responding to customer needs. This analysis goes beyond simply stating intentions; it delves into the concrete actions and evidence that support a claim of market orientation.
Analyzing mission statements offers a high-level view of a company’s overall purpose and priorities. Annual reports, on the other hand, provide a more detailed picture of a company’s performance, strategies, and stakeholder engagement, offering a richer source of information for assessing market orientation.
Mission Statement Analysis
Three publicly traded companies—Procter & Gamble (PG), Nike (NKE), and Apple (AAPL)—demonstrate varying degrees of market orientation in their mission statements. Procter & Gamble’s mission statement, while not explicitly stating “customer-centricity,” emphasizes improving lives through its products, implying a focus on consumer needs. Nike’s mission statement directly addresses inspiring and innovating for every athlete, showcasing a strong customer-focused approach. Apple’s mission statement, while focusing on innovation and design, indirectly reflects a market orientation by highlighting the creation of products that enrich users’ lives. A comparative analysis reveals that Nike exhibits the most explicit market orientation in its mission statement, while Procter & Gamble and Apple display a more implicit focus on customer needs. The level of explicitness, however, doesn’t necessarily equate to the degree of market orientation in practice.
Framework for Assessing Market Orientation from Annual Reports
A robust framework for assessing market orientation using annual reports should encompass several key areas. These areas are crucial for determining the extent to which a company’s actions reflect its stated market orientation.
- Customer Satisfaction Metrics: The inclusion and prominence of customer satisfaction metrics (e.g., Net Promoter Score, customer retention rates) indicate a focus on understanding and improving customer experience.
- Market Research and Development Expenditure: Significant investment in market research and product development demonstrates a commitment to understanding customer needs and developing products that meet those needs. A detailed breakdown of these expenditures and their correlation with market trends is highly informative.
- Customer Segmentation and Targeting Strategies: The articulation of specific customer segments and targeted marketing strategies shows a proactive approach to understanding and reaching diverse customer groups.
- Employee Training and Empowerment: Details on employee training programs focusing on customer service and empowerment suggest a company culture that prioritizes customer interaction and responsiveness.
- Competitive Analysis and Response: Discussion of competitive landscape analysis and strategies for responding to competitor actions indicates an awareness of market dynamics and a proactive approach to maintaining market share.
Communication of Market Orientation to Stakeholders
Companies communicate their market orientation to stakeholders through various channels. Annual reports often include sections dedicated to customer satisfaction, market share, and product innovation, demonstrating the company’s focus on customer needs. Investor presentations may highlight market research findings and customer feedback to showcase the company’s market understanding. Marketing campaigns often emphasize customer benefits and brand loyalty, reinforcing the company’s commitment to customer-centricity. For instance, a company might showcase customer testimonials in its marketing materials or highlight its commitment to sustainability as a response to growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
Key Aspects of a Company’s Market Orientation
The key aspects of a company’s market orientation can be structured as follows:
- Customer Focus: Prioritizing understanding and meeting customer needs. This includes actively seeking customer feedback and using it to inform product development and marketing strategies.
- Competitor Orientation: Monitoring and analyzing competitors’ actions to maintain a competitive advantage and adapt to market changes.
- Interfunctional Coordination: Ensuring effective collaboration between different departments (e.g., marketing, sales, product development) to achieve a unified customer-centric approach.
- Long-Term Perspective: Focusing on building long-term customer relationships rather than short-term gains.
- Profitability: Ultimately, a market-oriented strategy aims to generate profits by satisfying customer needs effectively.
Market Orientation and Competitive Advantage
Market orientation, a business philosophy centered on understanding and meeting customer needs, provides a significant competitive advantage. By prioritizing customer satisfaction and aligning internal processes to deliver superior value, market-oriented companies outperform their competitors in terms of profitability, market share, and longevity. This advantage stems from a deep understanding of the market, leading to more effective product development, marketing strategies, and overall business operations.
A market-oriented approach fosters a proactive and adaptable business model. Instead of reacting to market changes, these companies anticipate shifts in customer preferences and proactively adapt their offerings to maintain a competitive edge. This proactive approach minimizes risks associated with market volatility and allows for sustained growth, even during economic downturns. This contrasts sharply with companies that operate reactively, often playing catch-up to market trends and competitors’ innovations.
Competitive Strategies of Market-Oriented and Non-Market-Oriented Companies, Which of the following companies has a market-oriented business definition
Consider the contrasting approaches of Procter & Gamble (P&G), a company widely recognized for its market orientation, and a hypothetical company, “Generic Corp,” which lacks a robust market orientation. P&G invests heavily in market research, constantly analyzing consumer preferences and trends to inform product development and marketing campaigns. They leverage sophisticated data analytics to understand customer behavior and personalize their marketing efforts. In contrast, Generic Corp relies primarily on intuition and past sales data, with limited investment in understanding evolving customer needs. P&G’s proactive approach, fueled by deep market insights, allows them to consistently launch successful products and maintain a strong market position, while Generic Corp struggles to compete effectively, often losing market share to more agile and customer-centric competitors. P&G’s success is a testament to the power of market orientation in driving competitive advantage.
Market Orientation, Profitability, and Market Share
Market orientation directly contributes to increased profitability and market share. By understanding customer needs and delivering superior value, market-oriented companies build strong customer loyalty. This loyalty translates into repeat purchases, positive word-of-mouth referrals, and reduced customer acquisition costs, all of which boost profitability. Furthermore, a deep understanding of the market allows these companies to identify and capitalize on emerging opportunities, leading to expansion into new markets and increased market share. For example, a market-oriented company might identify a niche market segment with unmet needs and develop a product specifically tailored to those needs, capturing a significant portion of that market.
The Role of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) in Achieving Market Orientation
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems play a crucial role in enabling a market orientation. CRM systems provide a centralized repository of customer data, enabling companies to track customer interactions, preferences, and purchasing history. This data-driven approach allows for personalized marketing campaigns, targeted product development, and improved customer service. Effective use of CRM data helps companies understand customer lifetime value, enabling them to prioritize high-value customers and tailor their strategies accordingly. Companies like Salesforce have built their businesses on providing the tools and platforms that facilitate this data-driven approach to customer relationship management. Without robust CRM systems, the ability to truly understand and respond to customer needs is significantly hampered.
Illustrative Examples of Market Orientation
Market orientation, a business philosophy prioritizing customer needs and wants, manifests differently across companies. Understanding these variations helps illustrate its practical application and the spectrum of its implementation within organizations. The following examples showcase three hypothetical companies representing varying degrees of market orientation, highlighting their strategies, target markets, and overall business approaches.
Hypothetical Companies Demonstrating Varying Degrees of Market Orientation
Three hypothetical companies – “TechNova,” “GreenGrocer,” and “ClassicCraft” – illustrate different levels of market orientation. TechNova, a tech startup, exemplifies a high degree of market orientation. GreenGrocer, a mid-sized grocery chain, demonstrates a moderate level. Finally, ClassicCraft, a long-established furniture maker, represents a lower level of market orientation.
TechNova: This tech startup develops mobile applications. Their market research extensively identifies user needs and pain points before developing any product. They employ agile development methodologies, constantly gathering user feedback and iterating on their apps based on real-time data and market trends. Their target market is young professionals and students, with specific features tailored to their lifestyles and technological proficiency. TechNova’s success is directly tied to its responsiveness to customer feedback and its proactive adaptation to emerging market trends.
GreenGrocer: This grocery chain conducts regular customer surveys and analyzes sales data to understand shopping habits and preferences. They segment their customer base by demographics and purchasing behavior, tailoring promotions and product offerings accordingly. While they don’t possess the same level of real-time responsiveness as TechNova, GreenGrocer actively seeks to meet the needs of their diverse customer base through targeted marketing and strategic product placement. Their primary focus is on providing a wide variety of products at competitive prices, with a focus on customer convenience.
ClassicCraft: This furniture manufacturer primarily focuses on producing high-quality, handcrafted furniture using traditional techniques. Their product development is driven by internal expertise and established design principles, with less emphasis on direct customer feedback. While they acknowledge customer preferences to some extent, their marketing strategies are relatively traditional, focusing on showcasing the craftsmanship and longevity of their products. Their target market is affluent consumers who appreciate high-quality, durable goods. ClassicCraft’s approach is less market-driven and more reliant on established brand reputation.
Transitioning from a Product-Oriented to a Market-Oriented Approach
A company can transition from a product-oriented to a market-oriented approach through a systematic process involving several key steps. This includes conducting thorough market research to understand customer needs and preferences, developing products and services that directly address these needs, and establishing robust feedback mechanisms to continuously improve offerings.
For example, imagine a company initially producing a single type of shoe. A product-oriented approach would focus solely on improving the production efficiency and quality of that shoe. A market-oriented approach would involve researching diverse customer needs (running, walking, hiking, etc.), developing specialized shoe lines to meet those needs, and gathering feedback to refine designs and marketing strategies. This shift requires a cultural change within the organization, emphasizing customer centricity in all aspects of business operations.
Market-Oriented Companies Adapting to Changing Customer Needs and Market Trends
Market-oriented companies demonstrate adaptability through continuous monitoring of market trends and customer feedback. They leverage this information to adjust their product offerings, marketing strategies, and overall business models to remain competitive.
For instance, consider a clothing retailer noticing a growing demand for sustainable and ethically produced clothing. A market-oriented response would involve sourcing sustainable materials, partnering with ethical manufacturers, and promoting these aspects in their marketing campaigns. This proactive adaptation allows them to capitalize on changing consumer preferences and maintain a strong market position.
Elements of a Successful Market-Oriented Business Model
A successful market-oriented business model integrates several key elements. This visual representation illustrates the interconnectedness of these components:
[Text-Based Visual Representation]
Imagine a central circle labeled “Customer Needs.” Radiating outwards from this central circle are four other circles representing key elements: “Market Research,” “Product Development,” “Marketing & Sales,” and “Customer Feedback.” Arrows connect the central circle to each of these, and arrows also connect the four outer circles to each other, illustrating the cyclical and interconnected nature of a market-oriented business model. Each outer circle is further elaborated on with short descriptions to explain how they feed into the central circle of “Customer Needs”. For example, “Market Research” would provide information about customer needs, which in turn would inform “Product Development” and “Marketing & Sales”. “Customer Feedback” then loops back into “Market Research”, creating a continuous feedback loop.






